Fabrice Rousselle
Generative Detail Enhancement for Physically Based Materials
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:We present a tool for enhancing the detail of physically based materials using an off-the-shelf diffusion model and inverse rendering. Our goal is to enhance the visual fidelity of materials with detail that is often tedious to author, by adding signs of wear, aging, weathering, etc. As these appearance details are often rooted in real-world processes, we leverage a generative image model trained on a large dataset of natural images with corresponding visuals in context. Starting with a given geometry, UV mapping, and basic appearance, we render multiple views of the object. We use these views, together with an appearance-defining text prompt, to condition a diffusion model. The details it generates are then backpropagated from the enhanced images to the material parameters via inverse differentiable rendering. For inverse rendering to be successful, the generated appearance has to be consistent across all the images. We propose two priors to address the multi-view consistency of the diffusion model. First, we ensure that the initial noise that seeds the diffusion process is itself consistent across views by integrating it from a view-independent UV space. Second, we enforce geometric consistency by biasing the attention mechanism via a projective constraint so that pixels attend strongly to their corresponding pixel locations in other views. Our approach does not require any training or finetuning of the diffusion model, is agnostic of the material model used, and the enhanced material properties, i.e., 2D PBR textures, can be further edited by artists.
A Radiance Field Loss for Fast and Simple Emissive Surface Reconstruction
Jan 27, 2025Abstract:We present a fast and simple technique to convert images into an emissive surface-based scene representation. Building on existing emissive volume reconstruction algorithms, we introduce a subtle yet impactful modification of the loss function requiring changes to only a few lines of code: instead of integrating the radiance field along rays and supervising the resulting images, we project the training images into the scene to directly supervise the spatio-directional radiance field. The primary outcome of this change is the complete removal of alpha blending and ray marching from the image formation model, instead moving these steps into the loss computation. In addition to promoting convergence to surfaces, this formulation assigns explicit semantic meaning to 2D subsets of the radiance field, turning them into well-defined emissive surfaces. We finally extract a level set from this representation, which results in a high-quality emissive surface model. Our method retains much of the speed and quality of the baseline algorithm. For instance, a suitably modified variant of Instant~NGP maintains comparable computational efficiency, while achieving an average PSNR that is only 0.1 dB lower. Most importantly, our method generates explicit surfaces in place of an exponential volume, doing so with a level of simplicity not seen in prior work.
Inverse Global Illumination using a Neural Radiometric Prior
May 03, 2023Abstract:Inverse rendering methods that account for global illumination are becoming more popular, but current methods require evaluating and automatically differentiating millions of path integrals by tracing multiple light bounces, which remains expensive and prone to noise. Instead, this paper proposes a radiometric prior as a simple alternative to building complete path integrals in a traditional differentiable path tracer, while still correctly accounting for global illumination. Inspired by the Neural Radiosity technique, we use a neural network as a radiance function, and we introduce a prior consisting of the norm of the residual of the rendering equation in the inverse rendering loss. We train our radiance network and optimize scene parameters simultaneously using a loss consisting of both a photometric term between renderings and the multi-view input images, and our radiometric prior (the residual term). This residual term enforces a physical constraint on the optimization that ensures that the radiance field accounts for global illumination. We compare our method to a vanilla differentiable path tracer, and more advanced techniques such as Path Replay Backpropagation. Despite the simplicity of our approach, we can recover scene parameters with comparable and in some cases better quality, at considerably lower computation times.
Real-time Neural Radiance Caching for Path Tracing
Jun 25, 2021
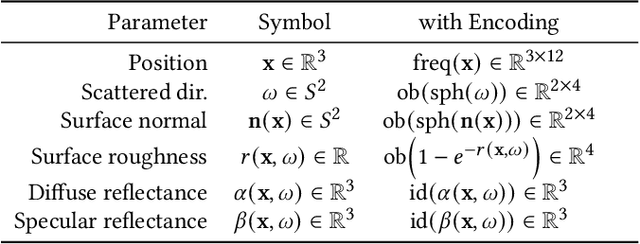

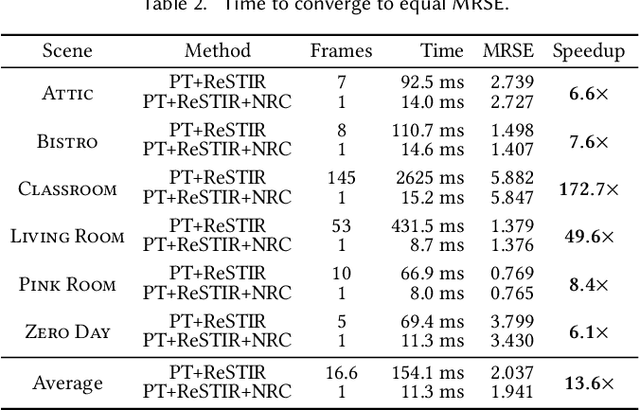
Abstract:We present a real-time neural radiance caching method for path-traced global illumination. Our system is designed to handle fully dynamic scenes, and makes no assumptions about the lighting, geometry, and materials. The data-driven nature of our approach sidesteps many difficulties of caching algorithms, such as locating, interpolating, and updating cache points. Since pretraining neural networks to handle novel, dynamic scenes is a formidable generalization challenge, we do away with pretraining and instead achieve generalization via adaptation, i.e. we opt for training the radiance cache while rendering. We employ self-training to provide low-noise training targets and simulate infinite-bounce transport by merely iterating few-bounce training updates. The updates and cache queries incur a mild overhead -- about 2.6ms on full HD resolution -- thanks to a streaming implementation of the neural network that fully exploits modern hardware. We demonstrate significant noise reduction at the cost of little induced bias, and report state-of-the-art, real-time performance on a number of challenging scenarios.
Neural Control Variates
Jun 02, 2020
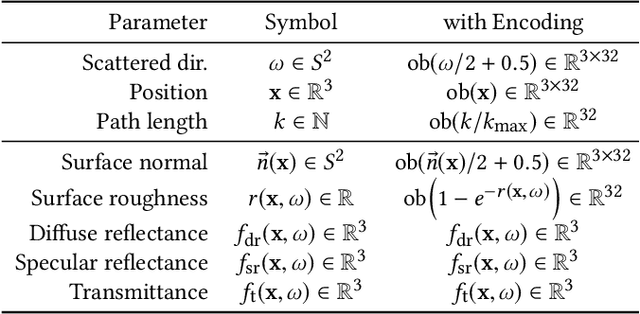
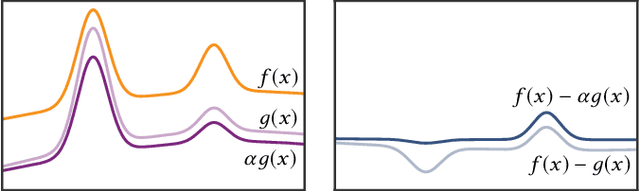
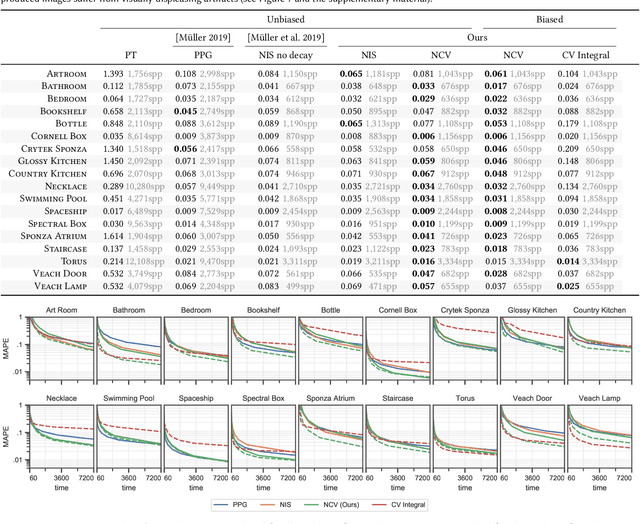
Abstract:We propose the concept of neural control variates (NCV) for unbiased variance reduction in parametric Monte Carlo integration for solving integral equations. So far, the core challenge of applying the method of control variates has been finding a good approximation of the integrand that is cheap to integrate. We show that a set of neural networks can face that challenge: a normalizing flow that approximates the shape of the integrand and another neural network that infers the solution of the integral equation. We also propose to leverage a neural importance sampler to estimate the difference between the original integrand and the learned control variate. To optimize the resulting parametric estimator, we derive a theoretically optimal, variance-minimizing loss function, and propose an alternative, composite loss for stable online training in practice. When applied to light transport simulation, neural control variates are capable of matching the state-of-the-art performance of other unbiased approaches, while providing means to develop more performant, practical solutions. Specifically, we show that the learned light-field approximation is of sufficient quality for high-order bounces, allowing us to omit the error correction and thereby dramatically reduce the noise at the cost of insignificant visible bias.
Neural Importance Sampling
Sep 27, 2018



Abstract:We propose to use deep neural networks for generating samples in Monte Carlo integration. Our work is based on non-linear independent components estimation (NICE), which we extend in numerous ways to improve performance and enable its application to integration problems. First, we introduce piecewise-polynomial coupling transforms that greatly increase the modeling power of individual coupling layers. Second, we propose to preprocess the inputs of neural networks using one-blob encoding, which stimulates localization of computation and improves inference. Third, we derive a gradient-descent-based optimization for the KL and the $\chi^2$ divergence for the specific application of Monte Carlo integration with unnormalized stochastic estimates of the target distribution. Our approach enables fast and accurate inference and efficient sample generation independently of the dimensionality of the integration domain. We show its benefits on generating natural images and in two applications to light-transport simulation: first, we demonstrate learning of joint path-sampling densities in the primary sample space and importance sampling of multi-dimensional path prefixes thereof. Second, we use our technique to extract conditional directional densities driven by the triple product of the rendering equation and leverage them for path guiding. In all applications, our approach yields on-par or higher performance than competing techniques at equal sample count.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge