Hans Chalupsky
Creating and Querying Personalized Versions of Wikidata on a Laptop
Aug 18, 2021
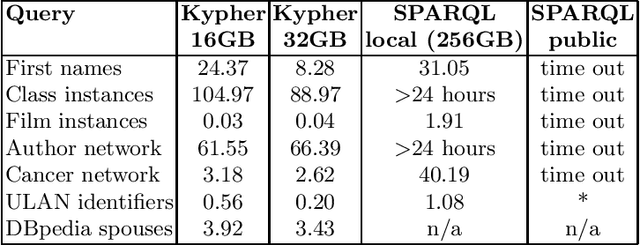

Abstract:Application developers today have three choices for exploiting the knowledge present in Wikidata: they can download the Wikidata dumps in JSON or RDF format, they can use the Wikidata API to get data about individual entities, or they can use the Wikidata SPARQL endpoint. None of these methods can support complex, yet common, query use cases, such as retrieval of large amounts of data or aggregations over large fractions of Wikidata. This paper introduces KGTK Kypher, a query language and processor that allows users to create personalized variants of Wikidata on a laptop. We present several use cases that illustrate the types of analyses that Kypher enables users to run on the full Wikidata KG on a laptop, combining data from external resources such as DBpedia. The Kypher queries for these use cases run much faster on a laptop than the equivalent SPARQL queries on a Wikidata clone running on a powerful server with 24h time-out limits.
KGTK: A Toolkit for Large Knowledge Graph Manipulation and Analysis
May 29, 2020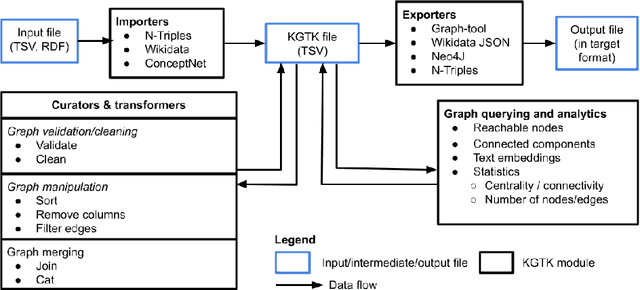
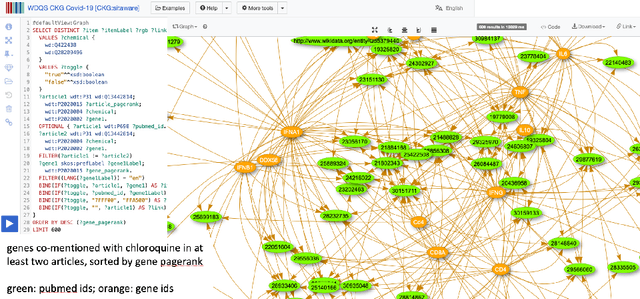
Abstract:Knowledge graphs (KGs) have become the preferred technology for representing, sharing and adding knowledge to modern AI applications. While KGs have become a mainstream technology, the RDF/SPARQL-centric toolset for operating with them at scale is heterogeneous, difficult to integrate and only covers a subset of the operations that are commonly needed in data science applications. In this paper, we present KGTK, a data science-centric toolkit to represent, create, transform, enhance and analyze KGs. KGTK represents graphs in tables and leverages popular libraries developed for data science applications, enabling a wide audience of developers to easily construct knowledge graph pipelines for their applications. We illustrate KGTK with real-world scenarios in which we have used KGTK to integrate and manipulate large KGs, such as Wikidata, DBpedia and ConceptNet, in our own work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge