Heather Yu
SIRR-LMM: Single-image Reflection Removal via Large Multimodal Model
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Glass surfaces create complex interactions of reflected and transmitted light, making single-image reflection removal (SIRR) challenging. Existing datasets suffer from limited physical realism in synthetic data or insufficient scale in real captures. We introduce a synthetic dataset generation framework that path-traces 3D glass models over real background imagery to create physically accurate reflection scenarios with varied glass properties, camera settings, and post-processing effects. To leverage the capabilities of Large Multimodal Model (LMM), we concatenate the image layers into a single composite input, apply joint captioning, and fine-tune the model using task-specific LoRA rather than full-parameter training. This enables our approach to achieve improved reflection removal and separation performance compared to state-of-the-art methods.
OT-Talk: Animating 3D Talking Head with Optimal Transportation
May 03, 2025Abstract:Animating 3D head meshes using audio inputs has significant applications in AR/VR, gaming, and entertainment through 3D avatars. However, bridging the modality gap between speech signals and facial dynamics remains a challenge, often resulting in incorrect lip syncing and unnatural facial movements. To address this, we propose OT-Talk, the first approach to leverage optimal transportation to optimize the learning model in talking head animation. Building on existing learning frameworks, we utilize a pre-trained Hubert model to extract audio features and a transformer model to process temporal sequences. Unlike previous methods that focus solely on vertex coordinates or displacements, we introduce Chebyshev Graph Convolution to extract geometric features from triangulated meshes. To measure mesh dissimilarities, we go beyond traditional mesh reconstruction errors and velocity differences between adjacent frames. Instead, we represent meshes as probability measures and approximate their surfaces. This allows us to leverage the sliced Wasserstein distance for modeling mesh variations. This approach facilitates the learning of smooth and accurate facial motions, resulting in coherent and natural facial animations. Our experiments on two public audio-mesh datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art techniques both quantitatively and qualitatively in terms of mesh reconstruction accuracy and temporal alignment. In addition, we conducted a user perception study with 20 volunteers to further assess the effectiveness of our approach.
Scene Perceived Image Perceptual Score (SPIPS): combining global and local perception for image quality assessment
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence and widespread use of smartphones have resulted in an exponential growth of image data, both real (camera-captured) and virtual (AI-generated). This surge underscores the critical need for robust image quality assessment (IQA) methods that accurately reflect human visual perception. Traditional IQA techniques primarily rely on spatial features - such as signal-to-noise ratio, local structural distortions, and texture inconsistencies - to identify artifacts. While effective for unprocessed or conventionally altered images, these methods fall short in the context of modern image post-processing powered by deep neural networks (DNNs). The rise of DNN-based models for image generation, enhancement, and restoration has significantly improved visual quality, yet made accurate assessment increasingly complex. To address this, we propose a novel IQA approach that bridges the gap between deep learning methods and human perception. Our model disentangles deep features into high-level semantic information and low-level perceptual details, treating each stream separately. These features are then combined with conventional IQA metrics to provide a more comprehensive evaluation framework. This hybrid design enables the model to assess both global context and intricate image details, better reflecting the human visual process, which first interprets overall structure before attending to fine-grained elements. The final stage employs a multilayer perceptron (MLP) to map the integrated features into a concise quality score. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves improved consistency with human perceptual judgments compared to existing IQA models.
ePBR: Extended PBR Materials in Image Synthesis
Apr 23, 2025Abstract:Realistic indoor or outdoor image synthesis is a core challenge in computer vision and graphics. The learning-based approach is easy to use but lacks physical consistency, while traditional Physically Based Rendering (PBR) offers high realism but is computationally expensive. Intrinsic image representation offers a well-balanced trade-off, decomposing images into fundamental components (intrinsic channels) such as geometry, materials, and illumination for controllable synthesis. However, existing PBR materials struggle with complex surface models, particularly high-specular and transparent surfaces. In this work, we extend intrinsic image representations to incorporate both reflection and transmission properties, enabling the synthesis of transparent materials such as glass and windows. We propose an explicit intrinsic compositing framework that provides deterministic, interpretable image synthesis. With the Extended PBR (ePBR) Materials, we can effectively edit the materials with precise controls.
REEF: Relevance-Aware and Efficient LLM Adapter for Video Understanding
Apr 07, 2025Abstract:Integrating vision models into large language models (LLMs) has sparked significant interest in creating vision-language foundation models, especially for video understanding. Recent methods often utilize memory banks to handle untrimmed videos for video-level understanding. However, they typically compress visual memory using similarity-based greedy approaches, which can overlook the contextual importance of individual tokens. To address this, we introduce an efficient LLM adapter designed for video-level understanding of untrimmed videos that prioritizes the contextual relevance of spatio-temporal tokens. Our framework leverages scorer networks to selectively compress the visual memory bank and filter spatial tokens based on relevance, using a differentiable Top-K operator for end-to-end training. Across three key video-level understanding tasks$\unicode{x2013}$ untrimmed video classification, video question answering, and video captioning$\unicode{x2013}$our method achieves competitive or superior results on four large-scale datasets while reducing computational overhead by up to 34%. The code will be available soon on GitHub.
OccludeNeRF: Geometric-aware 3D Scene Inpainting with Collaborative Score Distillation in NeRF
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:With Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) arising as a powerful 3D representation, research has investigated its various downstream tasks, including inpainting NeRFs with 2D images. Despite successful efforts addressing the view consistency and geometry quality, prior methods yet suffer from occlusion in NeRF inpainting tasks, where 2D prior is severely limited in forming a faithful reconstruction of the scene to inpaint. To address this, we propose a novel approach that enables cross-view information sharing during knowledge distillation from a diffusion model, effectively propagating occluded information across limited views. Additionally, to align the distillation direction across multiple sampled views, we apply a grid-based denoising strategy and incorporate additional rendered views to enhance cross-view consistency. To assess our approach's capability of handling occlusion cases, we construct a dataset consisting of challenging scenes with severe occlusion, in addition to existing datasets. Compared with baseline methods, our method demonstrates better performance in cross-view consistency and faithfulness in reconstruction, while preserving high rendering quality and fidelity.
Envisioning a Next Generation Extended Reality Conferencing System with Efficient Photorealistic Human Rendering
Jun 28, 2023Abstract:Meeting online is becoming the new normal. Creating an immersive experience for online meetings is a necessity towards more diverse and seamless environments. Efficient photorealistic rendering of human 3D dynamics is the core of immersive meetings. Current popular applications achieve real-time conferencing but fall short in delivering photorealistic human dynamics, either due to limited 2D space or the use of avatars that lack realistic interactions between participants. Recent advances in neural rendering, such as the Neural Radiance Field (NeRF), offer the potential for greater realism in metaverse meetings. However, the slow rendering speed of NeRF poses challenges for real-time conferencing. We envision a pipeline for a future extended reality metaverse conferencing system that leverages monocular video acquisition and free-viewpoint synthesis to enhance data and hardware efficiency. Towards an immersive conferencing experience, we explore an accelerated NeRF-based free-viewpoint synthesis algorithm for rendering photorealistic human dynamics more efficiently. We show that our algorithm achieves comparable rendering quality while performing training and inference 44.5% and 213% faster than state-of-the-art methods, respectively. Our exploration provides a design basis for constructing metaverse conferencing systems that can handle complex application scenarios, including dynamic scene relighting with customized themes and multi-user conferencing that harmonizes real-world people into an extended world.
Context-Aware Single-Shot Detector
Mar 24, 2018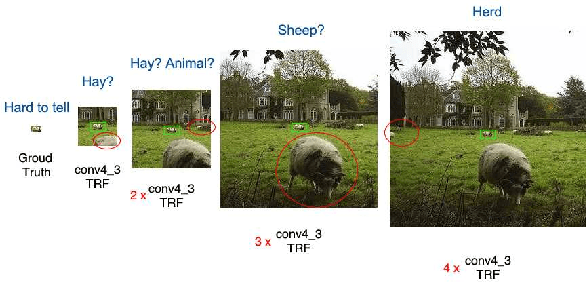

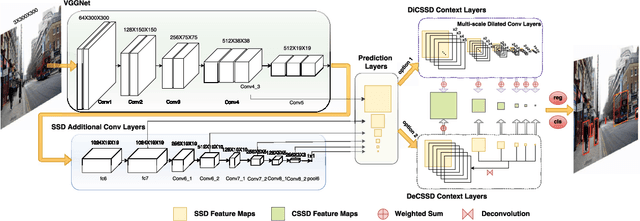
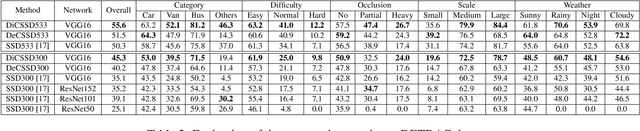
Abstract:SSD is one of the state-of-the-art object detection algorithms, and it combines high detection accuracy with real-time speed. However, it is widely recognized that SSD is less accurate in detecting small objects compared to large objects, because it ignores the context from outside the proposal boxes. In this paper, we present CSSD--a shorthand for context-aware single-shot multibox object detector. CSSD is built on top of SSD, with additional layers modeling multi-scale contexts. We describe two variants of CSSD, which differ in their context layers, using dilated convolution layers (DiCSSD) and deconvolution layers (DeCSSD) respectively. The experimental results show that the multi-scale context modeling significantly improves the detection accuracy. In addition, we study the relationship between effective receptive fields (ERFs) and the theoretical receptive fields (TRFs), particularly on a VGGNet. The empirical results further strengthen our conclusion that SSD coupled with context layers achieves better detection results especially for small objects ($+3.2\% {\rm AP}_{@0.5}$ on MS-COCO compared to the newest SSD), while maintaining comparable runtime performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge