Erwan Nogues
NTIRE 2020 Challenge on Image Demoireing: Methods and Results
May 06, 2020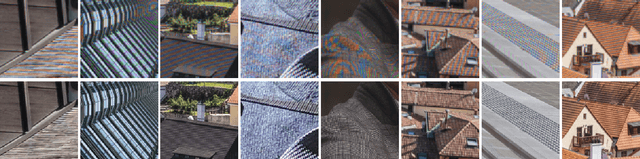
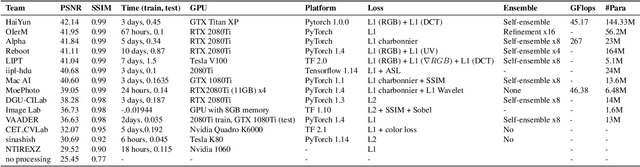
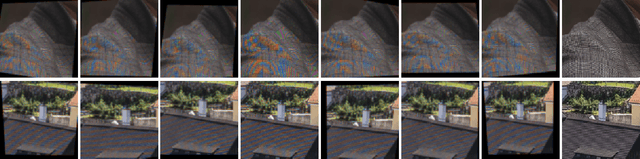
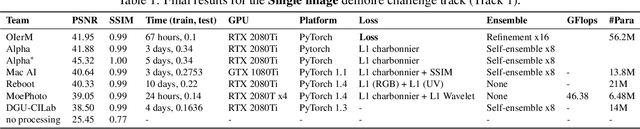
Abstract:This paper reviews the Challenge on Image Demoireing that was part of the New Trends in Image Restoration and Enhancement (NTIRE) workshop, held in conjunction with CVPR 2020. Demoireing is a difficult task of removing moire patterns from an image to reveal an underlying clean image. The challenge was divided into two tracks. Track 1 targeted the single image demoireing problem, which seeks to remove moire patterns from a single image. Track 2 focused on the burst demoireing problem, where a set of degraded moire images of the same scene were provided as input, with the goal of producing a single demoired image as output. The methods were ranked in terms of their fidelity, measured using the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) between the ground truth clean images and the restored images produced by the participants' methods. The tracks had 142 and 99 registered participants, respectively, with a total of 14 and 6 submissions in the final testing stage. The entries span the current state-of-the-art in image and burst image demoireing problems.
NoiseBreaker: Gradual Image Denoising Guided by Noise Analysis
Feb 18, 2020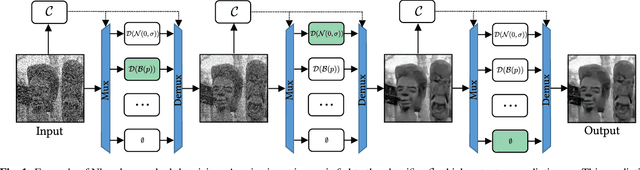
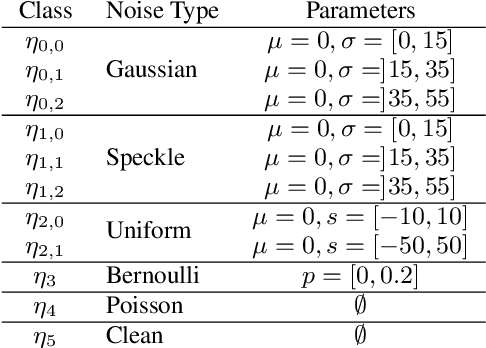

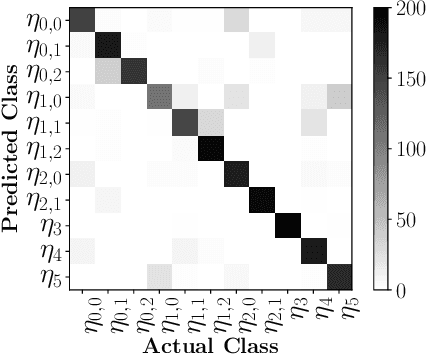
Abstract:Fully supervised deep-learning based denoisers are currently the most performing image denoising solutions. However, they require clean reference images. When the target noise is complex, e.g. composed of an unknown mixture of primary noises with unknown intensity, fully supervised solutions are limited by the difficulty to build a suited training set for the problem. This paper proposes a gradual denoising strategy that iteratively detects the dominating noise in an image, and removes it using a tailored denoiser. The method is shown to keep up with state of the art blind denoisers on mixture noises. Moreover, noise analysis is demonstrated to guide denoisers efficiently not only on noise type, but also on noise intensity. The method provides an insight on the nature of the encountered noise, and it makes it possible to extend an existing denoiser with new noise nature. This feature makes the method adaptive to varied denoising cases.
OpenDenoising: an Extensible Benchmark for Building Comparative Studies of Image Denoisers
Oct 18, 2019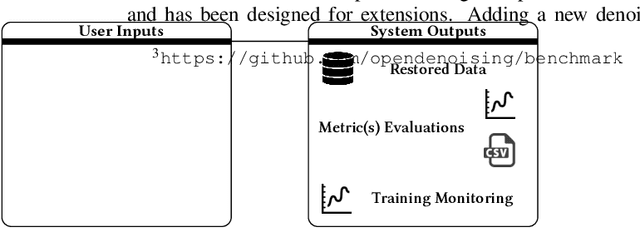
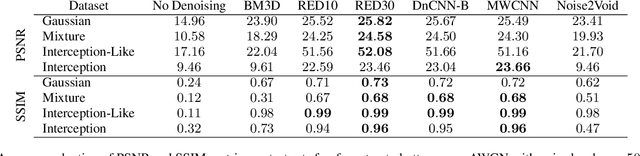
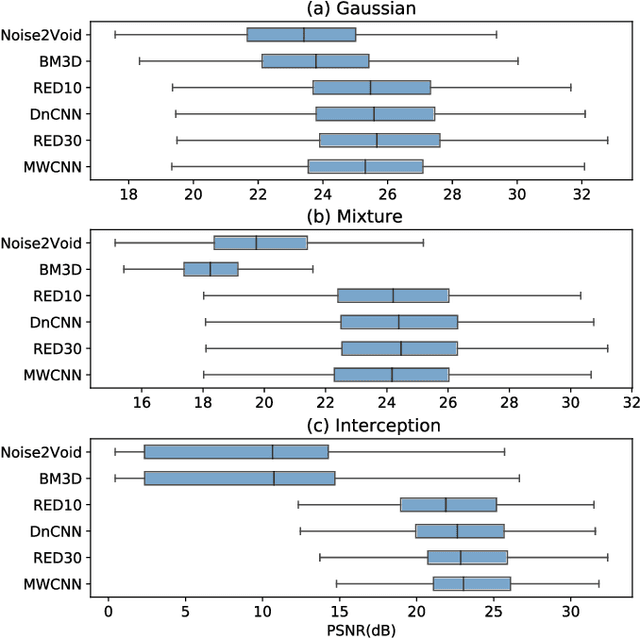

Abstract:Image denoising has recently taken a leap forward due to machine learning. However, image denoisers, both expert-based and learning-based, are mostly tested on well-behaved generated noises (usually Gaussian) rather than on real-life noises, making performance comparisons difficult in real-world conditions. This is especially true for learning-based denoisers which performance depends on training data. Hence, choosing which method to use for a specific denoising problem is difficult. This paper proposes a comparative study of existing denoisers, as well as an extensible open tool that makes it possible to reproduce and extend the study. MWCNN is shown to outperform other methods when trained for a real-world image interception noise, and additionally is the second least compute hungry of the tested methods. To evaluate the robustness of conclusions, three test sets are compared. A Kendall's Tau correlation of only 60% is obtained on methods ranking between noise types, demonstrating the need for a benchmarking tool.
Electro-Magnetic Side-Channel Attack Through Learned Denoising and Classification
Oct 16, 2019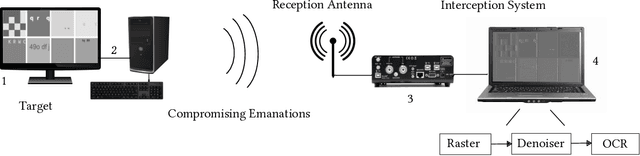
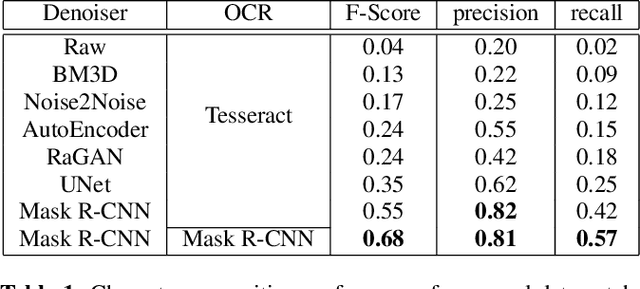
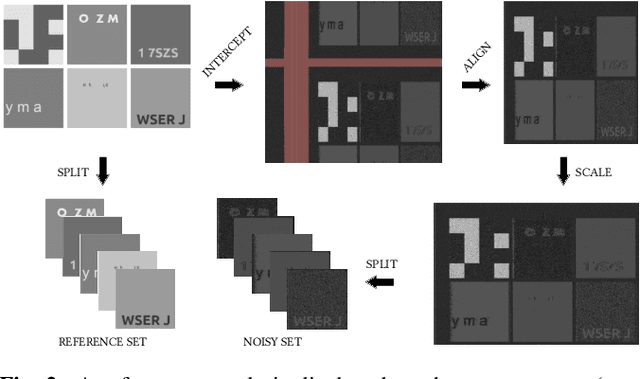
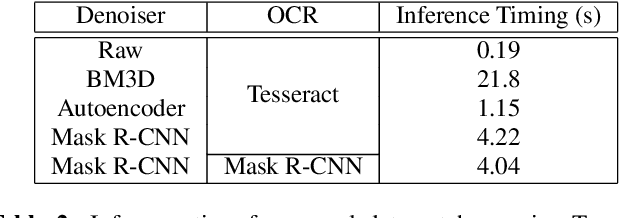
Abstract:This paper proposes an upgraded electro-magnetic side-channel attack that automatically reconstructs the intercepted data. A novel system is introduced, running in parallel with leakage signal interception and catching compromising data in real-time. Based on deep learning and character recognition the proposed system retrieves more than 57% of characters present in intercepted signals regardless of signal type: analog or digital. The approach is also extended to a protection system that triggers an alarm if the system is compromised, demonstrating a success rate over 95%. Based on software-defined radio and graphics processing unit architectures, this solution can be easily deployed onto existing information systems where information shall be kept secret.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge