Fangzhou Wang
Quantum Machine Learning for Semiconductor Fabrication: Modeling GaN HEMT Contact Process
Sep 17, 2024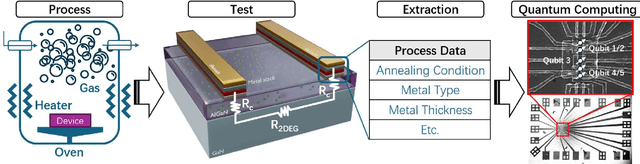
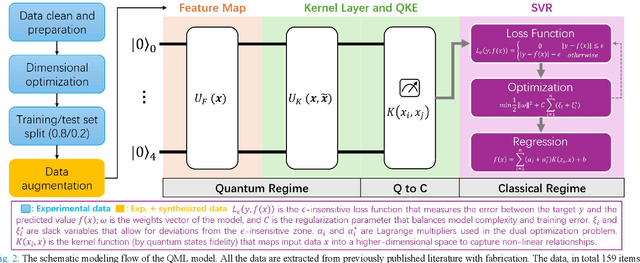
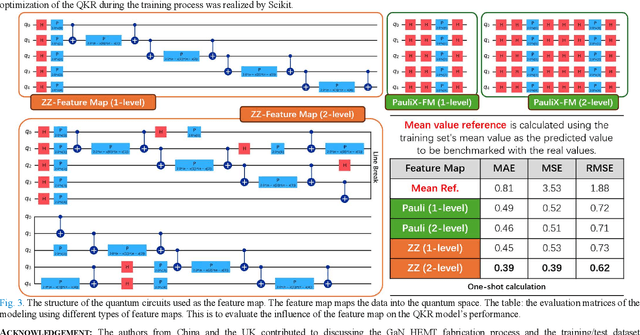
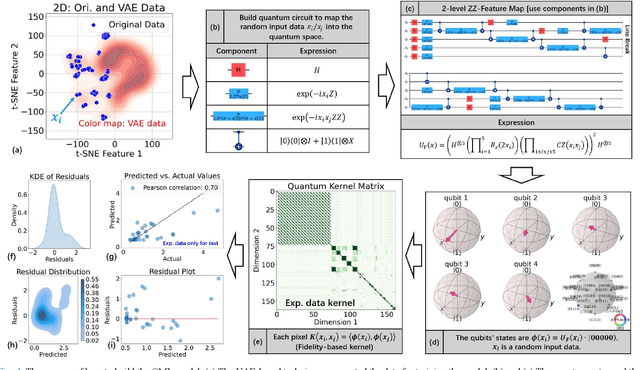
Abstract:This paper pioneers the use of quantum machine learning (QML) for modeling the Ohmic contact process in GaN high-electron-mobility transistors (HEMTs) for the first time. Utilizing data from 159 devices and variational auto-encoder-based augmentation, we developed a quantum kernel-based regressor (QKR) with a 2-level ZZ-feature map. Benchmarking against six classical machine learning (CML) models, our QKR consistently demonstrated the lowest mean absolute error (MAE), mean squared error (MSE), and root mean squared error (RMSE). Repeated statistical analysis confirmed its robustness. Additionally, experiments verified an MAE of 0.314 ohm-mm, underscoring the QKR's superior performance and potential for semiconductor applications, and demonstrating significant advancements over traditional CML methods.
TroLLoc: Logic Locking and Layout Hardening for IC Security Closure against Hardware Trojans
May 09, 2024



Abstract:Due to cost benefits, supply chains of integrated circuits (ICs) are largely outsourced nowadays. However, passing ICs through various third-party providers gives rise to many security threats, like piracy of IC intellectual property or insertion of hardware Trojans, i.e., malicious circuit modifications. In this work, we proactively and systematically protect the physical layouts of ICs against post-design insertion of Trojans. Toward that end, we propose TroLLoc, a novel scheme for IC security closure that employs, for the first time, logic locking and layout hardening in unison. TroLLoc is fully integrated into a commercial-grade design flow, and TroLLoc is shown to be effective, efficient, and robust. Our work provides in-depth layout and security analysis considering the challenging benchmarks of the ISPD'22/23 contests for security closure. We show that TroLLoc successfully renders layouts resilient, with reasonable overheads, against (i) general prospects for Trojan insertion as in the ISPD'22 contest, (ii) actual Trojan insertion as in the ISPD'23 contest, and (iii) potential second-order attacks where adversaries would first (i.e., before Trojan insertion) try to bypass the locking defense, e.g., using advanced machine learning attacks. Finally, we release all our artifacts for independent verification [2].
Scaling Up LLM Reviews for Google Ads Content Moderation
Feb 07, 2024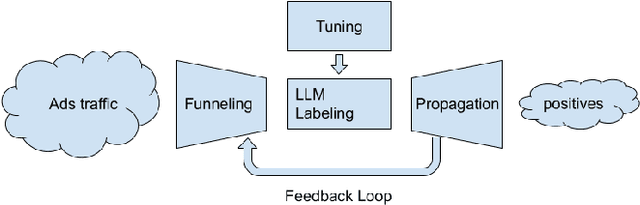
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are powerful tools for content moderation, but their inference costs and latency make them prohibitive for casual use on large datasets, such as the Google Ads repository. This study proposes a method for scaling up LLM reviews for content moderation in Google Ads. First, we use heuristics to select candidates via filtering and duplicate removal, and create clusters of ads for which we select one representative ad per cluster. We then use LLMs to review only the representative ads. Finally, we propagate the LLM decisions for the representative ads back to their clusters. This method reduces the number of reviews by more than 3 orders of magnitude while achieving a 2x recall compared to a baseline non-LLM model. The success of this approach is a strong function of the representations used in clustering and label propagation; we found that cross-modal similarity representations yield better results than uni-modal representations.
Applications of Absorptive Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces in Interference Mitigation and Physical Layer Security
Feb 03, 2023Abstract:This paper explores the use of reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS) in mitigating cross-system interference in spectrum sharing and secure wireless applications. Unlike conventional RIS that can only adjust the phase of the incoming signal and essentially reflect all impinging energy, or active RIS, which also amplify the reflected signal at the cost of significantly higher complexity, noise, and power consumption, an absorptive RIS (ARIS) is considered. An ARIS can in principle modify both the phase and modulus of the impinging signal by absorbing a portion of the signal energy, providing a compromise between its conventional and active counterparts in terms of complexity, power consumption, and degrees of freedom (DoFs). We first use a toy example to illustrate the benefit of ARIS, and then we consider three applications: (1) Spectral coexistence of radar and communication systems, where a convex optimization problem is formulated to minimize the Frobenius norm of the channel matrix from the communication base station to the radar receiver; (2) Spectrum sharing in device-to-device (D2D) communications, where a max-min scheme that maximizes the worst-case signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR) among the D2D links is developed and then solved via fractional programming; (3) The physical layer security of a downlink communication system, where the secrecy rate is maximized and the resulting nonconvex problem is solved by a fractional programming algorithm together with a sequential convex relaxation procedure. Numerical results are then presented to show the significant benefit of ARIS in these applications.
Security Closure of IC Layouts Against Hardware Trojans
Nov 15, 2022Abstract:Due to cost benefits, supply chains of integrated circuits (ICs) are largely outsourced nowadays. However, passing ICs through various third-party providers gives rise to many threats, like piracy of IC intellectual property or insertion of hardware Trojans, i.e., malicious circuit modifications. In this work, we proactively and systematically harden the physical layouts of ICs against post-design insertion of Trojans. Toward that end, we propose a multiplexer-based logic-locking scheme that is (i) devised for layout-level Trojan prevention, (ii) resilient against state-of-the-art, oracle-less machine learning attacks, and (iii) fully integrated into a tailored, yet generic, commercial-grade design flow. Our work provides in-depth security and layout analysis on a challenging benchmark suite. We show that ours can render layouts resilient, with reasonable overheads, against Trojan insertion in general and also against second-order attacks (i.e., adversaries seeking to bypass the locking defense in an oracle-less setting). We release our layout artifacts for independent verification [29] and we will release our methodology's source code.
Joint Active and Passive Beamforming for IRS-Assisted Radar
Aug 09, 2021


Abstract:Intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) is a promising technology being considered for future wireless communications due to its ability to control signal propagation. This paper considers the joint active and passive beamforming problem for an IRS-assisted radar, where multiple IRSs are deployed to assist the surveillance of multiple targets in cluttered environments. Specifically, we aim to maximize the minimum target illumination power at multiple target locations by jointly optimizing the active beamformer at the radar transmitter and the passive phase-shift matrices at the IRSs, subject to an upperbound on the clutter power at each clutter scatterer. The resulting optimization problem is nonconvex and solved with a sequential optimization procedure along with semedefinite relaxation (SDR). Simulation results show that IRSs can help create effective line-of-sight (LOS) paths and thus substantially improve the radar robustness against target blockage.
Signal Detection in Distributed MIMO Radar with Non-Orthogonal Waveforms and Sync Errors
Feb 19, 2021



Abstract:Although routinely utilized in literature, orthogonal waveforms may lose orthogonality in distributed multi-input multi-output (MIMO) radar with spatially separated transmit (TX) and receive (RX) antennas, as the waveforms may experience distinct delays and Doppler frequency offsets unique to different TX-RX propagation paths. In such cases, the output of each waveform-specific matched filter (MF), employed to unravel the waveforms at the RXs, contains both an \auto term and multiple cross terms, i.e., the filtered response of the desired and, respectively, undesired waveforms. We consider the impact of non-orthogonal waveforms and their cross terms on target detection with or without timing, frequency, and phase errors. To this end, we present a general signal model for distributed MIMO radar, examine target detection using existing coherent/non-coherent detectors and two new detectors, including a hybrid detector that requires phase coherence locally but not across distributed antennas, and provide a statistical analysis leading to closed-form expressions of false alarm and detection probabilities for all detectors. Our results show that cross terms can behave like foes or allies, respectively, if they and the auto term add destructively or constructively, depending on the propagation delay, frequency, and phase offsets. Regarding sync errors, we show that phase errors affect only coherent detectors, frequency errors degrade all but the non-coherent detector, while all are impacted by timing errors, which result in a loss in the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge