Giancarlo Mauri
Università degli Studi di Milano-Bicocca
Combining Noise-to-Image and Image-to-Image GANs: Brain MR Image Augmentation for Tumor Detection
May 31, 2019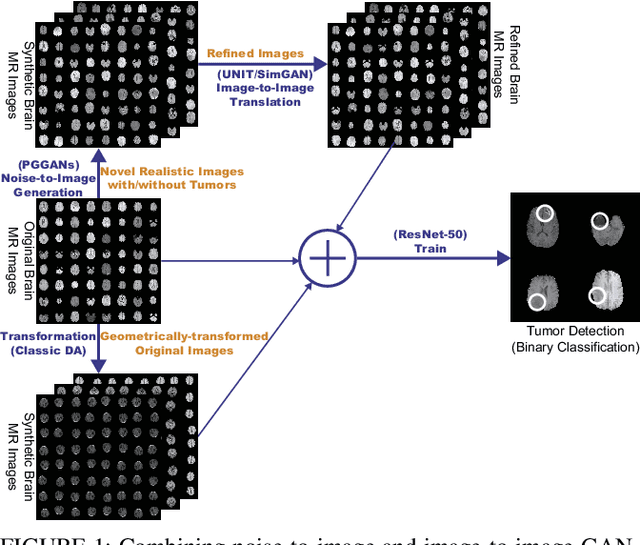
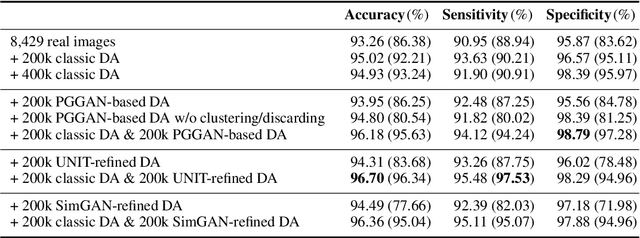
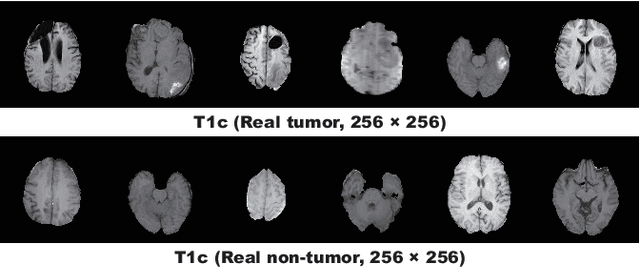
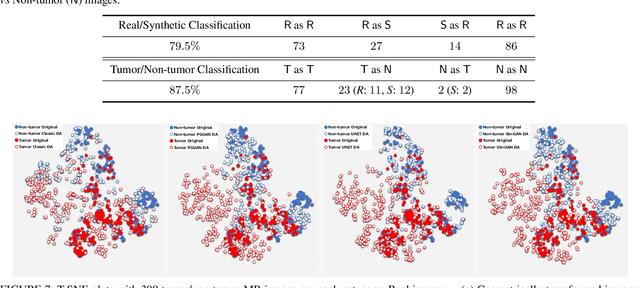
Abstract:Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) can achieve excellent computer-assisted diagnosis performance, relying on sufficient annotated training data. Unfortunately, most medical imaging datasets, often collected from various scanners, are small and fragmented. In this context, as a Data Augmentation (DA) technique, Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) can synthesize realistic/diverse additional training images to fill the data lack in the real image distribution; researchers have improved classification by augmenting images with noise-to-image (e.g., random noise samples to diverse pathological images) or image-to-image GANs (e.g., a benign image to a malignant one). Yet, no research has reported results combining (i) noise-to-image GANs and image-to-image GANs or (ii) GANs and other deep generative models, for further performance boost. Therefore, to maximize the DA effect with the GAN combinations, we propose a two-step GAN-based DA that generates and refines brain MR images with/without tumors separately: (i) Progressive Growing of GANs (PGGANs), multi-stage noise-to-image GAN for high-resolution image generation, first generates realistic/diverse 256 x 256 images--even a physician cannot accurately distinguish them from real ones via Visual Turing Test; (ii) UNsupervised Image-to-image Translation or SimGAN, image-to-image GAN combining GANs/Variational AutoEncoders or using a GAN loss for DA, further refines the texture/shape of the PGGAN-generated images similarly to the real ones. We thoroughly investigate CNN-based tumor classification results, also considering the influence of pre-training on ImageNet and discarding weird-looking GAN-generated images. The results show that, when combined with classic DA, our two-step GAN-based DA can significantly outperform the classic DA alone, in tumor detection (i.e., boosting sensitivity from 93.63% to 97.53%) and also in other tasks.
USE-Net: incorporating Squeeze-and-Excitation blocks into U-Net for prostate zonal segmentation of multi-institutional MRI datasets
Apr 17, 2019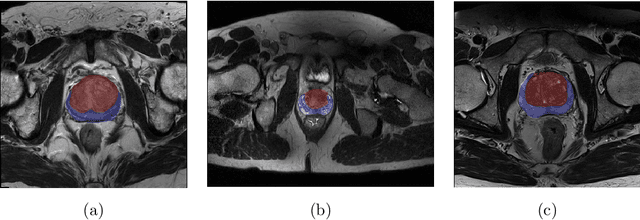
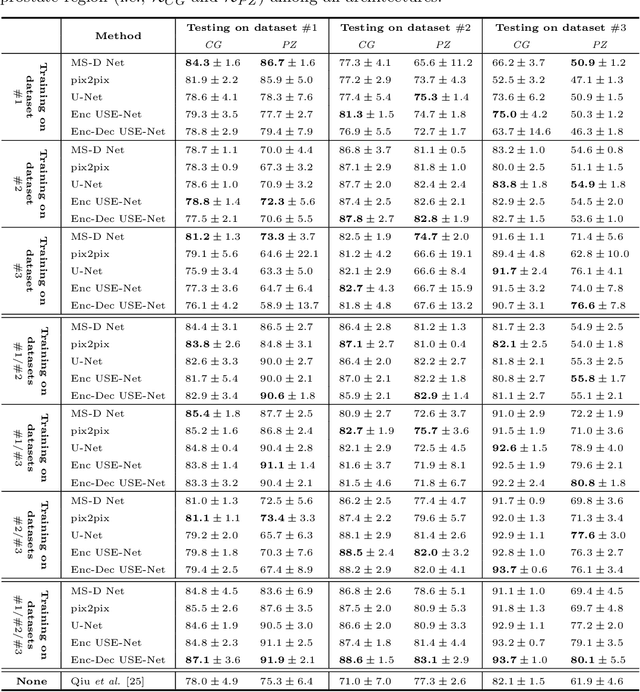
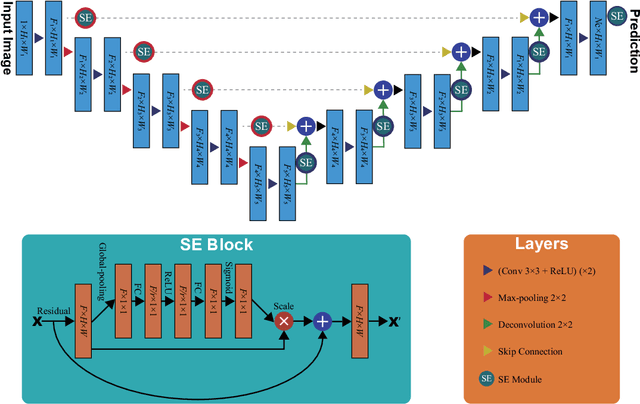
Abstract:Prostate cancer is the most common malignant tumors in men but prostate Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) analysis remains challenging. Besides whole prostate gland segmentation, the capability to differentiate between the blurry boundary of the Central Gland (CG) and Peripheral Zone (PZ) can lead to differential diagnosis, since tumor's frequency and severity differ in these regions. To tackle the prostate zonal segmentation task, we propose a novel Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), called USE-Net, which incorporates Squeeze-and-Excitation (SE) blocks into U-Net. Especially, the SE blocks are added after every Encoder (Enc USE-Net) or Encoder-Decoder block (Enc-Dec USE-Net). This study evaluates the generalization ability of CNN-based architectures on three T2-weighted MRI datasets, each one consisting of a different number of patients and heterogeneous image characteristics, collected by different institutions. The following mixed scheme is used for training/testing: (i) training on either each individual dataset or multiple prostate MRI datasets and (ii) testing on all three datasets with all possible training/testing combinations. USE-Net is compared against three state-of-the-art CNN-based architectures (i.e., U-Net, pix2pix, and Mixed-Scale Dense Network), along with a semi-automatic continuous max-flow model. The results show that training on the union of the datasets generally outperforms training on each dataset separately, allowing for both intra-/cross-dataset generalization. Enc USE-Net shows good overall generalization under any training condition, while Enc-Dec USE-Net remarkably outperforms the other methods when trained on all datasets. These findings reveal that the SE blocks' adaptive feature recalibration provides excellent cross-dataset generalization when testing is performed on samples of the datasets used during training.
CNN-based Prostate Zonal Segmentation on T2-weighted MR Images: A Cross-dataset Study
Mar 29, 2019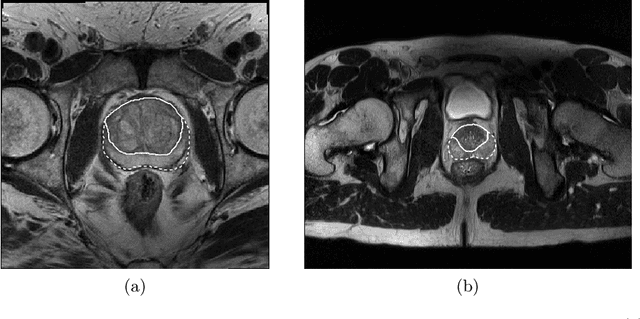
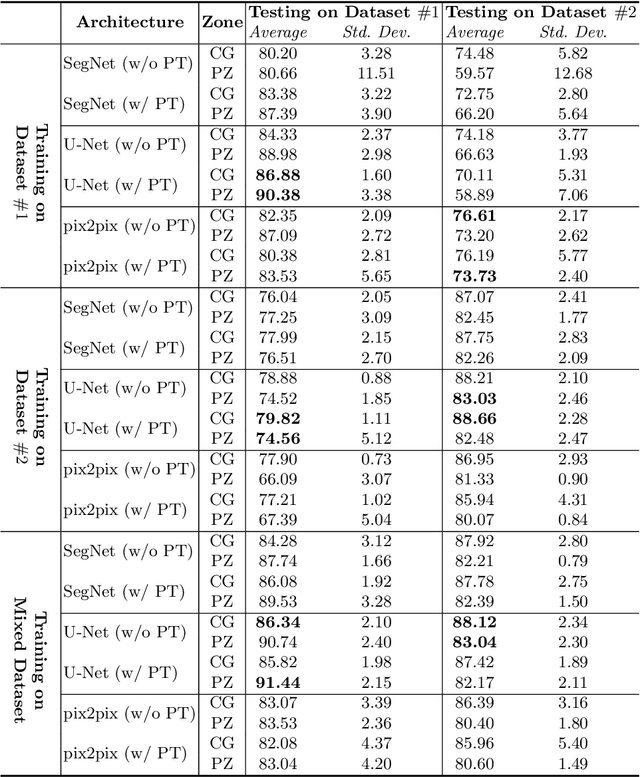
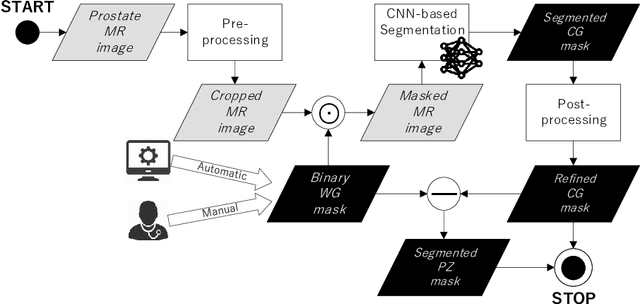
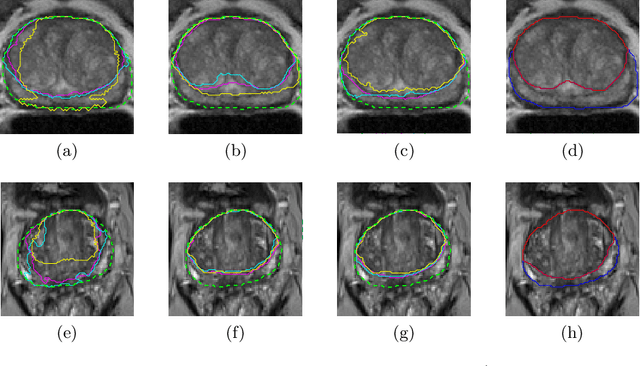
Abstract:Prostate cancer is the most common cancer among US men. However, prostate imaging is still challenging despite the advances in multi-parametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), which provides both morphologic and functional information pertaining to the pathological regions. Along with whole prostate gland segmentation, distinguishing between the Central Gland (CG) and Peripheral Zone (PZ) can guide towards differential diagnosis, since the frequency and severity of tumors differ in these regions; however, their boundary is often weak and fuzzy. This work presents a preliminary study on Deep Learning to automatically delineate the CG and PZ, aiming at evaluating the generalization ability of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) on two multi-centric MRI prostate datasets. Especially, we compared three CNN-based architectures: SegNet, U-Net, and pix2pix. In such a context, the segmentation performances achieved with/without pre-training were compared in 4-fold cross-validation. In general, U-Net outperforms the other methods, especially when training and testing are performed on multiple datasets.
Infinite Brain MR Images: PGGAN-based Data Augmentation for Tumor Detection
Mar 29, 2019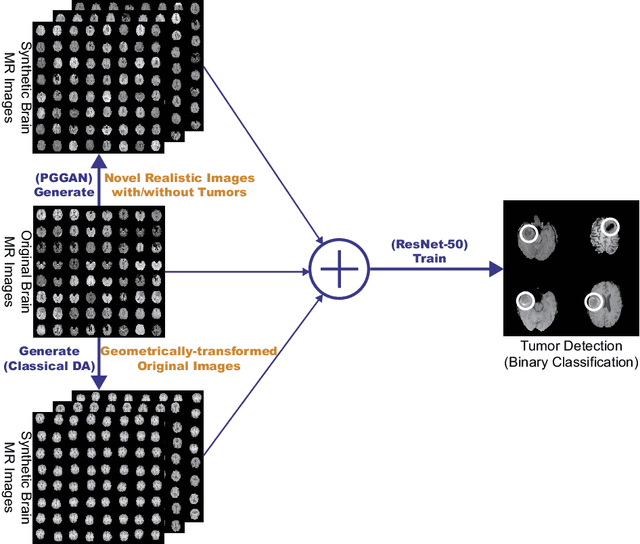

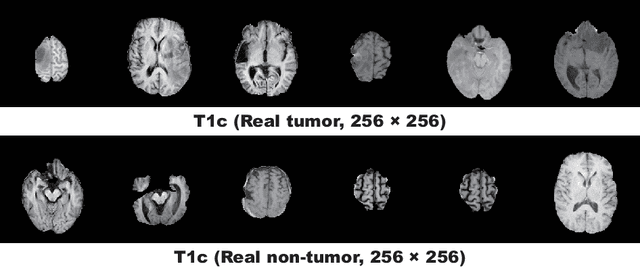
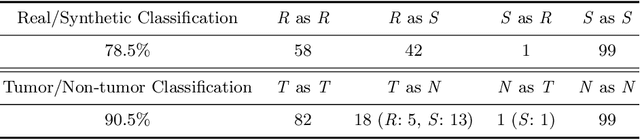
Abstract:Due to the lack of available annotated medical images, accurate computer-assisted diagnosis requires intensive Data Augmentation (DA) techniques, such as geometric/intensity transformations of original images; however, those transformed images intrinsically have a similar distribution to the original ones, leading to limited performance improvement. To fill the data lack in the real image distribution, we synthesize brain contrast-enhanced Magnetic Resonance (MR) images---realistic but completely different from the original ones---using Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs). This study exploits Progressive Growing of GANs (PGGANs), a multi-stage generative training method, to generate original-sized 256 X 256 MR images for Convolutional Neural Network-based brain tumor detection, which is challenging via conventional GANs; difficulties arise due to unstable GAN training with high resolution and a variety of tumors in size, location, shape, and contrast. Our preliminary results show that this novel PGGAN-based DA method can achieve promising performance improvement, when combined with classical DA, in tumor detection and also in other medical imaging tasks.
Parallel Implementation of Efficient Search Schemes for the Inference of Cancer Progression Models
Mar 08, 2017
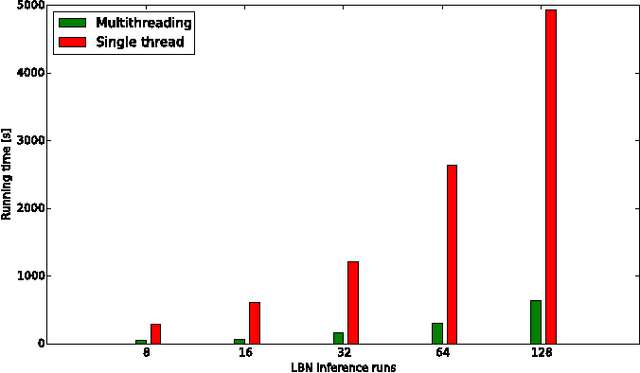
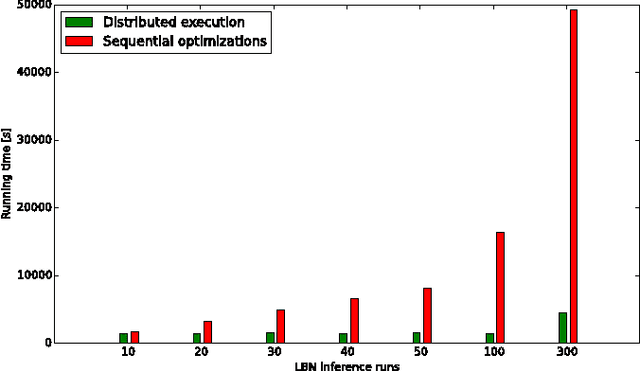
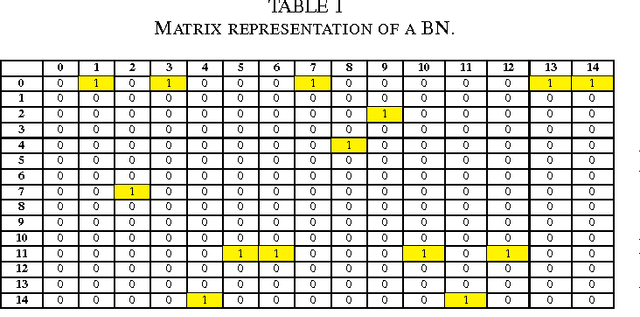
Abstract:The emergence and development of cancer is a consequence of the accumulation over time of genomic mutations involving a specific set of genes, which provides the cancer clones with a functional selective advantage. In this work, we model the order of accumulation of such mutations during the progression, which eventually leads to the disease, by means of probabilistic graphic models, i.e., Bayesian Networks (BNs). We investigate how to perform the task of learning the structure of such BNs, according to experimental evidence, adopting a global optimization meta-heuristics. In particular, in this work we rely on Genetic Algorithms, and to strongly reduce the execution time of the inference -- which can also involve multiple repetitions to collect statistically significant assessments of the data -- we distribute the calculations using both multi-threading and a multi-node architecture. The results show that our approach is characterized by good accuracy and specificity; we also demonstrate its feasibility, thanks to a 84x reduction of the overall execution time with respect to a traditional sequential implementation.
A Hybrid Monte Carlo Ant Colony Optimization Approach for Protein Structure Prediction in the HP Model
Sep 30, 2013

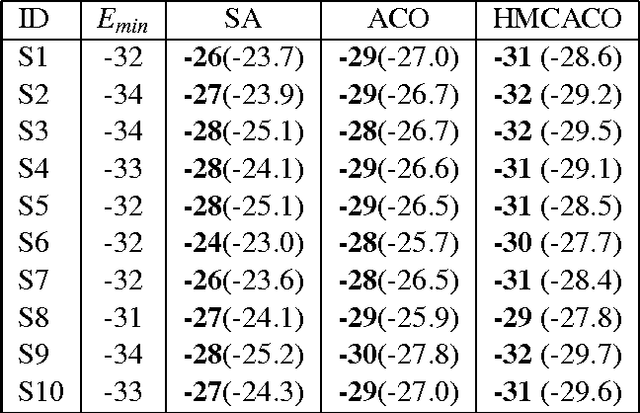
Abstract:The hydrophobic-polar (HP) model has been widely studied in the field of protein structure prediction (PSP) both for theoretical purposes and as a benchmark for new optimization strategies. In this work we introduce a new heuristics based on Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) and Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) that we called Hybrid Monte Carlo Ant Colony Optimization (HMCACO). We describe this method and compare results obtained on well known HP instances in the 3 dimensional cubic lattice to those obtained with standard ACO and Simulated Annealing (SA). All methods were implemented using an unconstrained neighborhood and a modified objective function to prevent the creation of overlapping walks. Results show that our methods perform better than the other heuristics in all benchmark instances.
* In Proceedings Wivace 2013, arXiv:1309.7122
Proceedings Wivace 2013 - Italian Workshop on Artificial Life and Evolutionary Computation
Sep 27, 2013Abstract:The Wivace 2013 Electronic Proceedings in Theoretical Computer Science (EPTCS) contain some selected long and short articles accepted for the presentation at Wivace 2013 - Italian Workshop on Artificial Life and Evolutionary Computation, which was held at the University of Milan-Bicocca, Milan, on the 1st and 2nd of July, 2013.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge