Haichuan Song
MOS: Modeling Object-Scene Associations in Generalized Category Discovery
Mar 15, 2025Abstract:Generalized Category Discovery (GCD) is a classification task that aims to classify both base and novel classes in unlabeled images, using knowledge from a labeled dataset. In GCD, previous research overlooks scene information or treats it as noise, reducing its impact during model training. However, in this paper, we argue that scene information should be viewed as a strong prior for inferring novel classes. We attribute the misinterpretation of scene information to a key factor: the Ambiguity Challenge inherent in GCD. Specifically, novel objects in base scenes might be wrongly classified into base categories, while base objects in novel scenes might be mistakenly recognized as novel categories. Once the ambiguity challenge is addressed, scene information can reach its full potential, significantly enhancing the performance of GCD models. To more effectively leverage scene information, we propose the Modeling Object-Scene Associations (MOS) framework, which utilizes a simple MLP-based scene-awareness module to enhance GCD performance. It achieves an exceptional average accuracy improvement of 4% on the challenging fine-grained datasets compared to state-of-the-art methods, emphasizing its superior performance in fine-grained GCD. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/JethroPeng/MOS.
Prototype-Aware Heterogeneous Task for Point Cloud Completion
Sep 05, 2022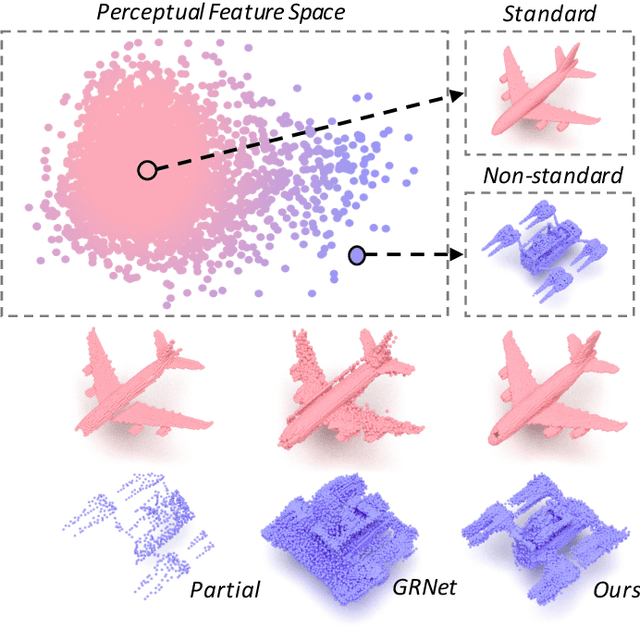
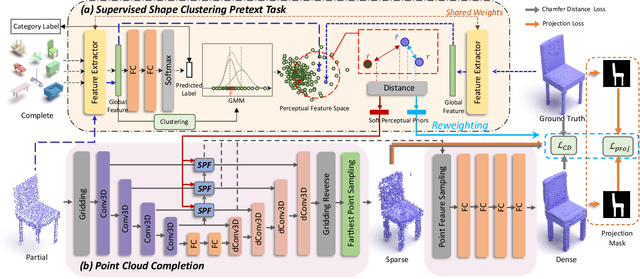
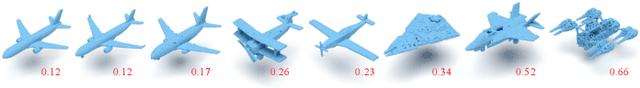
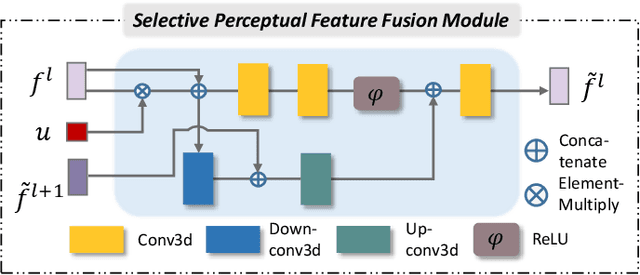
Abstract:Point cloud completion, which aims at recovering original shape information from partial point clouds, has attracted attention on 3D vision community. Existing methods usually succeed in completion for standard shape, while failing to generate local details of point clouds for some non-standard shapes. To achieve desirable local details, guidance from global shape information is of critical importance. In this work, we design an effective way to distinguish standard/non-standard shapes with the help of intra-class shape prototypical representation, which can be calculated by the proposed supervised shape clustering pretext task, resulting in a heterogeneous component w.r.t completion network. The representative prototype, defined as feature centroid of shape categories, can provide global shape guidance, which is referred to as soft-perceptual prior, to inject into downstream completion network by the desired selective perceptual feature fusion module in a multi-scale manner. Moreover, for effective training, we consider difficulty-based sampling strategy to encourage the network to pay more attention to some partial point clouds with fewer geometric information. Experimental results show that our method outperforms other state-of-the-art methods and has strong ability on completing complex geometric shapes.
Omni-supervised Point Cloud Segmentation via Gradual Receptive Field Component Reasoning
May 21, 2021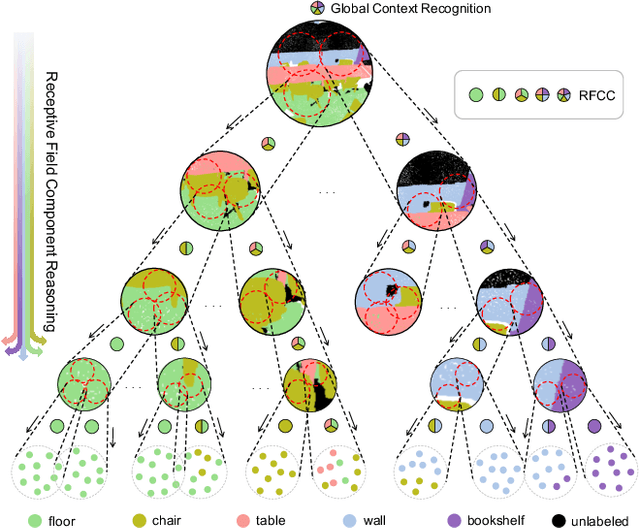
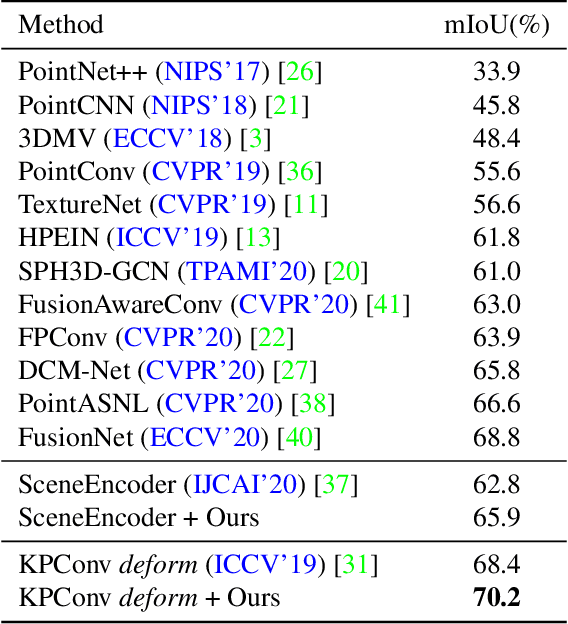
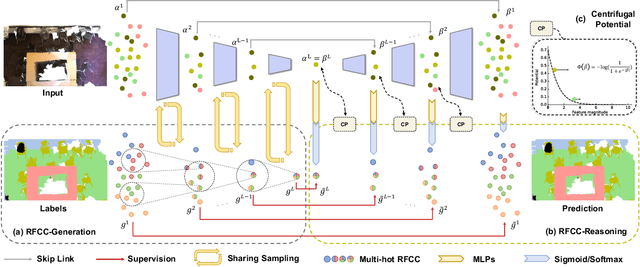
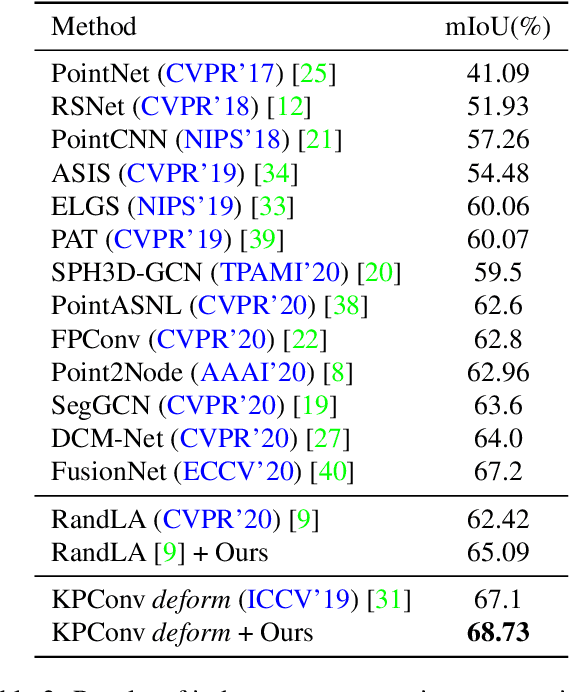
Abstract:Hidden features in neural network usually fail to learn informative representation for 3D segmentation as supervisions are only given on output prediction, while this can be solved by omni-scale supervision on intermediate layers. In this paper, we bring the first omni-scale supervision method to point cloud segmentation via the proposed gradual Receptive Field Component Reasoning (RFCR), where target Receptive Field Component Codes (RFCCs) are designed to record categories within receptive fields for hidden units in the encoder. Then, target RFCCs will supervise the decoder to gradually infer the RFCCs in a coarse-to-fine categories reasoning manner, and finally obtain the semantic labels. Because many hidden features are inactive with tiny magnitude and make minor contributions to RFCC prediction, we propose a Feature Densification with a centrifugal potential to obtain more unambiguous features, and it is in effect equivalent to entropy regularization over features. More active features can further unleash the potential of our omni-supervision method. We embed our method into four prevailing backbones and test on three challenging benchmarks. Our method can significantly improve the backbones in all three datasets. Specifically, our method brings new state-of-the-art performances for S3DIS as well as Semantic3D and ranks the 1st in the ScanNet benchmark among all the point-based methods. Code will be publicly available at https://github.com/azuki-miho/RFCR.
Face Anti-Spoofing Via Disentangled Representation Learning
Aug 19, 2020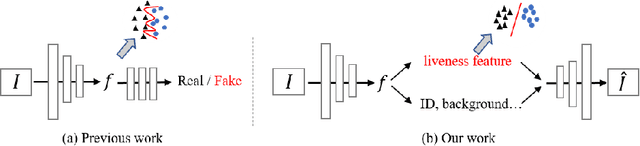
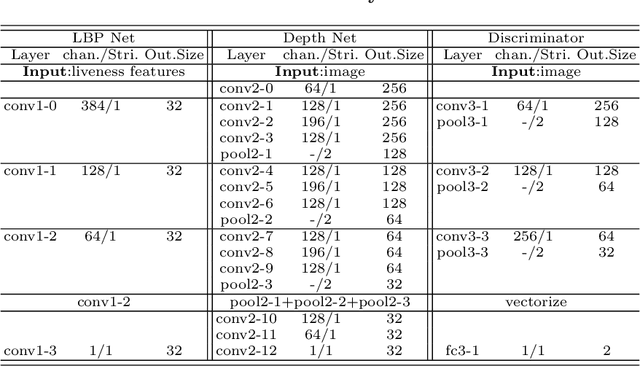
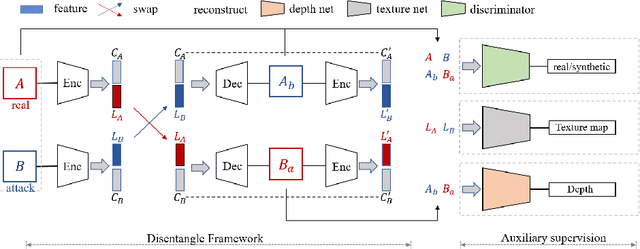
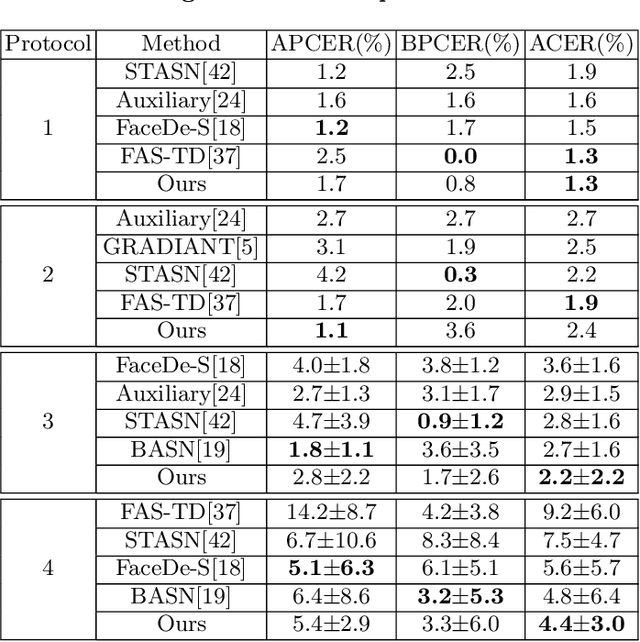
Abstract:Face anti-spoofing is crucial to security of face recognition systems. Previous approaches focus on developing discriminative models based on the features extracted from images, which may be still entangled between spoof patterns and real persons. In this paper, motivated by the disentangled representation learning, we propose a novel perspective of face anti-spoofing that disentangles the liveness features and content features from images, and the liveness features is further used for classification. We also put forward a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architecture with the process of disentanglement and combination of low-level and high-level supervision to improve the generalization capabilities. We evaluate our method on public benchmark datasets and extensive experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method against the state-of-the-art competitors. Finally, we further visualize some results to help understand the effect and advantage of disentanglement.
Acoustic anomaly detection via latent regularized gaussian mixture generative adversarial networks
Feb 05, 2020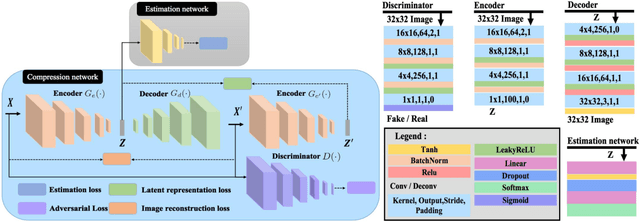
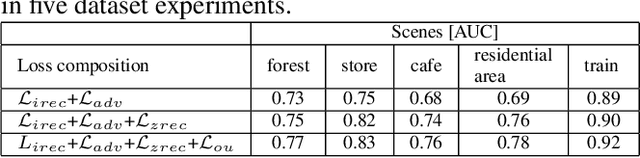
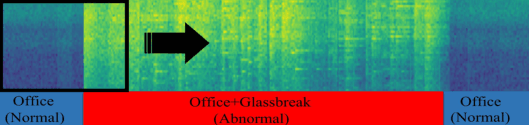
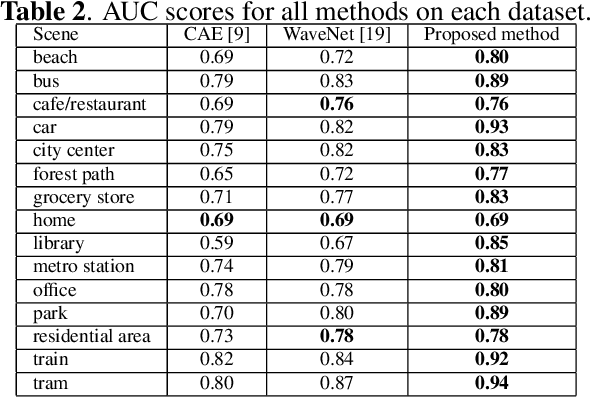
Abstract:Acoustic anomaly detection aims at distinguishing abnormal acoustic signals from the normal ones. It suffers from the class imbalance issue and the lacking in the abnormal instances. In addition, collecting all kinds of abnormal or unknown samples for training purpose is impractical and timeconsuming. In this paper, a novel Gaussian Mixture Generative Adversarial Network (GMGAN) is proposed under semi-supervised learning framework, in which the underlying structure of training data is not only captured in spectrogram reconstruction space, but also can be further restricted in the space of latent representation in a discriminant manner. Experiments show that our model has clear superiority over previous methods, and achieves the state-of-the-art results on DCASE dataset.
Anomaly Detection by Latent Regularized Dual Adversarial Networks
Feb 05, 2020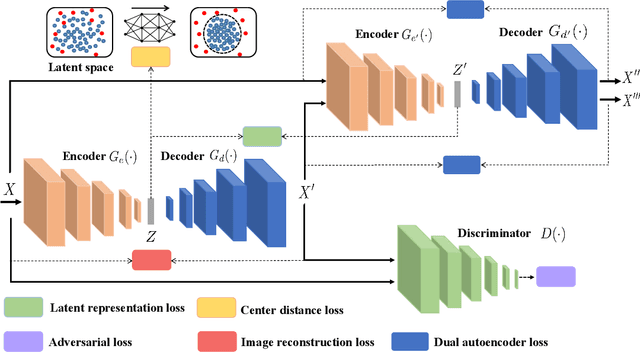
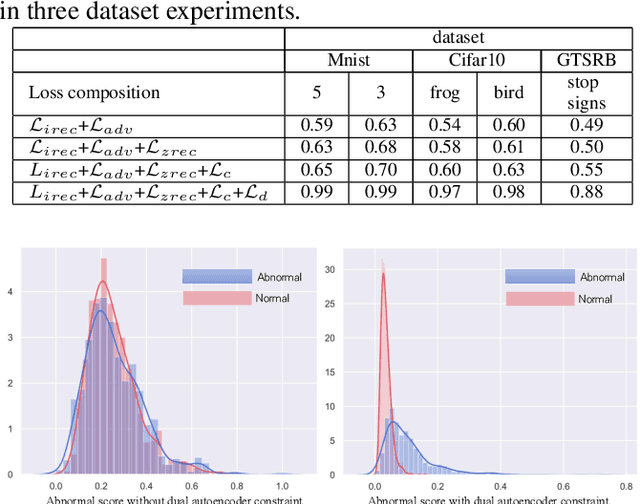
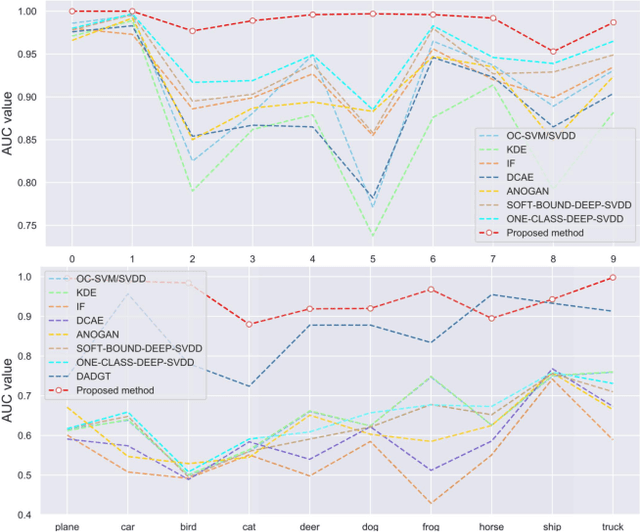
Abstract:Anomaly detection is a fundamental problem in computer vision area with many real-world applications. Given a wide range of images belonging to the normal class, emerging from some distribution, the objective of this task is to construct the model to detect out-of-distribution images belonging to abnormal instances. Semi-supervised Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN)-based methods have been gaining popularity in anomaly detection task recently. However, the training process of GAN is still unstable and challenging. To solve these issues, a novel adversarial dual autoencoder network is proposed, in which the underlying structure of training data is not only captured in latent feature space, but also can be further restricted in the space of latent representation in a discriminant manner, leading to a more accurate detector. In addition, the auxiliary autoencoder regarded as a discriminator could obtain an more stable training process. Experiments show that our model achieves the state-of-the-art results on MNIST and CIFAR10 datasets as well as GTSRB stop signs dataset.
Novelty Detection via Non-Adversarial Generative Network
Feb 03, 2020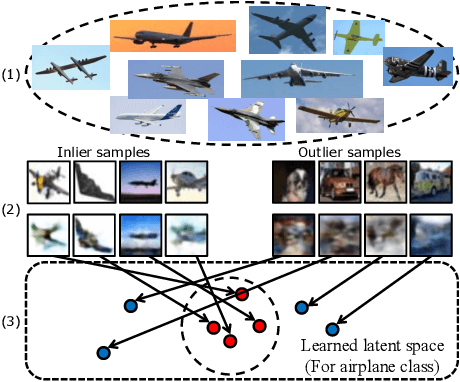

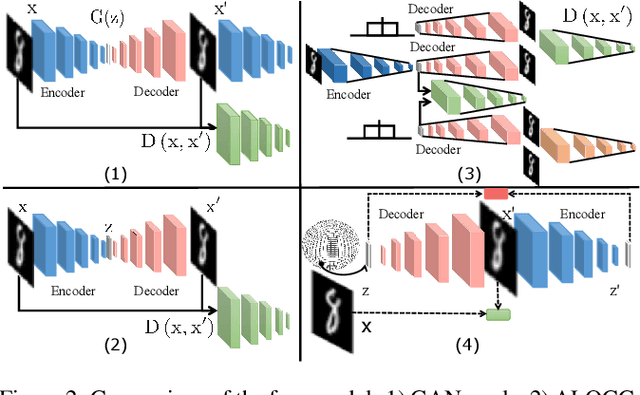
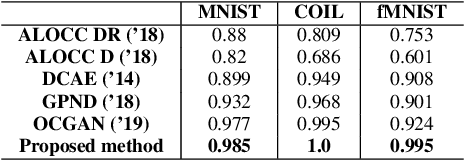
Abstract:One-class novelty detection is the process of determining if a query example differs from the training examples (the target class). Most of previous strategies attempt to learn the real characteristics of target sample by using generative adversarial networks (GANs) methods. However, the training process of GANs remains challenging, suffering from instability issues such as mode collapse and vanishing gradients. In this paper, by adopting non-adversarial generative networks, a novel decoder-encoder framework is proposed for novelty detection task, insteading of classical encoder-decoder style. Under the non-adversarial framework, both latent space and image reconstruction space are jointly optimized, leading to a more stable training process with super fast convergence and lower training losses. During inference, inspired by cycleGAN, we design a new testing scheme to conduct image reconstruction, which is the reverse way of training sequence. Experiments show that our model has the clear superiority over cutting-edge novelty detectors and achieves the state-of-the-art results on the datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge