Fan Luo
Learning Positional Attention for Sequential Recommendation
Jul 03, 2024
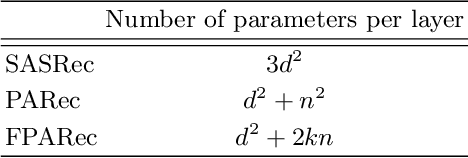

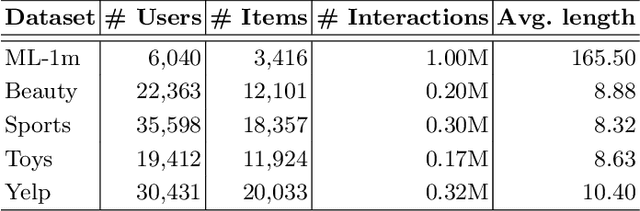
Abstract:Self-attention-based networks have achieved remarkable performance in sequential recommendation tasks. A crucial component of these models is positional encoding. In this study, we delve into the learned positional embedding, demonstrating that it often captures the distance between tokens. Building on this insight, we introduce novel attention models that directly learn positional relations. Extensive experiments reveal that our proposed models, \textbf{PARec} and \textbf{FPARec} outperform previous self-attention-based approaches.Our code is available at the link for anonymous review: https://anonymous.4open.science/ r/FPARec-2C55/
Divide & Conquer for Entailment-aware Multi-hop Evidence Retrieval
Nov 05, 2023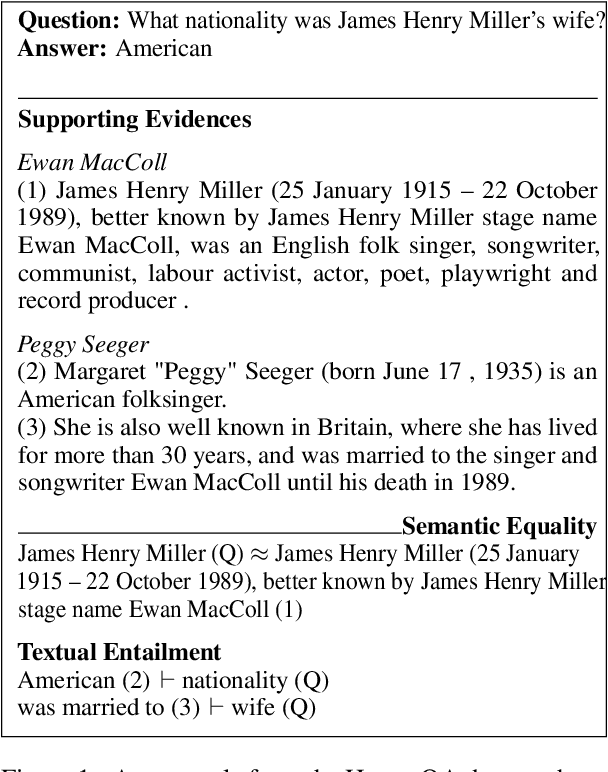
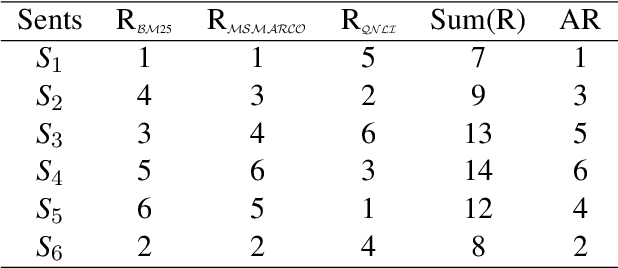
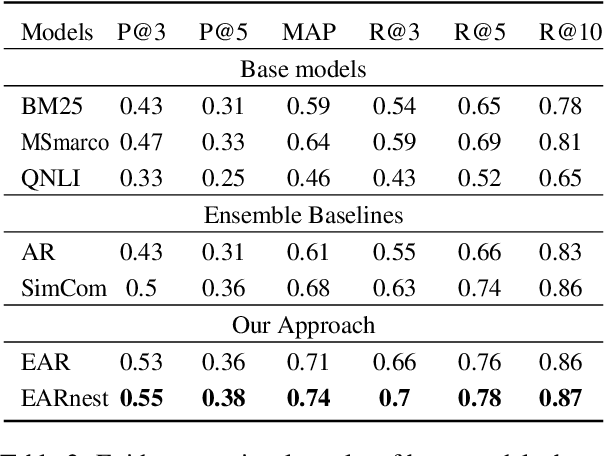
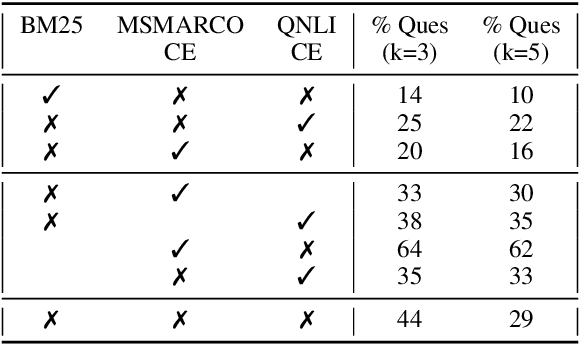
Abstract:Lexical and semantic matches are commonly used as relevance measurements for information retrieval. Together they estimate the semantic equivalence between the query and the candidates. However, semantic equivalence is not the only relevance signal that needs to be considered when retrieving evidences for multi-hop questions. In this work, we demonstrate that textual entailment relation is another important relevance dimension that should be considered. To retrieve evidences that are either semantically equivalent to or entailed by the question simultaneously, we divide the task of evidence retrieval for multi-hop question answering (QA) into two sub-tasks, i.e., semantic textual similarity and inference similarity retrieval. We propose two ensemble models, EAR and EARnest, which tackle each of the sub-tasks separately and then jointly re-rank sentences with the consideration of the diverse relevance signals. Experimental results on HotpotQA verify that our models not only significantly outperform all the single retrieval models it is based on, but is also more effective than two intuitive ensemble baseline models.
Perturbation-based Active Learning for Question Answering
Nov 04, 2023Abstract:Building a question answering (QA) model with less annotation costs can be achieved by utilizing active learning (AL) training strategy. It selects the most informative unlabeled training data to update the model effectively. Acquisition functions for AL are used to determine how informative each training example is, such as uncertainty or diversity based sampling. In this work, we propose a perturbation-based active learning acquisition strategy and demonstrate it is more effective than existing commonly used strategies.
Self-supervised Learning for Semi-supervised Temporal Language Grounding
Sep 23, 2021


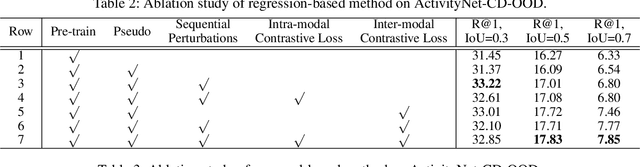
Abstract:Given a text description, Temporal Language Grounding (TLG) aims to localize temporal boundaries of the segments that contain the specified semantics in an untrimmed video. TLG is inherently a challenging task, as it requires to have comprehensive understanding of both video contents and text sentences. Previous works either tackle this task in a fully-supervised setting that requires a large amount of manual annotations or in a weakly supervised setting that cannot achieve satisfactory performance. To achieve good performance with limited annotations, we tackle this task in a semi-supervised way and propose a unified Semi-supervised Temporal Language Grounding (STLG) framework. STLG consists of two parts: (1) A pseudo label generation module that produces adaptive instant pseudo labels for unlabeled data based on predictions from a teacher model; (2) A self-supervised feature learning module with two sequential perturbations, i.e., time lagging and time scaling, for improving the video representation by inter-modal and intra-modal contrastive learning. We conduct experiments on the ActivityNet-CD-OOD and Charades-CD-OOD datasets and the results demonstrate that our proposed STLG framework achieve competitive performance compared to fully-supervised state-of-the-art methods with only a small portion of temporal annotations.
Learning Models for Suicide Prediction from Social Media Posts
Apr 29, 2021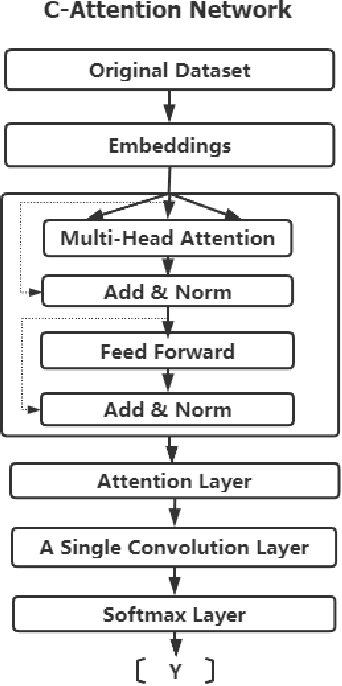
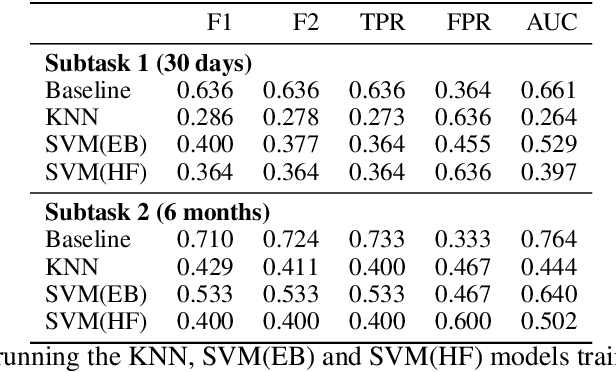

Abstract:We propose a deep learning architecture and test three other machine learning models to automatically detect individuals that will attempt suicide within (1) 30 days and (2) six months, using their social media post data provided in the CLPsych 2021 shared task. Additionally, we create and extract three sets of handcrafted features for suicide risk detection based on the three-stage theory of suicide and prior work on emotions and the use of pronouns among persons exhibiting suicidal ideations. Extensive experimentations show that some of the traditional machine learning methods outperform the baseline with an F1 score of 0.741 and F2 score of 0.833 on subtask 1 (prediction of a suicide attempt 30 days prior). However, the proposed deep learning method outperforms the baseline with F1 score of 0.737 and F2 score of 0.843 on subtask 2 (prediction of suicide 6 months prior).
Personalized Early Stage Alzheimer's Disease Detection: A Case Study of President Reagan's Speeches
May 08, 2020Abstract:Alzheimer`s disease (AD)-related global healthcare cost is estimated to be $1 trillion by 2050. Currently, there is no cure for this disease; however, clinical studies show that early diagnosis and intervention helps to extend the quality of life and inform technologies for personalized mental healthcare. Clinical research indicates that the onset and progression of Alzheimer`s disease lead to dementia and other mental health issues. As a result, the language capabilities of patient start to decline. In this paper, we show that machine learning-based unsupervised clustering of and anomaly detection with linguistic biomarkers are promising approaches for intuitive visualization and personalized early stage detection of Alzheimer`s disease. We demonstrate this approach on 10 year`s (1980 to 1989) of President Ronald Reagan`s speech data set. Key linguistic biomarkers that indicate early-stage AD are identified. Experimental results show that Reagan had early onset of Alzheimer`s sometime between 1983 and 1987. This finding is corroborated by prior work that analyzed his interviews using a statistical technique. The proposed technique also identifies the exact speeches that reflect linguistic biomarkers for early stage AD.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge