Eugene Tunik
User Training with Error Augmentation for Electromyogram-based Gesture Classification
Sep 13, 2023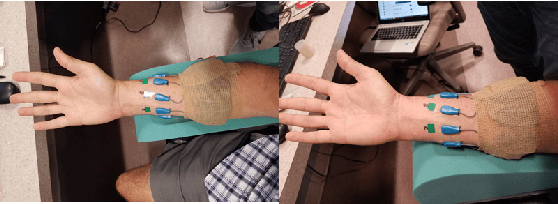
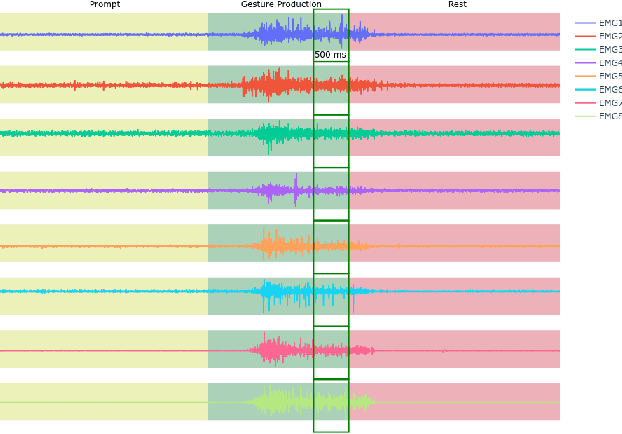
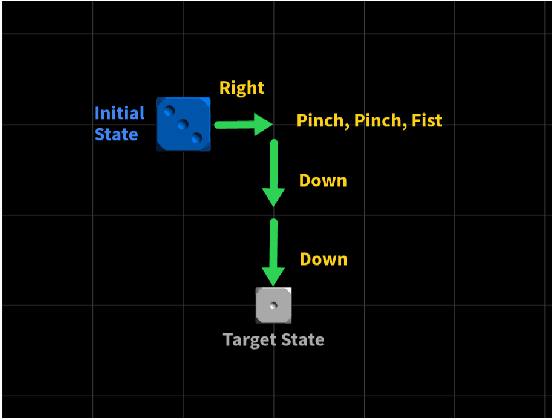
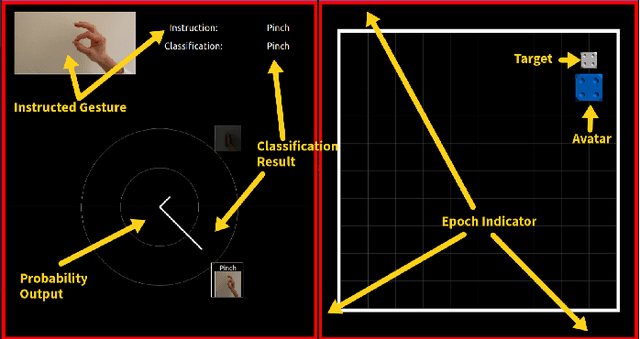
Abstract:We designed and tested a system for real-time control of a user interface by extracting surface electromyographic (sEMG) activity from eight electrodes in a wrist-band configuration. sEMG data were streamed into a machine-learning algorithm that classified hand gestures in real-time. After an initial model calibration, participants were presented with one of three types of feedback during a human-learning stage: veridical feedback, in which predicted probabilities from the gesture classification algorithm were displayed without alteration, modified feedback, in which we applied a hidden augmentation of error to these probabilities, and no feedback. User performance was then evaluated in a series of minigames, in which subjects were required to use eight gestures to manipulate their game avatar to complete a task. Experimental results indicated that, relative to baseline, the modified feedback condition led to significantly improved accuracy and improved gesture class separation. These findings suggest that real-time feedback in a gamified user interface with manipulation of feedback may enable intuitive, rapid, and accurate task acquisition for sEMG-based gesture recognition applications.
A Multi-label Classification Approach to Increase Expressivity of EMG-based Gesture Recognition
Sep 13, 2023Abstract:Objective: The objective of the study is to efficiently increase the expressivity of surface electromyography-based (sEMG) gesture recognition systems. Approach: We use a problem transformation approach, in which actions were subset into two biomechanically independent components - a set of wrist directions and a set of finger modifiers. To maintain fast calibration time, we train models for each component using only individual gestures, and extrapolate to the full product space of combination gestures by generating synthetic data. We collected a supervised dataset with high-confidence ground truth labels in which subjects performed combination gestures while holding a joystick, and conducted experiments to analyze the impact of model architectures, classifier algorithms, and synthetic data generation strategies on the performance of the proposed approach. Main Results: We found that a problem transformation approach using a parallel model architecture in combination with a non-linear classifier, along with restricted synthetic data generation, shows promise in increasing the expressivity of sEMG-based gestures with a short calibration time. Significance: sEMG-based gesture recognition has applications in human-computer interaction, virtual reality, and the control of robotic and prosthetic devices. Existing approaches require exhaustive model calibration. The proposed approach increases expressivity without requiring users to demonstrate all combination gesture classes. Our results may be extended to larger gesture vocabularies and more complicated model architectures.
Mapping Motor Cortex Stimulation to Muscle Responses: A Deep Neural Network Modeling Approach
Feb 14, 2020



Abstract:A deep neural network (DNN) that can reliably model muscle responses from corresponding brain stimulation has the potential to increase knowledge of coordinated motor control for numerous basic science and applied use cases. Such cases include the understanding of abnormal movement patterns due to neurological injury from stroke, and stimulation based interventions for neurological recovery such as paired associative stimulation. In this work, potential DNN models are explored and the one with the minimum squared errors is recommended for the optimal performance of the M2M-Net, a network that maps transcranial magnetic stimulation of the motor cortex to corresponding muscle responses, using: a finite element simulation, an empirical neural response profile, a convolutional autoencoder, a separate deep network mapper, and recordings of multi-muscle activation. We discuss the rationale behind the different modeling approaches and architectures, and contrast their results. Additionally, to obtain a comparative insight of the trade-off between complexity and performance analysis, we explore different techniques, including the extension of two classical information criteria for M2M-Net. Finally, we find that the model analogous to mapping the motor cortex stimulation to a combination of direct and synergistic connection to the muscles performs the best, when the neural response profile is used at the input.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge