Fabio Celli
Language Models reach higher Agreement than Humans in Historical Interpretation
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:This paper compares historical annotations by humans and Large Language Models. The findings reveal that both exhibit some cultural bias, but Large Language Models achieve a higher consensus on the interpretation of historical facts from short texts. While humans tend to disagree on the basis of their personal biases, Large Models disagree when they skip information or produce hallucinations. These findings have significant implications for digital humanities, enabling large-scale annotation and quantitative analysis of historical data. This offers new educational and research opportunities to explore historical interpretations from different Language Models, fostering critical thinking about bias.
Twenty Years of Personality Computing: Threats, Challenges and Future Directions
Mar 03, 2025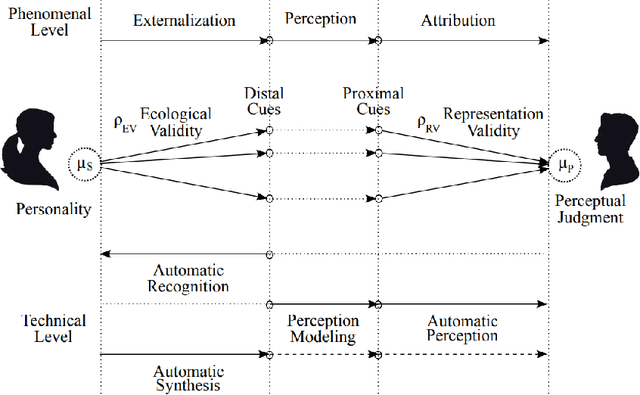
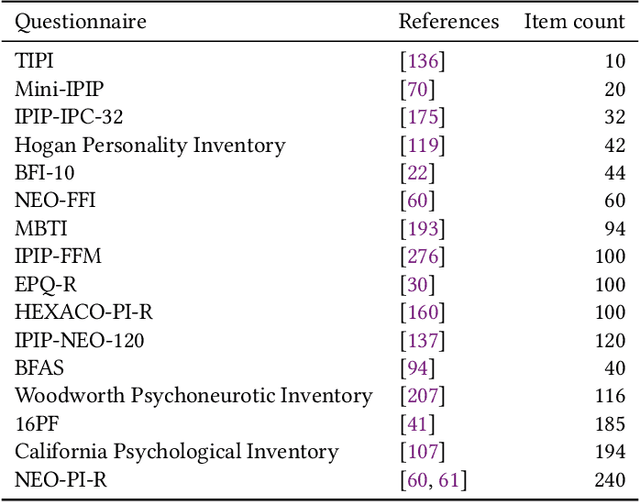
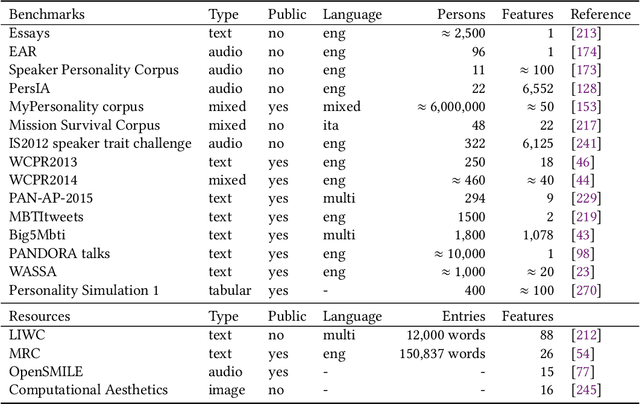
Abstract:Personality Computing is a field at the intersection of Personality Psychology and Computer Science. Started in 2005, research in the field utilizes computational methods to understand and predict human personality traits. The expansion of the field has been very rapid and, by analyzing digital footprints (text, images, social media, etc.), it helped to develop systems that recognize and even replicate human personality. While offering promising applications in talent recruiting, marketing and healthcare, the ethical implications of Personality Computing are significant. Concerns include data privacy, algorithmic bias, and the potential for manipulation by personality-aware Artificial Intelligence. This paper provides an overview of the field, explores key methodologies, discusses the challenges and threats, and outlines potential future directions for responsible development and deployment of Personality Computing technologies.
Hate versus Politics: Detection of Hate against Policy makers in Italian tweets
Jul 12, 2021
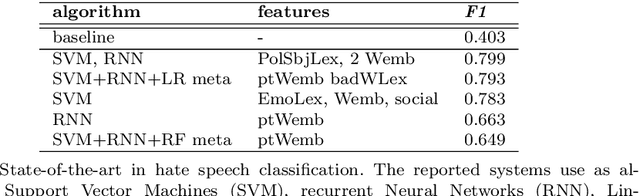
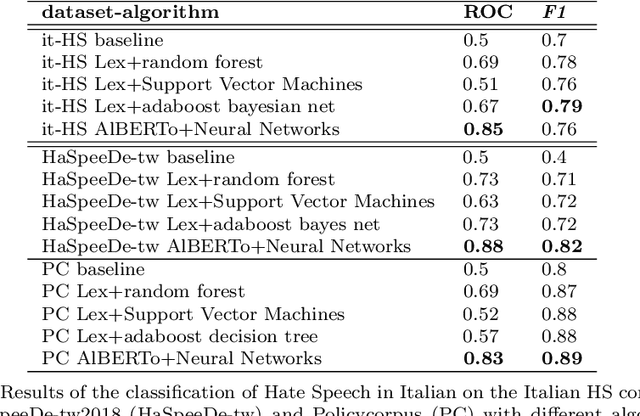
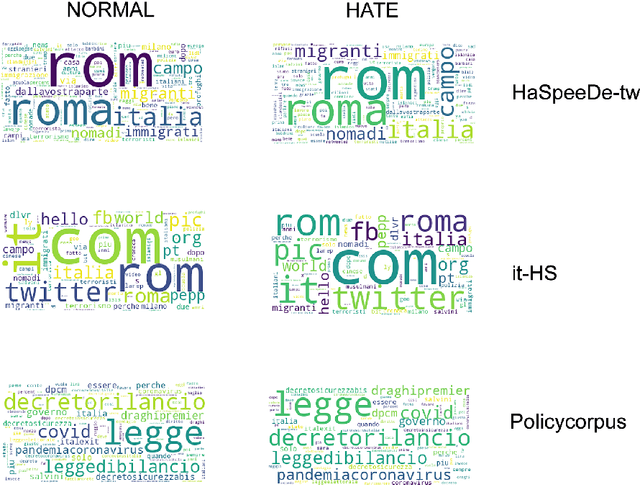
Abstract:Accurate detection of hate speech against politicians, policy making and political ideas is crucial to maintain democracy and free speech. Unfortunately, the amount of labelled data necessary for training models to detect hate speech are limited and domain-dependent. In this paper, we address the issue of classification of hate speech against policy makers from Twitter in Italian, producing the first resource of this type in this language. We collected and annotated 1264 tweets, examined the cases of disagreements between annotators, and performed in-domain and cross-domain hate speech classifications with different features and algorithms. We achieved a performance of ROC AUC 0.83 and analyzed the most predictive attributes, also finding the different language features in the anti-policymakers and anti-immigration domains. Finally, we visualized networks of hashtags to capture the topics used in hateful and normal tweets.
Lex2vec: making Explainable Word Embedding via Distant Supervision
Mar 03, 2021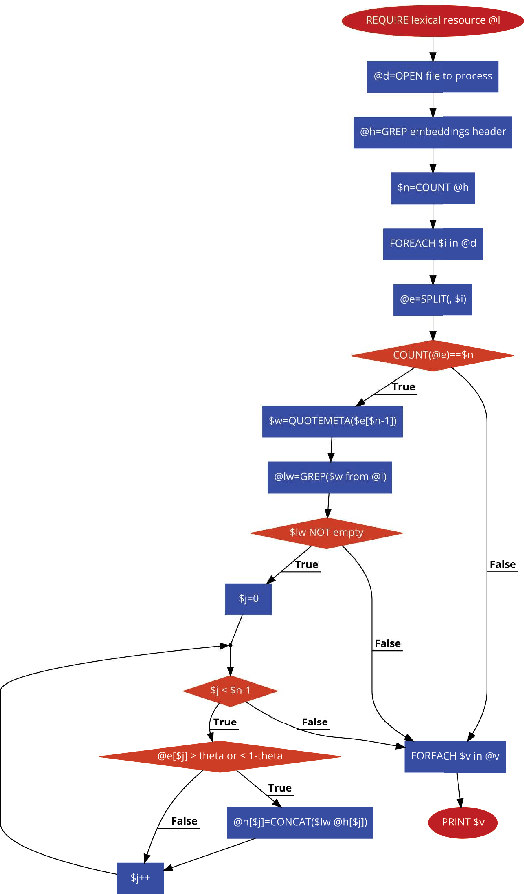
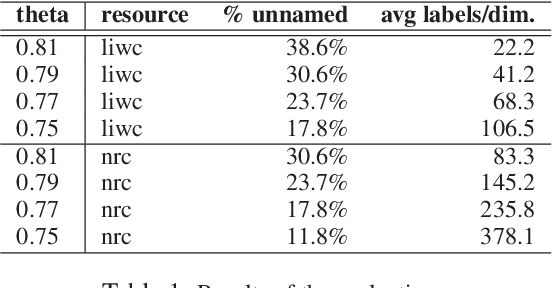
Abstract:In this technical report we propose an algorithm, called Lex2vec, that exploits lexical resources to inject information into word embeddings and name the embedding dimensions by means of distant supervision. We evaluate the optimal parameters to extract a number of informative labels that is readable and has a good coverage for the embedding dimensions.
The Wiki Music dataset: A tool for computational analysis of popular music
Aug 27, 2019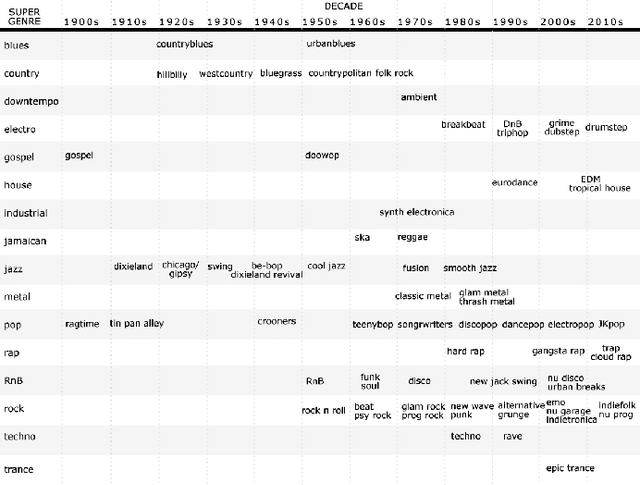
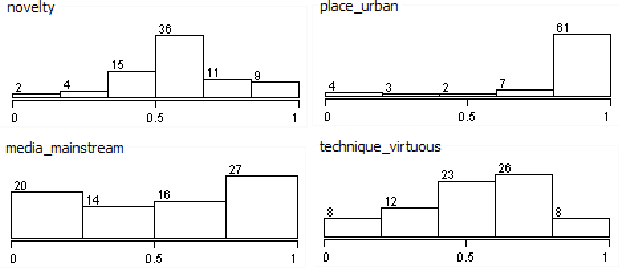
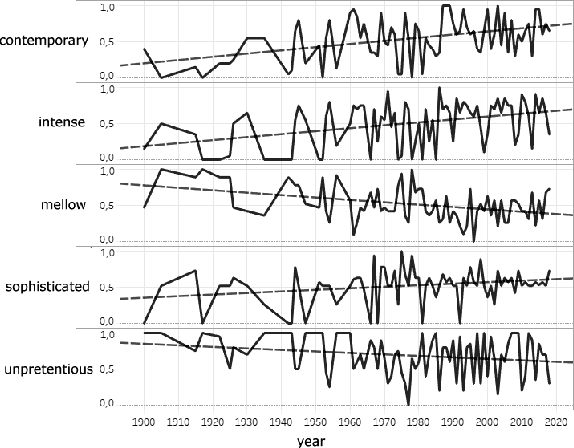
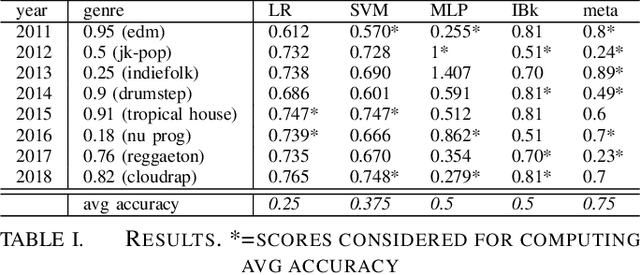
Abstract:Is it possible use algorithms to find trends in the history of popular music? And is it possible to predict the characteristics of future music genres? In order to answer these questions, we produced a hand-crafted dataset with the intent to put together features about style, psychology, sociology and typology, annotated by music genre and indexed by time and decade. We collected a list of popular genres by decade from Wikipedia and scored music genres based on Wikipedia descriptions. Using statistical and machine learning techniques, we find trends in the musical preferences and use time series forecasting to evaluate the prediction of future music genres.
What your Facebook Profile Picture Reveals about your Personality
Aug 13, 2017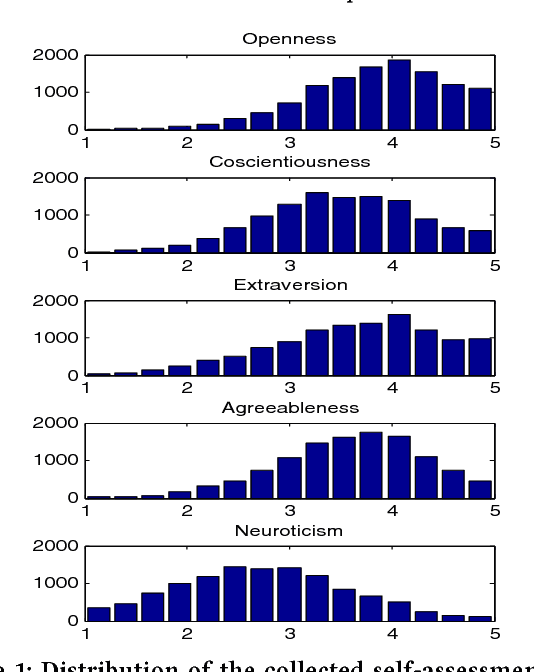
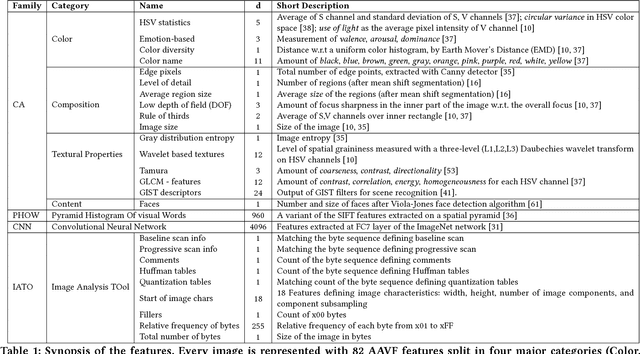
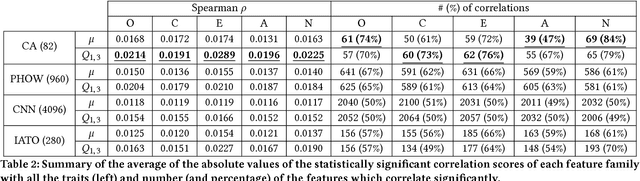

Abstract:People spend considerable effort managing the impressions they give others. Social psychologists have shown that people manage these impressions differently depending upon their personality. Facebook and other social media provide a new forum for this fundamental process; hence, understanding people's behaviour on social media could provide interesting insights on their personality. In this paper we investigate automatic personality recognition from Facebook profile pictures. We analyze the effectiveness of four families of visual features and we discuss some human interpretable patterns that explain the personality traits of the individuals. For example, extroverts and agreeable individuals tend to have warm colored pictures and to exhibit many faces in their portraits, mirroring their inclination to socialize; while neurotic ones have a prevalence of pictures of indoor places. Then, we propose a classification approach to automatically recognize personality traits from these visual features. Finally, we compare the performance of our classification approach to the one obtained by human raters and we show that computer-based classifications are significantly more accurate than averaged human-based classifications for Extraversion and Neuroticism.
PR2: A Language Independent Unsupervised Tool for Personality Recognition from Text
Feb 12, 2014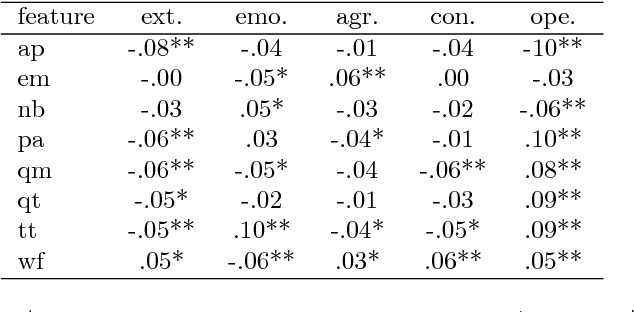
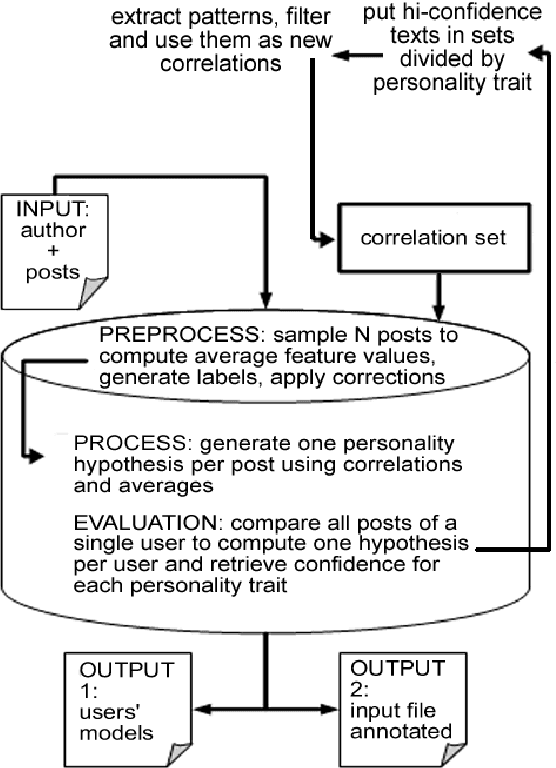
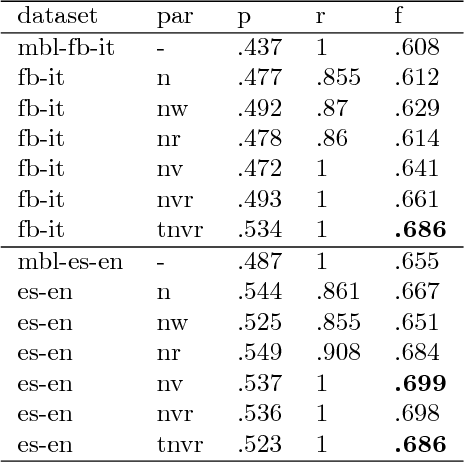
Abstract:We present PR2, a personality recognition system available online, that performs instance-based classification of Big5 personality types from unstructured text, using language-independent features. It has been tested on English and Italian, achieving performances up to f=.68.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge