Farnoosh Javadi
LLM-based Weak Supervision Framework for Query Intent Classification in Video Search
Sep 13, 2024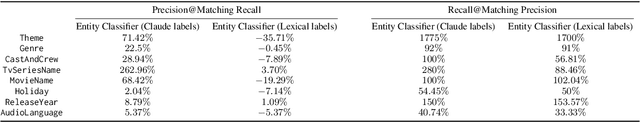
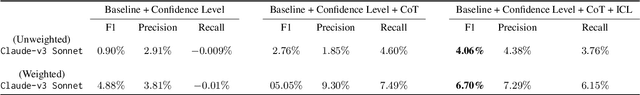
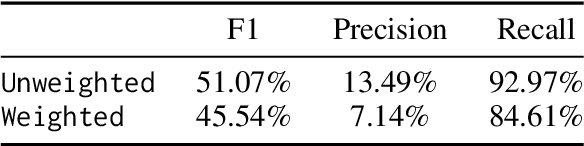
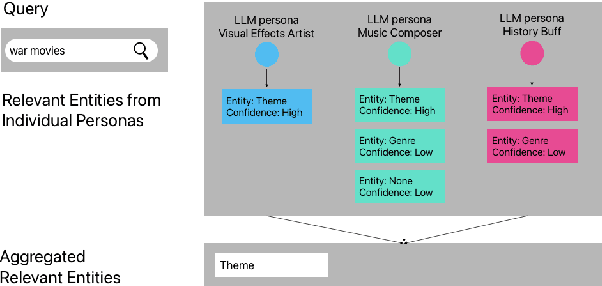
Abstract:Streaming services have reshaped how we discover and engage with digital entertainment. Despite these advancements, effectively understanding the wide spectrum of user search queries continues to pose a significant challenge. An accurate query understanding system that can handle a variety of entities that represent different user intents is essential for delivering an enhanced user experience. We can build such a system by training a natural language understanding (NLU) model; however, obtaining high-quality labeled training data in this specialized domain is a substantial obstacle. Manual annotation is costly and impractical for capturing users' vast vocabulary variations. To address this, we introduce a novel approach that leverages large language models (LLMs) through weak supervision to automatically annotate a vast collection of user search queries. Using prompt engineering and a diverse set of LLM personas, we generate training data that matches human annotator expectations. By incorporating domain knowledge via Chain of Thought and In-Context Learning, our approach leverages the labeled data to train low-latency models optimized for real-time inference. Extensive evaluations demonstrated that our approach outperformed the baseline with an average relative gain of 113% in recall. Furthermore, our novel prompt engineering framework yields higher quality LLM-generated data to be used for weak supervision; we observed 47.60% improvement over baseline in agreement rate between LLM predictions and human annotations with respect to F1 score, weighted according to the distribution of occurrences of the search queries. Our persona selection routing mechanism further adds an additional 3.67% increase in weighted F1 score on top of our novel prompt engineering framework.
SkipViT: Speeding Up Vision Transformers with a Token-Level Skip Connection
Jan 27, 2024Abstract:Vision transformers are known to be more computationally and data-intensive than CNN models. These transformer models such as ViT, require all the input image tokens to learn the relationship among them. However, many of these tokens are not informative and may contain irrelevant information such as unrelated background or unimportant scenery. These tokens are overlooked by the multi-head self-attention (MHSA), resulting in many redundant and unnecessary computations in MHSA and the feed-forward network (FFN). In this work, we propose a method to optimize the amount of unnecessary interactions between unimportant tokens by separating and sending them through a different low-cost computational path. Our method does not add any parameters to the ViT model and aims to find the best trade-off between training throughput and achieving a 0% loss in the Top-1 accuracy of the final model. Our experimental results on training ViT-small from scratch show that SkipViT is capable of effectively dropping 55% of the tokens while gaining more than 13% training throughput and maintaining classification accuracy at the level of the baseline model on Huawei Ascend910A.
SwiftLearn: A Data-Efficient Training Method of Deep Learning Models using Importance Sampling
Nov 25, 2023
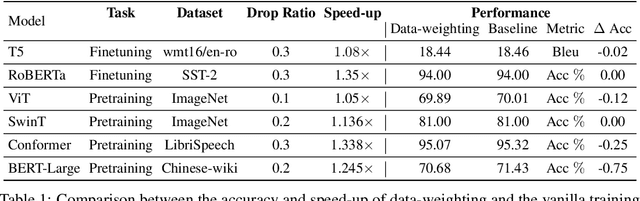
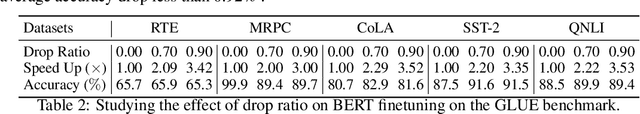
Abstract:In this paper, we present SwiftLearn, a data-efficient approach to accelerate training of deep learning models using a subset of data samples selected during the warm-up stages of training. This subset is selected based on an importance criteria measured over the entire dataset during warm-up stages, aiming to preserve the model performance with fewer examples during the rest of training. The importance measure we propose could be updated during training every once in a while, to make sure that all of the data samples have a chance to return to the training loop if they show a higher importance. The model architecture is unchanged but since the number of data samples controls the number of forward and backward passes during training, we can reduce the training time by reducing the number of training samples used in each epoch of training. Experimental results on a variety of CV and NLP models during both pretraining and finetuning show that the model performance could be preserved while achieving a significant speed-up during training. More specifically, BERT finetuning on GLUE benchmark shows that almost 90% of the data can be dropped achieving an end-to-end average speedup of 3.36x while keeping the average accuracy drop less than 0.92%.
GQKVA: Efficient Pre-training of Transformers by Grouping Queries, Keys, and Values
Nov 06, 2023Abstract:Massive transformer-based models face several challenges, including slow and computationally intensive pre-training and over-parametrization. This paper addresses these challenges by proposing a versatile method called GQKVA, which generalizes query, key, and value grouping techniques. GQKVA is designed to speed up transformer pre-training while reducing the model size. Our experiments with various GQKVA variants highlight a clear trade-off between performance and model size, allowing for customized choices based on resource and time limitations. Our findings also indicate that the conventional multi-head attention approach is not always the best choice, as there are lighter and faster alternatives available. We tested our method on ViT, which achieved an approximate 0.3% increase in accuracy while reducing the model size by about 4% in the task of image classification. Additionally, our most aggressive model reduction experiment resulted in a reduction of approximately 15% in model size, with only around a 1% drop in accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge