Ge Fan
Hallucination Detection: Robustly Discerning Reliable Answers in Large Language Models
Jul 04, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have gained widespread adoption in various natural language processing tasks, including question answering and dialogue systems. However, a major drawback of LLMs is the issue of hallucination, where they generate unfaithful or inconsistent content that deviates from the input source, leading to severe consequences. In this paper, we propose a robust discriminator named RelD to effectively detect hallucination in LLMs' generated answers. RelD is trained on the constructed RelQA, a bilingual question-answering dialogue dataset along with answers generated by LLMs and a comprehensive set of metrics. Our experimental results demonstrate that the proposed RelD successfully detects hallucination in the answers generated by diverse LLMs. Moreover, it performs well in distinguishing hallucination in LLMs' generated answers from both in-distribution and out-of-distribution datasets. Additionally, we also conduct a thorough analysis of the types of hallucinations that occur and present valuable insights. This research significantly contributes to the detection of reliable answers generated by LLMs and holds noteworthy implications for mitigating hallucination in the future work.
MAPO: Boosting Large Language Model Performance with Model-Adaptive Prompt Optimization
Jul 04, 2024



Abstract:Prompt engineering, as an efficient and effective way to leverage Large Language Models (LLM), has drawn a lot of attention from the research community. The existing research primarily emphasizes the importance of adapting prompts to specific tasks, rather than specific LLMs. However, a good prompt is not solely defined by its wording, but also binds to the nature of the LLM in question. In this work, we first quantitatively demonstrate that different prompts should be adapted to different LLMs to enhance their capabilities across various downstream tasks in NLP. Then we novelly propose a model-adaptive prompt optimizer (MAPO) method that optimizes the original prompts for each specific LLM in downstream tasks. Extensive experiments indicate that the proposed method can effectively refine prompts for an LLM, leading to significant improvements over various downstream tasks.
CUPID: Improving Battle Fairness and Position Satisfaction in Online MOBA Games with a Re-matchmaking System
Jun 28, 2024



Abstract:The multiplayer online battle arena (MOBA) genre has gained significant popularity and economic success, attracting considerable research interest within the Human-Computer Interaction community. Enhancing the gaming experience requires a deep understanding of player behavior, and a crucial aspect of MOBA games is matchmaking, which aims to assemble teams of comparable skill levels. However, existing matchmaking systems often neglect important factors such as players' position preferences and team assignment, resulting in imbalanced matches and reduced player satisfaction. To address these limitations, this paper proposes a novel framework called CUPID, which introduces a novel process called ``re-matchmaking'' to optimize team and position assignments to improve both fairness and player satisfaction. CUPID incorporates a pre-filtering step to ensure a minimum level of matchmaking quality, followed by a pre-match win-rate prediction model that evaluates the fairness of potential assignments. By simultaneously considering players' position satisfaction and game fairness, CUPID aims to provide an enhanced matchmaking experience. Extensive experiments were conducted on two large-scale, real-world MOBA datasets to validate the effectiveness of CUPID. The results surpass all existing state-of-the-art baselines, with an average relative improvement of 7.18% in terms of win prediction accuracy. Furthermore, CUPID has been successfully deployed in a popular online mobile MOBA game. The deployment resulted in significant improvements in match fairness and player satisfaction, as evidenced by critical Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) metrics covering usability, accessibility, and engagement, observed through A/B testing. To the best of our knowledge, CUPID is the first re-matchmaking system designed specifically for large-scale MOBA games.
MV-HAN: A Hybrid Attentive Networks based Multi-View Learning Model for Large-scale Contents Recommendation
Oct 14, 2022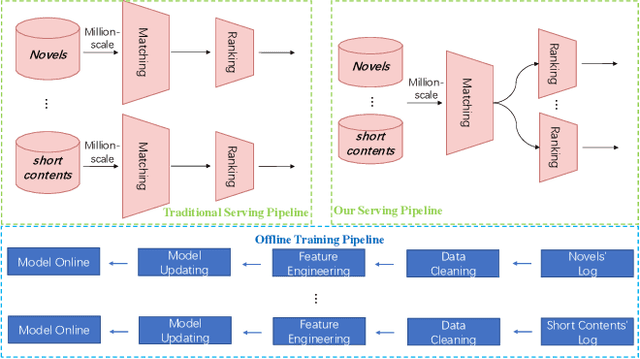
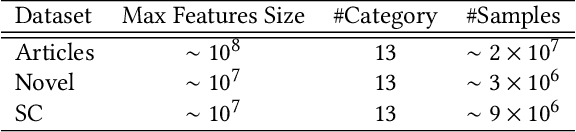
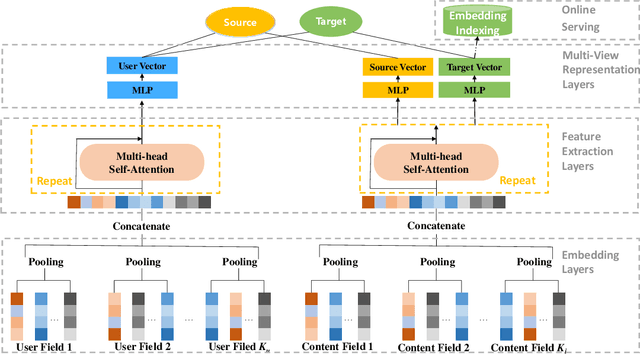
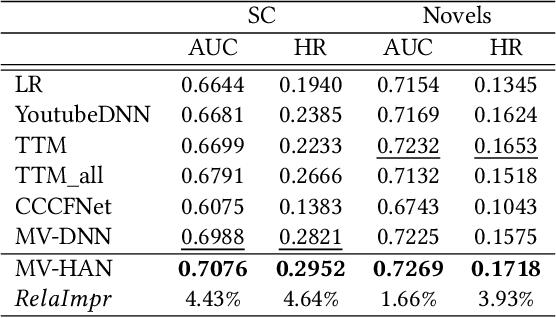
Abstract:Industrial recommender systems usually employ multi-source data to improve the recommendation quality, while effectively sharing information between different data sources remain a challenge. In this paper, we introduce a novel Multi-View Approach with Hybrid Attentive Networks (MV-HAN) for contents retrieval at the matching stage of recommender systems. The proposed model enables high-order feature interaction from various input features while effectively transferring knowledge between different types. By employing a well-placed parameters sharing strategy, the MV-HAN substantially improves the retrieval performance in sparse types. The designed MV-HAN inherits the efficiency advantages in the online service from the two-tower model, by mapping users and contents of different types into the same features space. This enables fast retrieval of similar contents with an approximate nearest neighbor algorithm. We conduct offline experiments on several industrial datasets, demonstrating that the proposed MV-HAN significantly outperforms baselines on the content retrieval tasks. Importantly, the MV-HAN is deployed in a real-world matching system. Online A/B test results show that the proposed method can significantly improve the quality of recommendations.
QuickSkill: Novice Skill Estimation in Online Multiplayer Games
Aug 15, 2022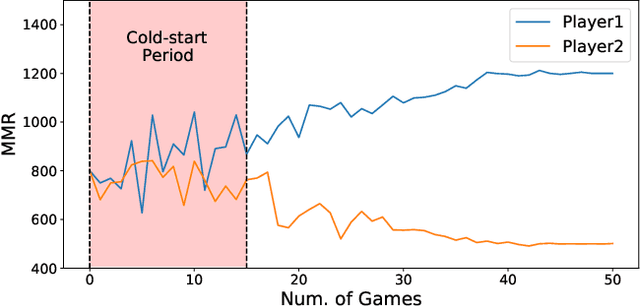

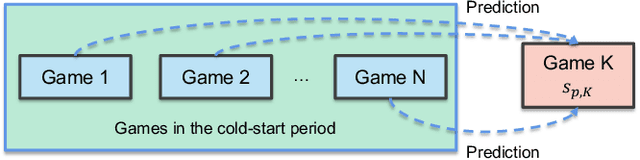
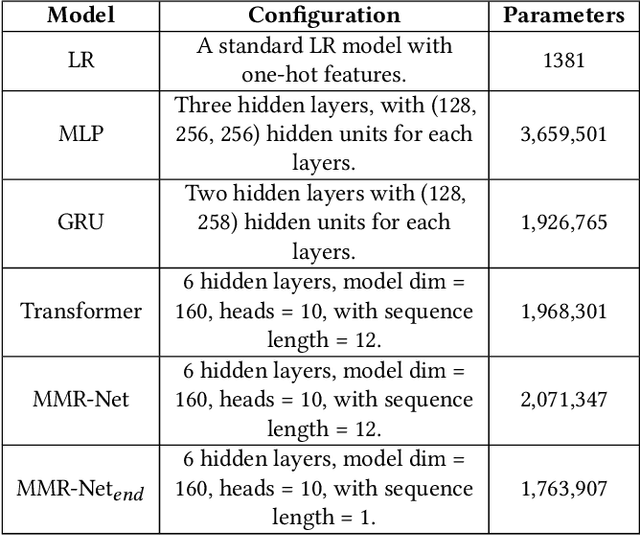
Abstract:Matchmaking systems are vital for creating fair matches in online multiplayer games, which directly affects players' satisfactions and game experience. Most of the matchmaking systems largely rely on precise estimation of players' game skills to construct equitable games. However, the skill rating of a novice is usually inaccurate, as current matchmaking rating algorithms require considerable amount of games for learning the true skill of a new player. Using these unreliable skill scores at early stages for matchmaking usually leads to disparities in terms of team performance, which causes negative game experience. This is known as the ''cold-start'' problem for matchmaking rating algorithms. To overcome this conundrum, this paper proposes QuickSKill, a deep learning based novice skill estimation framework to quickly probe abilities of new players in online multiplayer games. QuickSKill extracts sequential performance features from initial few games of a player to predict his/her future skill rating with a dedicated neural network, thus delivering accurate skill estimation at the player's early game stage. By employing QuickSKill for matchmaking, game fairness can be dramatically improved in the initial cold-start period. We conduct experiments in a popular mobile multiplayer game in both offline and online scenarios. Results obtained with two real-world anonymized gaming datasets demonstrate that proposed QuickSKill delivers precise estimation of game skills for novices, leading to significantly lower team skill disparities and better player game experience. To the best of our knowledge, proposed QuickSKill is the first framework that tackles the cold-start problem for traditional skill rating algorithms.
A collaborative filtering model with heterogeneous neural networks for recommender systems
May 27, 2019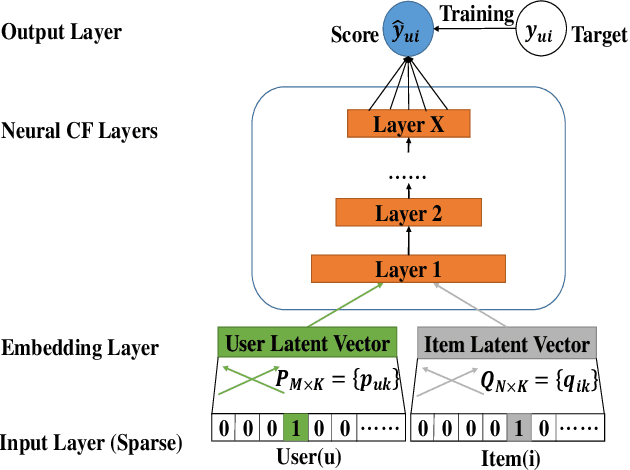
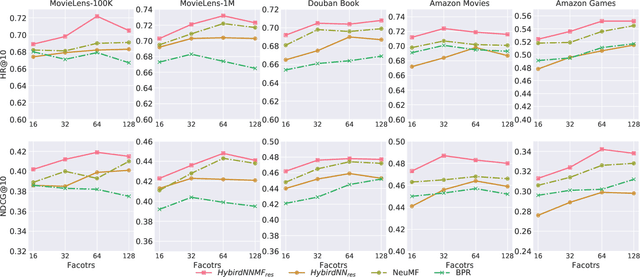
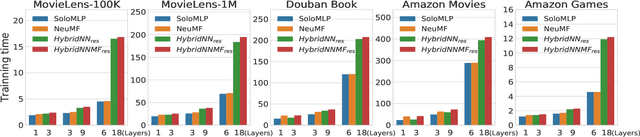
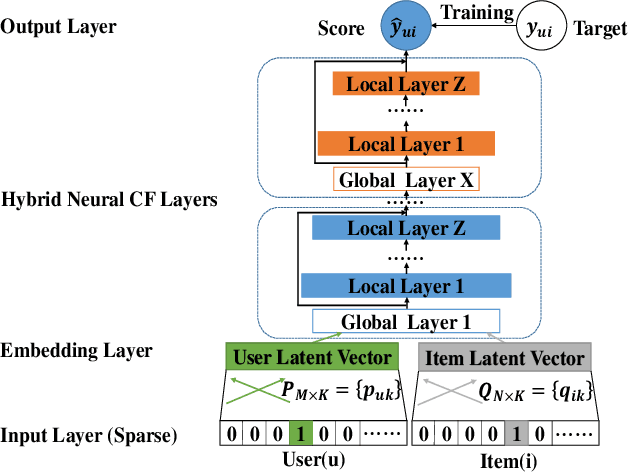
Abstract:In recent years, deep neural network is introduced in recommender systems to solve the collaborative filtering problem, which has achieved immense success on computer vision, speech recognition and natural language processing. On one hand, deep neural network can be used to model the auxiliary information in recommender systems. On the other hand, it is also capable of modeling nonlinear relationships between users and items. One advantage of deep neural network is that the performance of the algorithm can be easily enhanced by augmenting the depth of the neural network. However, two potential problems may emerge when the deep neural work is exploited to model relationships between users and items. The fundamental problem is that the complexity of the algorithm grows significantly with the increment in the depth of the neural network. The second one is that a deeper neural network may undermine the accuracy of the algorithm. In order to alleviate these problems, we propose a hybrid neural network that combines heterogeneous neural networks with different structures. The experimental results on real datasets reveal that our method is superior to the state-of-the-art methods in terms of the item ranking.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge