Harry Hemingway
Machine learning and AI research for Patient Benefit: 20 Critical Questions on Transparency, Replicability, Ethics and Effectiveness
Dec 21, 2018Abstract:Machine learning (ML), artificial intelligence (AI) and other modern statistical methods are providing new opportunities to operationalize previously untapped and rapidly growing sources of data for patient benefit. Whilst there is a lot of promising research currently being undertaken, the literature as a whole lacks: transparency; clear reporting to facilitate replicability; exploration for potential ethical concerns; and, clear demonstrations of effectiveness. There are many reasons for why these issues exist, but one of the most important that we provide a preliminary solution for here is the current lack of ML/AI- specific best practice guidance. Although there is no consensus on what best practice looks in this field, we believe that interdisciplinary groups pursuing research and impact projects in the ML/AI for health domain would benefit from answering a series of questions based on the important issues that exist when undertaking work of this nature. Here we present 20 questions that span the entire project life cycle, from inception, data analysis, and model evaluation, to implementation, as a means to facilitate project planning and post-hoc (structured) independent evaluation. By beginning to answer these questions in different settings, we can start to understand what constitutes a good answer, and we expect that the resulting discussion will be central to developing an international consensus framework for transparent, replicable, ethical and effective research in artificial intelligence (AI-TREE) for health.
Application of Clinical Concept Embeddings for Heart Failure Prediction in UK EHR data
Nov 28, 2018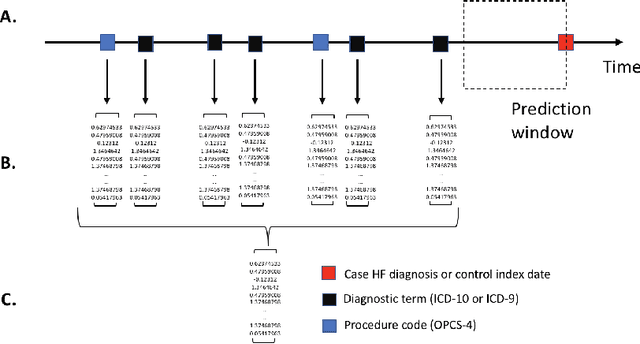
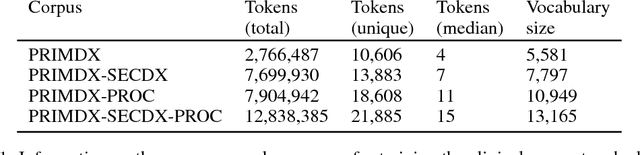
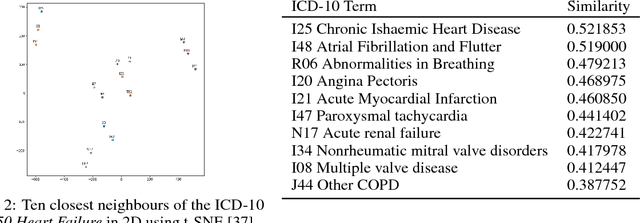
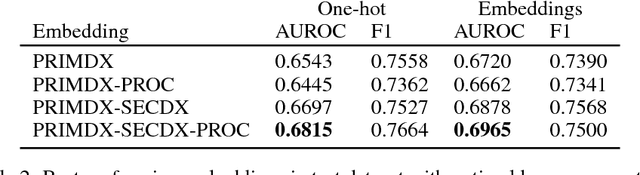
Abstract:Electronic health records (EHR) are increasingly being used for constructing disease risk prediction models. Feature engineering in EHR data however is challenging due to their highly dimensional and heterogeneous nature. Low-dimensional representations of EHR data can potentially mitigate these challenges. In this paper, we use global vectors (GloVe) to learn word embeddings for diagnoses and procedures recorded using 13 million ontology terms across 2.7 million hospitalisations in national UK EHR. We demonstrate the utility of these embeddings by evaluating their performance in identifying patients which are at higher risk of being hospitalised for congestive heart failure. Our findings indicate that embeddings can enable the creation of robust EHR-derived disease risk prediction models and address some the limitations associated with manual clinical feature engineering.
Evaluation of Semantic Web Technologies for Storing Computable Definitions of Electronic Health Records Phenotyping Algorithms
Jul 24, 2017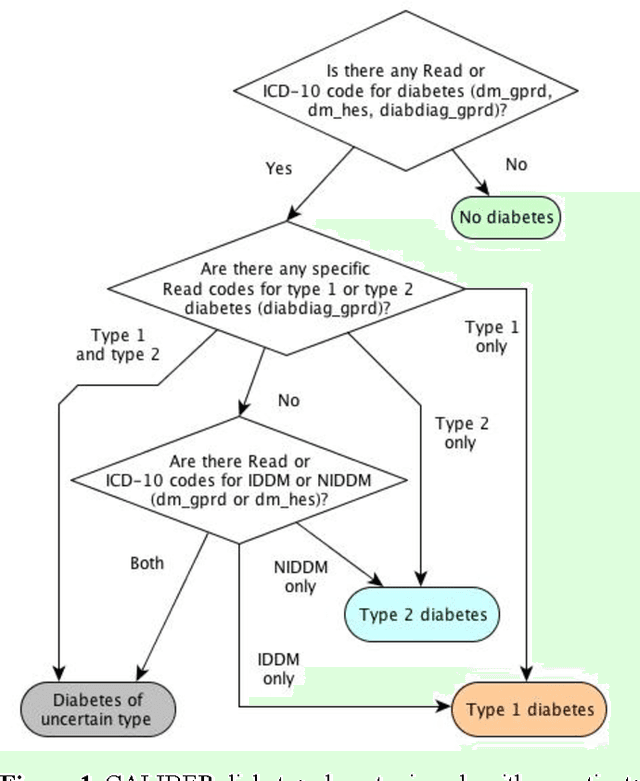
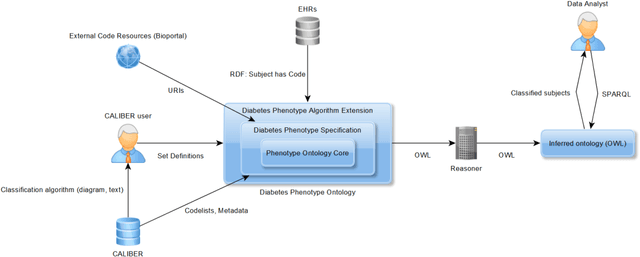
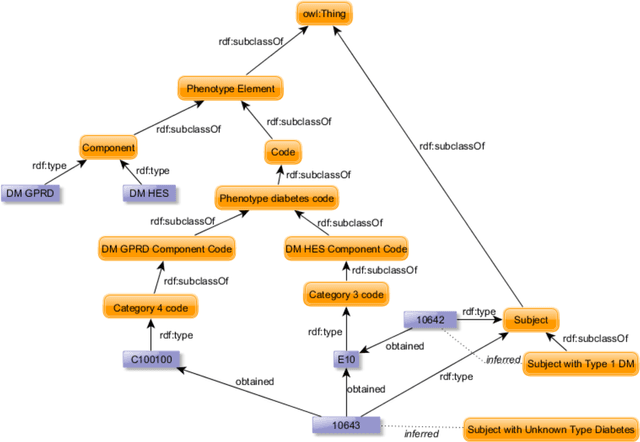
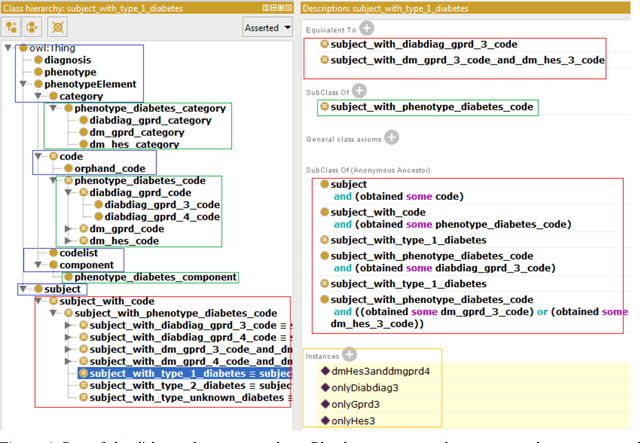
Abstract:Electronic Health Records are electronic data generated during or as a byproduct of routine patient care. Structured, semi-structured and unstructured EHR offer researchers unprecedented phenotypic breadth and depth and have the potential to accelerate the development of precision medicine approaches at scale. A main EHR use-case is defining phenotyping algorithms that identify disease status, onset and severity. Phenotyping algorithms utilize diagnoses, prescriptions, laboratory tests, symptoms and other elements in order to identify patients with or without a specific trait. No common standardized, structured, computable format exists for storing phenotyping algorithms. The majority of algorithms are stored as human-readable descriptive text documents making their translation to code challenging due to their inherent complexity and hinders their sharing and re-use across the community. In this paper, we evaluate the two key Semantic Web Technologies, the Web Ontology Language and the Resource Description Framework, for enabling computable representations of EHR-driven phenotyping algorithms.
Evaluation of Machine Learning Methods to Predict Coronary Artery Disease Using Metabolomic Data
Feb 28, 2017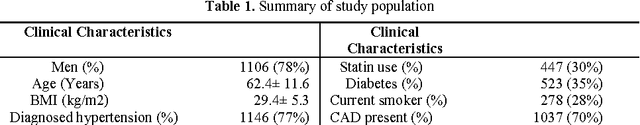
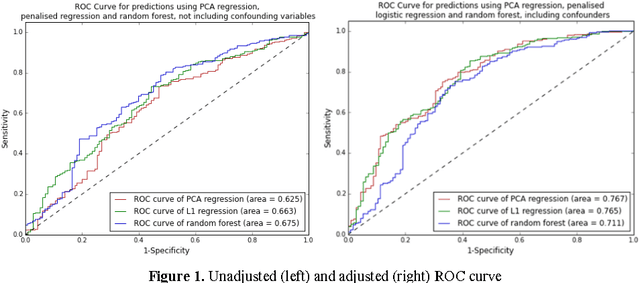
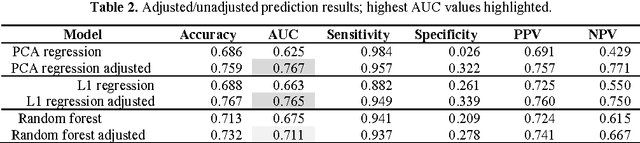
Abstract:Metabolomic data can potentially enable accurate, non-invasive and low-cost prediction of coronary artery disease. Regression-based analytical approaches however might fail to fully account for interactions between metabolites, rely on a priori selected input features and thus might suffer from poorer accuracy. Supervised machine learning methods can potentially be used in order to fully exploit the dimensionality and richness of the data. In this paper, we systematically implement and evaluate a set of supervised learning methods (L1 regression, random forest classifier) and compare them to traditional regression-based approaches for disease prediction using metabolomic data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge