Guangwei Xiong
Signal Adversarial Examples Generation for Signal Detection Network via White-Box Attack
Oct 02, 2024



Abstract:With the development and application of deep learning in signal detection tasks, the vulnerability of neural networks to adversarial attacks has also become a security threat to signal detection networks. This paper defines a signal adversarial examples generation model for signal detection network from the perspective of adding perturbations to the signal. The model uses the inequality relationship of L2-norm between time domain and time-frequency domain to constrain the energy of signal perturbations. Building upon this model, we propose a method for generating signal adversarial examples utilizing gradient-based attacks and Short-Time Fourier Transform. The experimental results show that under the constraint of signal perturbation energy ratio less than 3%, our adversarial attack resulted in a 28.1% reduction in the mean Average Precision (mAP), a 24.7% reduction in recall, and a 30.4% reduction in precision of the signal detection network. Compared to random noise perturbation of equivalent intensity, our adversarial attack demonstrates a significant attack effect.
The state of the art in kidney and kidney tumor segmentation in contrast-enhanced CT imaging: Results of the KiTS19 Challenge
Dec 02, 2019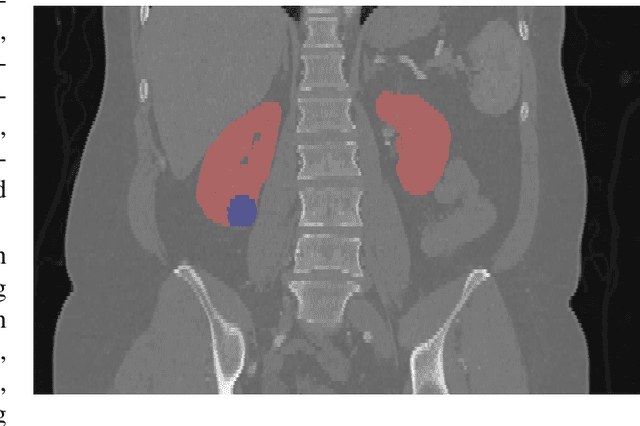
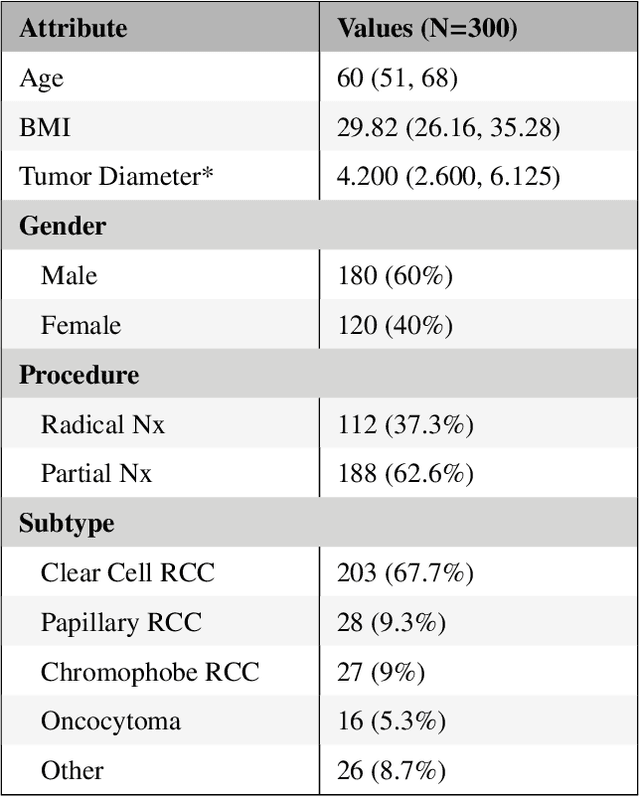
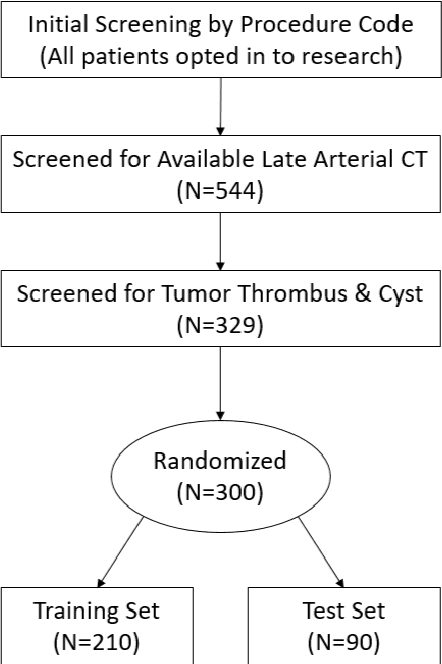
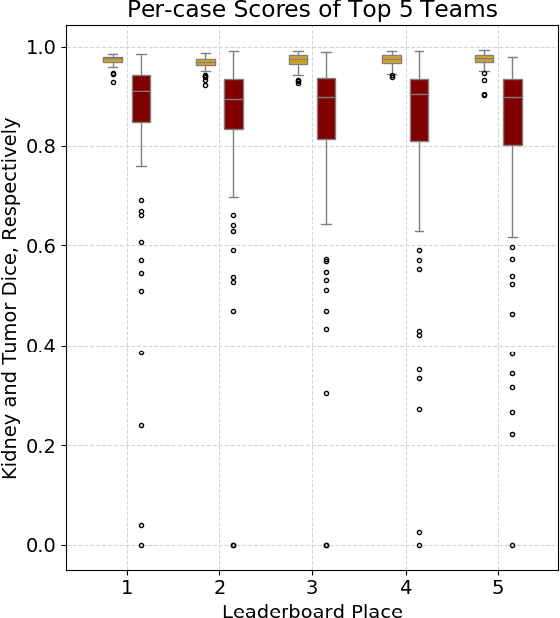
Abstract:There is a large body of literature linking anatomic and geometric characteristics of kidney tumors to perioperative and oncologic outcomes. Semantic segmentation of these tumors and their host kidneys is a promising tool for quantitatively characterizing these lesions, but its adoption is limited due to the manual effort required to produce high-quality 3D segmentations of these structures. Recently, methods based on deep learning have shown excellent results in automatic 3D segmentation, but they require large datasets for training, and there remains little consensus on which methods perform best. The 2019 Kidney and Kidney Tumor Segmentation challenge (KiTS19) was a competition held in conjunction with the 2019 International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) which sought to address these issues and stimulate progress on this automatic segmentation problem. A training set of 210 cross sectional CT images with kidney tumors was publicly released with corresponding semantic segmentation masks. 106 teams from five continents used this data to develop automated systems to predict the true segmentation masks on a test set of 90 CT images for which the corresponding ground truth segmentations were kept private. These predictions were scored and ranked according to their average So rensen-Dice coefficient between the kidney and tumor across all 90 cases. The winning team achieved a Dice of 0.974 for kidney and 0.851 for tumor, approaching the inter-annotator performance on kidney (0.983) but falling short on tumor (0.923). This challenge has now entered an "open leaderboard" phase where it serves as a challenging benchmark in 3D semantic segmentation.
Cascaded Volumetric Convolutional Network for Kidney Tumor Segmentation from CT volumes
Oct 05, 2019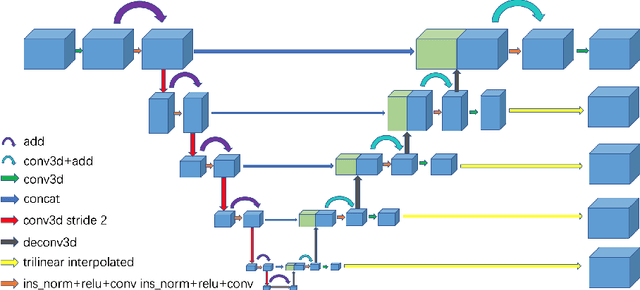
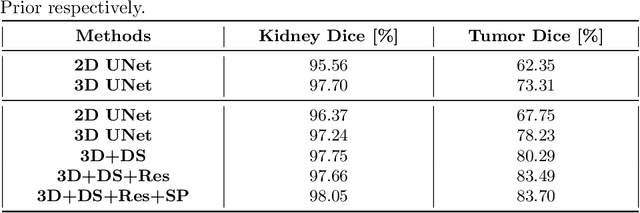
Abstract:Automated segmentation of kidney and tumor from 3D CT scans is necessary for the diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment planning of the disease. In this paper, we describe a two-stage framework for kidney and tumor segmentation based on 3D fully convolutional network (FCN). The first stage preliminarily locate the kidney and cut off the irrelevant background to reduce class imbalance and computation cost. Then the second stage precisely segment the kidney and tumor on the cropped patch. The proposed method achieves 98.05% and 83.70% of Dice score on the validation set of MICCAI 2019 KiTS Challenge.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge