Yixiang Yao
Privacy-Preserving Language Model Inference with Instance Obfuscation
Feb 13, 2024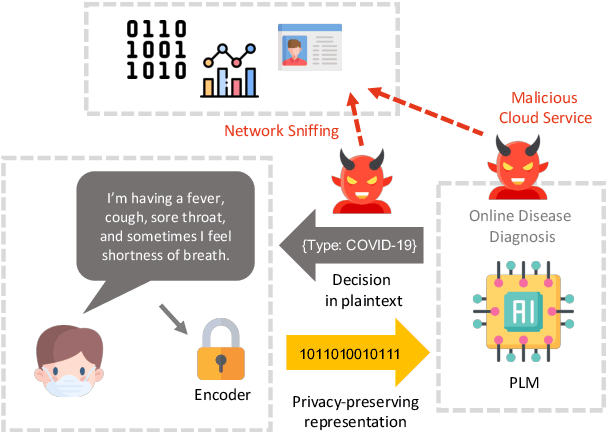
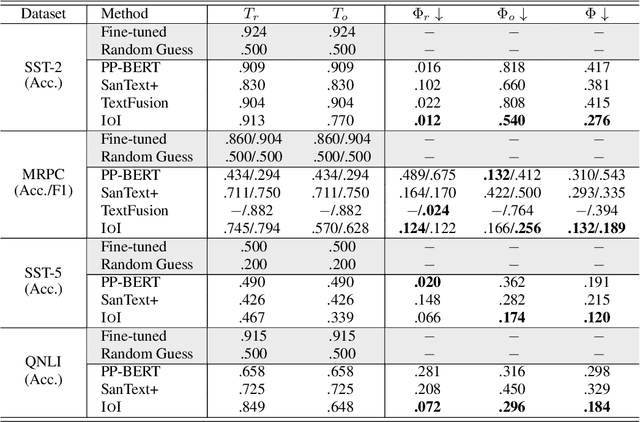
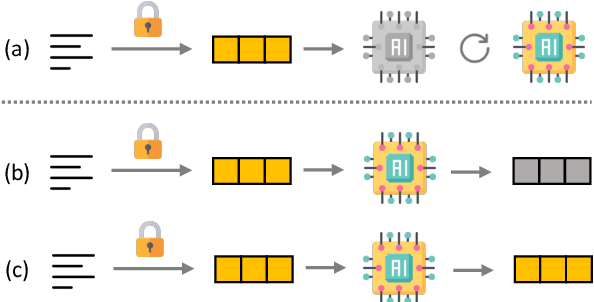
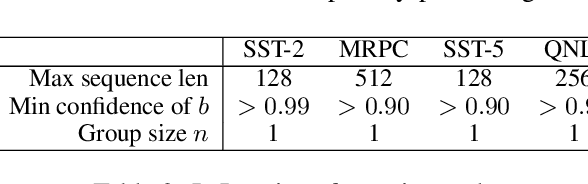
Abstract:Language Models as a Service (LMaaS) offers convenient access for developers and researchers to perform inference using pre-trained language models. Nonetheless, the input data and the inference results containing private information are exposed as plaintext during the service call, leading to privacy issues. Recent studies have started tackling the privacy issue by transforming input data into privacy-preserving representation from the user-end with the techniques such as noise addition and content perturbation, while the exploration of inference result protection, namely decision privacy, is still a blank page. In order to maintain the black-box manner of LMaaS, conducting data privacy protection, especially for the decision, is a challenging task because the process has to be seamless to the models and accompanied by limited communication and computation overhead. We thus propose Instance-Obfuscated Inference (IOI) method, which focuses on addressing the decision privacy issue of natural language understanding tasks in their complete life-cycle. Besides, we conduct comprehensive experiments to evaluate the performance as well as the privacy-protection strength of the proposed method on various benchmarking tasks.
Labeling without Seeing? Blind Annotation for Privacy-Preserving Entity Resolution
Aug 07, 2023



Abstract:The entity resolution problem requires finding pairs across datasets that belong to different owners but refer to the same entity in the real world. To train and evaluate solutions (either rule-based or machine-learning-based) to the entity resolution problem, generating a ground truth dataset with entity pairs or clusters is needed. However, such a data annotation process involves humans as domain oracles to review the plaintext data for all candidate record pairs from different parties, which inevitably infringes the privacy of data owners, especially in privacy-sensitive cases like medical records. To the best of our knowledge, there is no prior work on privacy-preserving ground truth dataset generation, especially in the domain of entity resolution. We propose a novel blind annotation protocol based on homomorphic encryption that allows domain oracles to collaboratively label ground truths without sharing data in plaintext with other parties. In addition, we design a domain-specific easy-to-use language that hides the sophisticated underlying homomorphic encryption layer. Rigorous proof of the privacy guarantee is provided and our empirical experiments via an annotation simulator indicate the feasibility of our privacy-preserving protocol (f-measure on average achieves more than 90\% compared with the real ground truths).
KGTK: A Toolkit for Large Knowledge Graph Manipulation and Analysis
May 29, 2020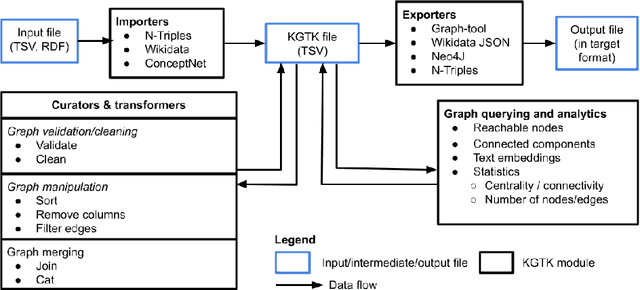
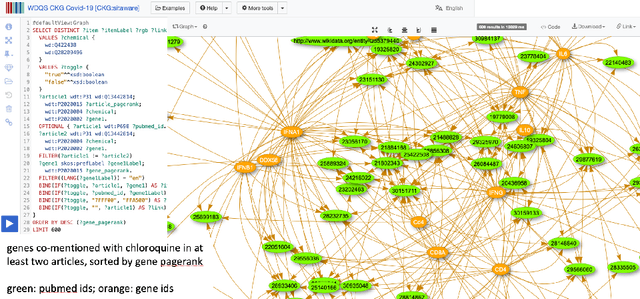
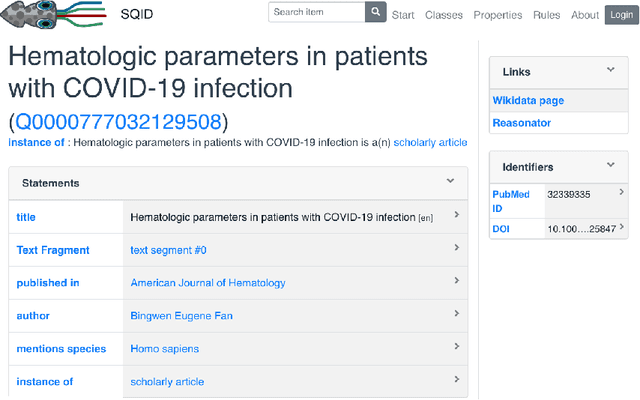
Abstract:Knowledge graphs (KGs) have become the preferred technology for representing, sharing and adding knowledge to modern AI applications. While KGs have become a mainstream technology, the RDF/SPARQL-centric toolset for operating with them at scale is heterogeneous, difficult to integrate and only covers a subset of the operations that are commonly needed in data science applications. In this paper, we present KGTK, a data science-centric toolkit to represent, create, transform, enhance and analyze KGs. KGTK represents graphs in tables and leverages popular libraries developed for data science applications, enabling a wide audience of developers to easily construct knowledge graph pipelines for their applications. We illustrate KGTK with real-world scenarios in which we have used KGTK to integrate and manipulate large KGs, such as Wikidata, DBpedia and ConceptNet, in our own work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge