Hee Rin Lee
Michigan State University, East Lansing, USA
Human-Robot Teaming Field Deployments: A Comparison Between Verbal and Non-verbal Communication
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Healthcare workers (HCWs) encounter challenges in hospitals, such as retrieving medical supplies quickly from crash carts, which could potentially result in medical errors and delays in patient care. Robotic crash carts (RCCs) have shown promise in assisting healthcare teams during medical tasks through guided object searches and task reminders. Limited exploration has been done to determine what communication modalities are most effective and least disruptive to patient care in real-world settings. To address this gap, we conducted a between-subjects experiment comparing the RCC's verbal and non-verbal communication of object search with a standard crash cart in resuscitation scenarios to understand the impact of robot communication on workload and attitudes toward using robots in the workplace. Our findings indicate that verbal communication significantly reduced mental demand and effort compared to visual cues and with a traditional crash cart. Although frustration levels were slightly higher during collaborations with the robot compared to a traditional cart, these research insights provide valuable implications for human-robot teamwork in high-stakes environments.
Rapidly Built Medical Crash Cart! Lessons Learned and Impacts on High-Stakes Team Collaboration in the Emergency Room
Feb 25, 2025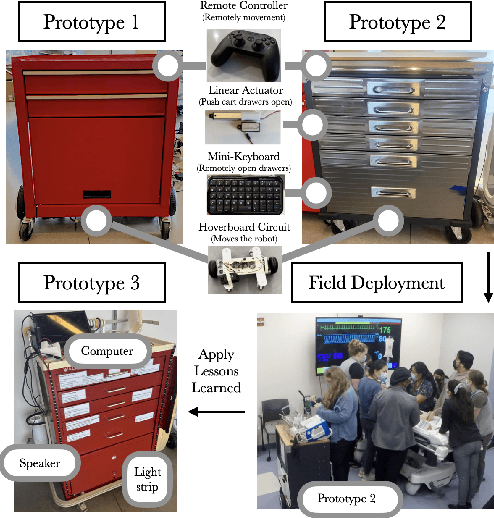
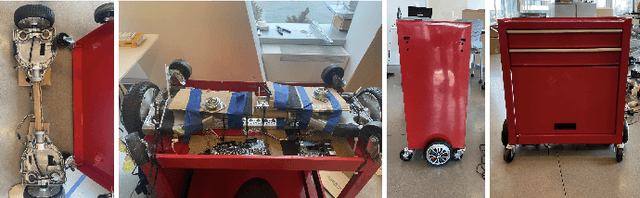
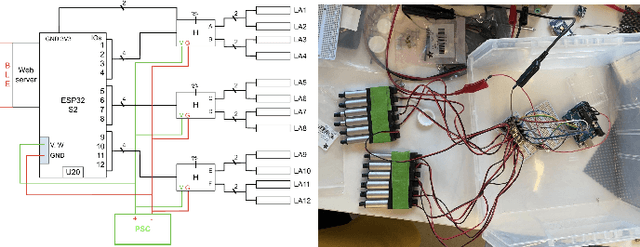
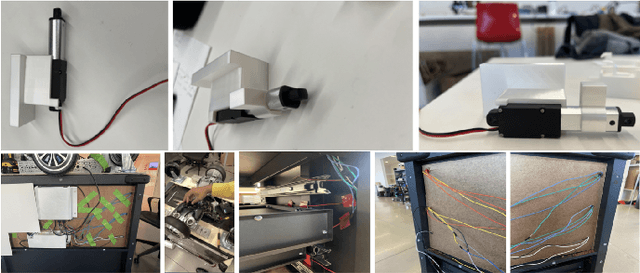
Abstract:Designing robots to support high-stakes teamwork in emergency settings presents unique challenges, including seamless integration into fast-paced environments, facilitating effective communication among team members, and adapting to rapidly changing situations. While teleoperated robots have been successfully used in high-stakes domains such as firefighting and space exploration, autonomous robots that aid highs-takes teamwork remain underexplored. To address this gap, we conducted a rapid prototyping process to develop a series of seemingly autonomous robot designed to assist clinical teams in the Emergency Room. We transformed a standard crash cart--which stores medical equipment and emergency supplies into a medical robotic crash cart (MCCR). The MCCR was evaluated through field deployments to assess its impact on team workload and usability, identified taxonomies of failure, and refined the MCCR in collaboration with healthcare professionals. Our work advances the understanding of robot design for high-stakes, time-sensitive settings, providing insights into useful MCCR capabilities and considerations for effective human-robot collaboration. By publicly disseminating our MCCR tutorial, we hope to encourage HRI researchers to explore the design of robots for high-stakes teamwork.
Co-Designing Augmented Reality Tools for High-Stakes Clinical Teamwork
Feb 24, 2025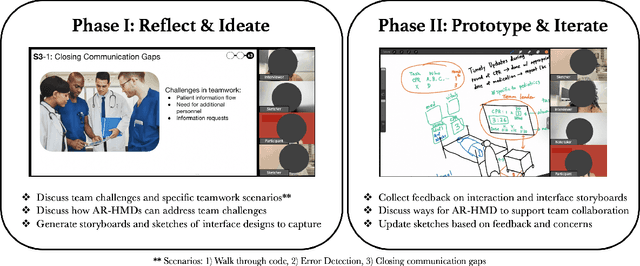
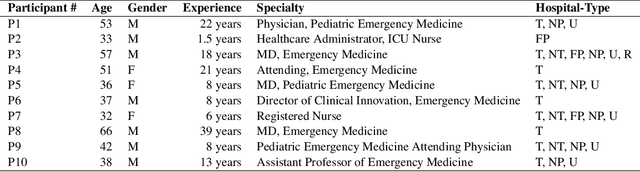
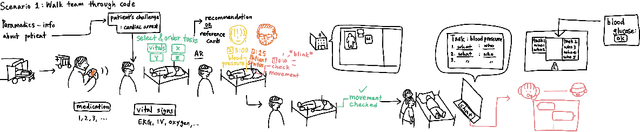
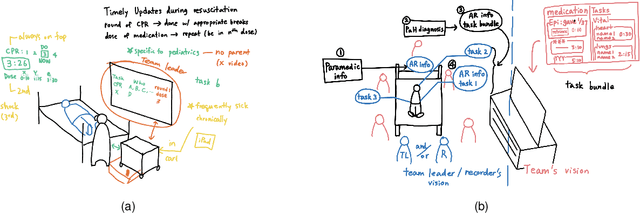
Abstract:How might healthcare workers (HCWs) leverage augmented reality head-mounted displays (AR-HMDs) to enhance teamwork? Although AR-HMDs have shown immense promise in supporting teamwork in healthcare settings, design for Emergency Department (ER) teams has received little attention. The ER presents unique challenges, including procedural recall, medical errors, and communication gaps. To address this gap, we engaged in a participatory design study with healthcare workers to gain a deep understanding of the potential for AR-HMDs to facilitate teamwork during ER procedures. Our results reveal that AR-HMDs can be used as an information-sharing and information-retrieval system to bridge knowledge gaps, and concerns about integrating AR-HMDs in ER workflows. We contribute design recommendations for seven role-based AR-HMD application scenarios involving HCWs with various expertise, working across multiple medical tasks. We hope our research inspires designers to embark on the development of new AR-HMD applications for high-stakes, team environments.
Proceedings of the SREC Workshop at HRI 2019
Sep 05, 2019Abstract:Robot-Assisted Therapy (RAT) has successfully been used in Human Robot Interaction (HRI) research by including social robots in health-care interventions by virtue of their ability to engage human users in both social and emotional dimensions. Robots used for these tasks must be designed with several user groups in mind, including both individuals receiving therapy and care professionals responsible for the treatment. These robots must also be able to perceive their context of use, recognize human actions and intentions, and follow the therapeutic goals to perform meaningful and personalized treatment. Effective interactions require for robots to be capable of coordinated, timely behavior in response to social cues. This means being able to estimate and predict levels of engagement, attention, intentionality and emotional state during human-robot interactions. An additional challenge for social robots in therapy and care is the wide range of needs and conditions the different users can have during their interventions, even if they may share the same pathologies their current requirements and the objectives of their therapies can varied extensively. Therefore, it becomes crucial for robots to adapt their behaviors and interaction scenario to the specific needs, preferences and requirements of the patients they interact with. This personalization should be considered in terms of the robot behavior and the intervention scenario and must reflect the needs, preferences and requirements of the user.
Proceedings of the Workshop on Social Robots in Therapy: Focusing on Autonomy and Ethical Challenges
Dec 18, 2018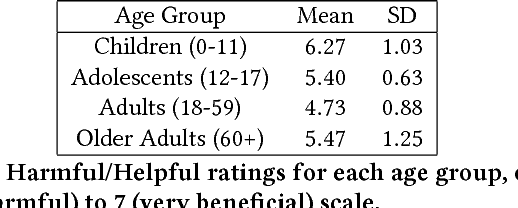
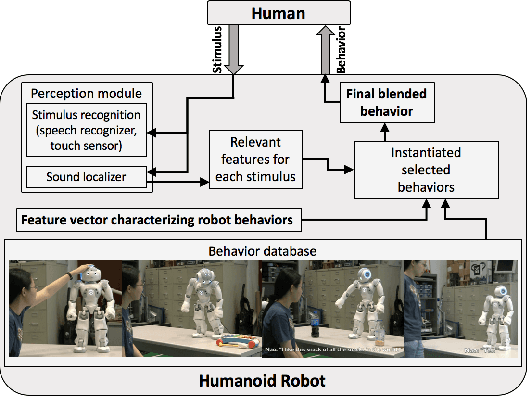
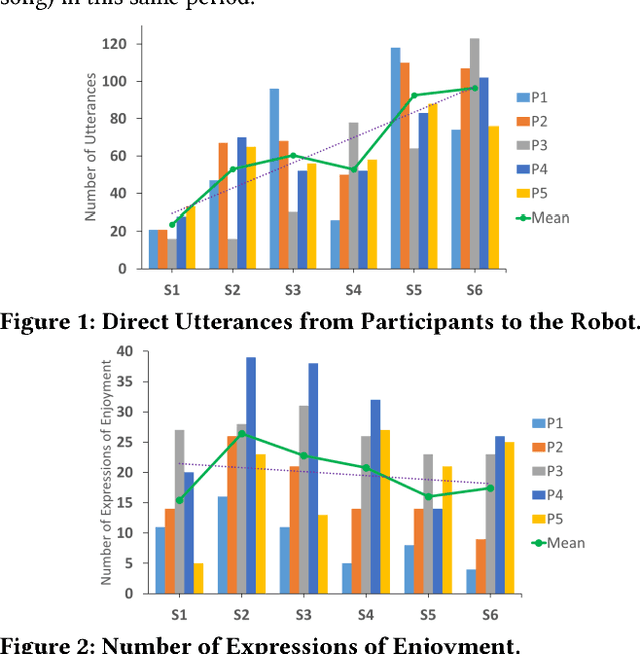
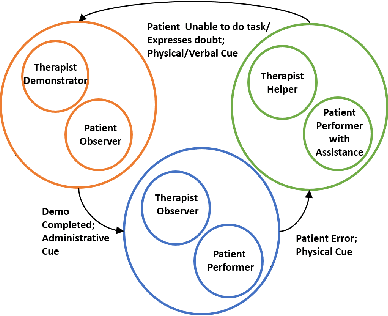
Abstract:Robot-Assisted Therapy (RAT) has successfully been used in HRI research by including social robots in health-care interventions by virtue of their ability to engage human users both social and emotional dimensions. Research projects on this topic exist all over the globe in the USA, Europe, and Asia. All of these projects have the overall ambitious goal to increase the well-being of a vulnerable population. Typical work in RAT is performed using remote controlled robots; a technique called Wizard-of-Oz (WoZ). The robot is usually controlled, unbeknownst to the patient, by a human operator. However, WoZ has been demonstrated to not be a sustainable technique in the long-term. Providing the robots with autonomy (while remaining under the supervision of the therapist) has the potential to lighten the therapists burden, not only in the therapeutic session itself but also in longer-term diagnostic tasks. Therefore, there is a need for exploring several degrees of autonomy in social robots used in therapy. Increasing the autonomy of robots might also bring about a new set of challenges. In particular, there will be a need to answer new ethical questions regarding the use of robots with a vulnerable population, as well as a need to ensure ethically-compliant robot behaviours. Therefore, in this workshop we want to gather findings and explore which degree of autonomy might help to improve health-care interventions and how we can overcome the ethical challenges inherent to it.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge