Eric Upschulte
From Fibers to Cells: Fourier-Based Registration Enables Virtual Cresyl Violet Staining From 3D Polarized Light Imaging
May 16, 2025Abstract:Comprehensive assessment of the various aspects of the brain's microstructure requires the use of complementary imaging techniques. This includes measuring the spatial distribution of cell bodies (cytoarchitecture) and nerve fibers (myeloarchitecture). The gold standard for cytoarchitectonic analysis is light microscopic imaging of cell-body stained tissue sections. To reveal the 3D orientations of nerve fibers, 3D Polarized Light Imaging (3D-PLI) has been introduced as a reliable technique providing a resolution in the micrometer range while allowing processing of series of complete brain sections. 3D-PLI acquisition is label-free and allows subsequent staining of sections after measurement. By post-staining for cell bodies, a direct link between fiber- and cytoarchitecture can potentially be established within the same section. However, inevitable distortions introduced during the staining process make a nonlinear and cross-modal registration necessary in order to study the detailed relationships between cells and fibers in the images. In addition, the complexity of processing histological sections for post-staining only allows for a limited number of samples. In this work, we take advantage of deep learning methods for image-to-image translation to generate a virtual staining of 3D-PLI that is spatially aligned at the cellular level. In a supervised setting, we build on a unique dataset of brain sections, to which Cresyl violet staining has been applied after 3D-PLI measurement. To ensure high correspondence between both modalities, we address the misalignment of training data using Fourier-based registration methods. In this way, registration can be efficiently calculated during training for local image patches of target and predicted staining. We demonstrate that the proposed method enables prediction of a Cresyl violet staining from 3D-PLI, matching individual cell instances.
A Survey on Self-Supervised Representation Learning
Aug 22, 2023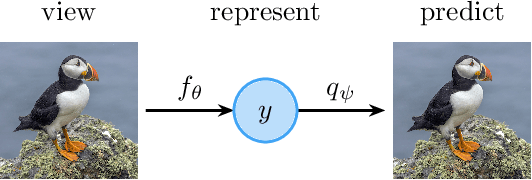

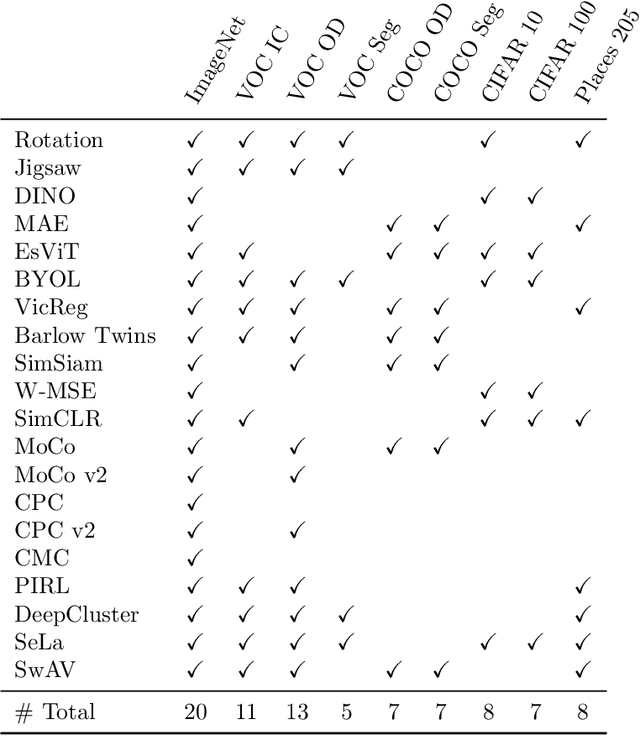
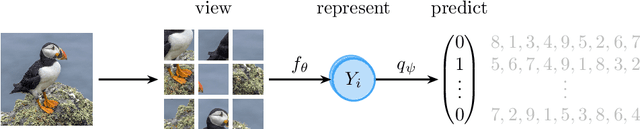
Abstract:Learning meaningful representations is at the heart of many tasks in the field of modern machine learning. Recently, a lot of methods were introduced that allow learning of image representations without supervision. These representations can then be used in downstream tasks like classification or object detection. The quality of these representations is close to supervised learning, while no labeled images are needed. This survey paper provides a comprehensive review of these methods in a unified notation, points out similarities and differences of these methods, and proposes a taxonomy which sets these methods in relation to each other. Furthermore, our survey summarizes the most-recent experimental results reported in the literature in form of a meta-study. Our survey is intended as a starting point for researchers and practitioners who want to dive into the field of representation learning.
The Multi-modality Cell Segmentation Challenge: Towards Universal Solutions
Aug 10, 2023Abstract:Cell segmentation is a critical step for quantitative single-cell analysis in microscopy images. Existing cell segmentation methods are often tailored to specific modalities or require manual interventions to specify hyperparameters in different experimental settings. Here, we present a multi-modality cell segmentation benchmark, comprising over 1500 labeled images derived from more than 50 diverse biological experiments. The top participants developed a Transformer-based deep-learning algorithm that not only exceeds existing methods, but can also be applied to diverse microscopy images across imaging platforms and tissue types without manual parameter adjustments. This benchmark and the improved algorithm offer promising avenues for more accurate and versatile cell analysis in microscopy imaging.
Contour Proposal Networks for Biomedical Instance Segmentation
Apr 07, 2021



Abstract:We present a conceptually simple framework for object instance segmentation called Contour Proposal Network (CPN), which detects possibly overlapping objects in an image while simultaneously fitting closed object contours using an interpretable, fixed-sized representation based on Fourier Descriptors. The CPN can incorporate state of the art object detection architectures as backbone networks into a single-stage instance segmentation model that can be trained end-to-end. We construct CPN models with different backbone networks, and apply them to instance segmentation of cells in datasets from different modalities. In our experiments, we show CPNs that outperform U-Nets and Mask R-CNNs in instance segmentation accuracy, and present variants with execution times suitable for real-time applications. The trained models generalize well across different domains of cell types. Since the main assumption of the framework are closed object contours, it is applicable to a wide range of detection problems also outside the biomedical domain. An implementation of the model architecture in PyTorch is freely available.
On the Vulnerability of Capsule Networks to Adversarial Attacks
Jun 09, 2019
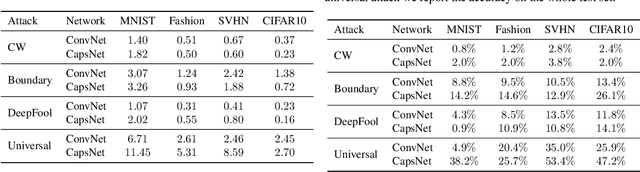

Abstract:This paper extensively evaluates the vulnerability of capsule networks to different adversarial attacks. Recent work suggests that these architectures are more robust towards adversarial attacks than other neural networks. However, our experiments show that capsule networks can be fooled as easily as convolutional neural networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge