Eric Gaussier
LIG, UGA
Identifiability in Causal Abstractions: A Hierarchy of Criteria
Jul 08, 2025Abstract:Identifying the effect of a treatment from observational data typically requires assuming a fully specified causal diagram. However, such diagrams are rarely known in practice, especially in complex or high-dimensional settings. To overcome this limitation, recent works have explored the use of causal abstractions-simplified representations that retain partial causal information. In this paper, we consider causal abstractions formalized as collections of causal diagrams, and focus on the identifiability of causal queries within such collections. We introduce and formalize several identifiability criteria under this setting. Our main contribution is to organize these criteria into a structured hierarchy, highlighting their relationships. This hierarchical view enables a clearer understanding of what can be identified under varying levels of causal knowledge. We illustrate our framework through examples from the literature and provide tools to reason about identifiability when full causal knowledge is unavailable.
Identifiability by common backdoor in summary causal graphs of time series
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:The identifiability problem for interventions aims at assessing whether the total effect of some given interventions can be written with a do-free formula, and thus be computed from observational data only. We study this problem, considering multiple interventions and multiple effects, in the context of time series when only abstractions of the true causal graph in the form of summary causal graphs are available. We focus in this study on identifiability by a common backdoor set, and establish, for time series with and without consistency throughout time, conditions under which such a set exists. We also provide algorithms of limited complexity to decide whether the problem is identifiable or not.
Complete Characterization for Adjustment in Summary Causal Graphs of Time Series
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:The identifiability problem for interventions aims at assessing whether the total causal effect can be written with a do-free formula, and thus be estimated from observational data only. We study this problem, considering multiple interventions, in the context of time series when only an abstraction of the true causal graph, in the form of a summary causal graph, is available. We propose in particular both necessary and sufficient conditions for the adjustment criterion, which we show is complete in this setting, and provide a pseudo-linear algorithm to decide whether the query is identifiable or not.
Enhanced Retrieval of Long Documents: Leveraging Fine-Grained Block Representations with Large Language Models
Jan 28, 2025


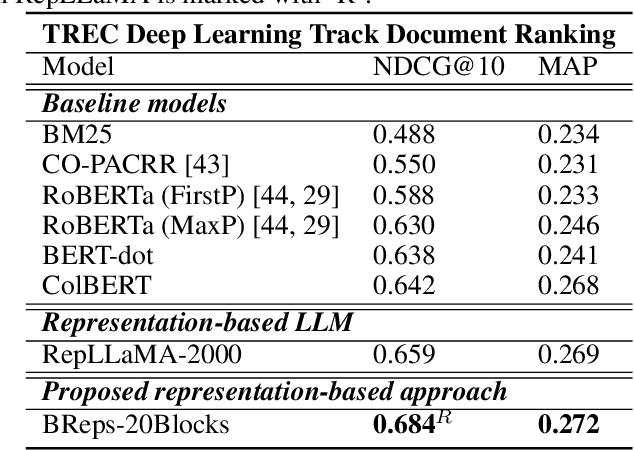
Abstract:In recent years, large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated exceptional power in various domains, including information retrieval. Most of the previous practices involve leveraging these models to create a single embedding for each query, each passage, or each document individually, a strategy exemplified and used by the Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) framework. While this method has proven effective, we argue that it falls short in fully capturing the nuanced intricacies of document-level texts due to its reliance on a relatively coarse-grained representation. To address this limitation, we introduce a novel, fine-grained approach aimed at enhancing the accuracy of relevance scoring for long documents. Our methodology firstly segments a long document into blocks, each of which is embedded using an LLM, for matching with the query representation. When calculating the relevance score, we aggregate the query-block relevance scores through a weighted sum method, yielding a comprehensive score for the query with the entire document. Despite its apparent simplicity, our experimental findings reveal that this approach outperforms standard representation methods and achieves a significant reduction in embedding generation latency. Moreover, by carefully optimizing pairwise loss functions, superior performances have been achieved.
GIFT: A Framework for Global Interpretable Faithful Textual Explanations of Vision Classifiers
Nov 23, 2024



Abstract:Understanding deep models is crucial for deploying them in safety-critical applications. We introduce GIFT, a framework for deriving post-hoc, global, interpretable, and faithful textual explanations for vision classifiers. GIFT starts from local faithful visual counterfactual explanations and employs (vision) language models to translate those into global textual explanations. Crucially, GIFT provides a verification stage measuring the causal effect of the proposed explanations on the classifier decision. Through experiments across diverse datasets, including CLEVR, CelebA, and BDD, we demonstrate that GIFT effectively reveals meaningful insights, uncovering tasks, concepts, and biases used by deep vision classifiers. Our code, data, and models are released at https://github.com/valeoai/GIFT.
KeyB2: Selecting Key Blocks is Also Important for Long Document Ranking with Large Language Models
Nov 09, 2024


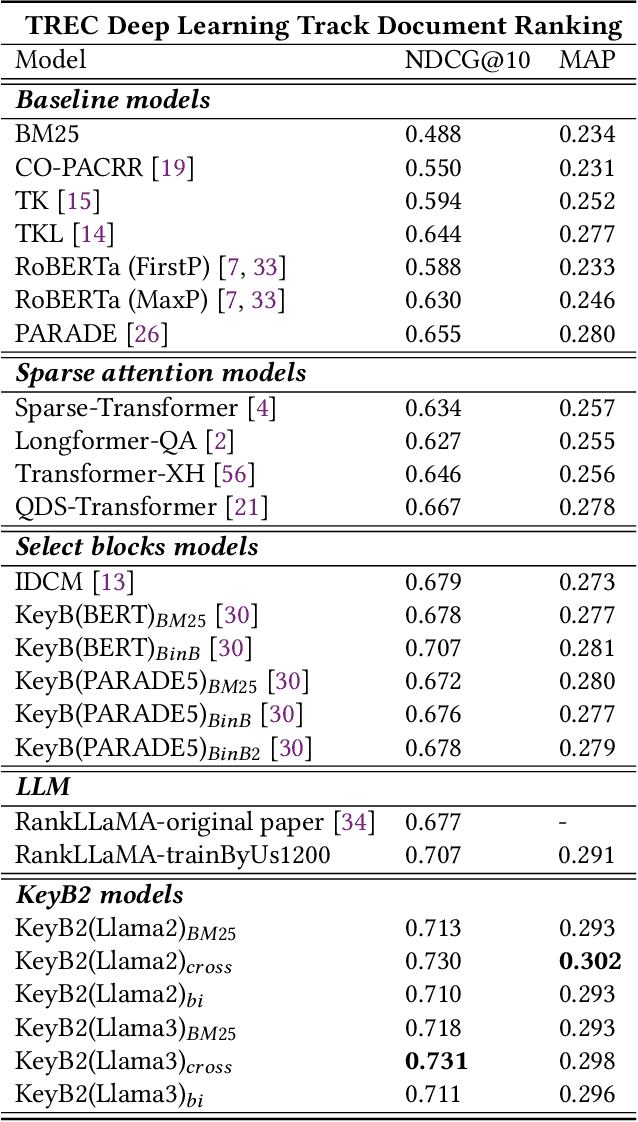
Abstract:The rapid development of large language models (LLMs) like Llama has significantly advanced information retrieval (IR) systems. However, using LLMs for long documents, as in RankLLaMA, remains challenging due to computational complexity, especially concerning input token length. Furthermore, the internal mechanisms of LLMs during ranking are still not fully understood. In this paper, we first explore the internal workings of LLMs during relevance judgement and identify that specific attention heads play a crucial role in aligning relevant tokens. This observation inspires us to revisit the block pre-ranking strategy used in KeyB, which remains state-of-the-art (SOTA) on the TREC 2019 DL document ranking dataset. Building on these insights, we develop KeyB2, an advanced long document IR approach that integrates block pre-ranking with the performance of LLMs. KeyB2 efficiently identifies and processes the most relevant blocks, reducing computational costs and improving ranking effectiveness. Additionally, we introduce a new bi-encoder block matching strategy for KeyB2. Comprehensive experiments on long-document datasets, including TREC 2019 DL, Robust04, and MLDR-zh, show that KeyB2 outperforms baselines like RankLLaMA and KeyB by reducing reranking time and GPU memory usage while enhancing retrieval performance, achieving new SOTA results on TREC 2019 DL with higher NDCG@10 and MAP scores.
Domain Adaptation for Dense Retrieval and Conversational Dense Retrieval through Self-Supervision by Meticulous Pseudo-Relevance Labeling
Mar 13, 2024
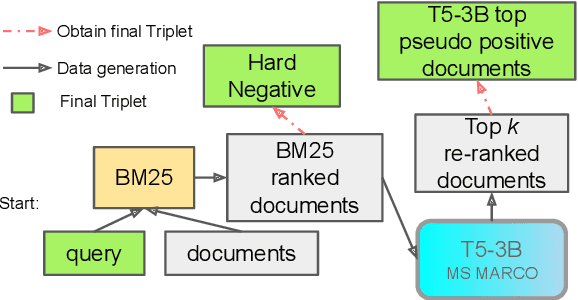
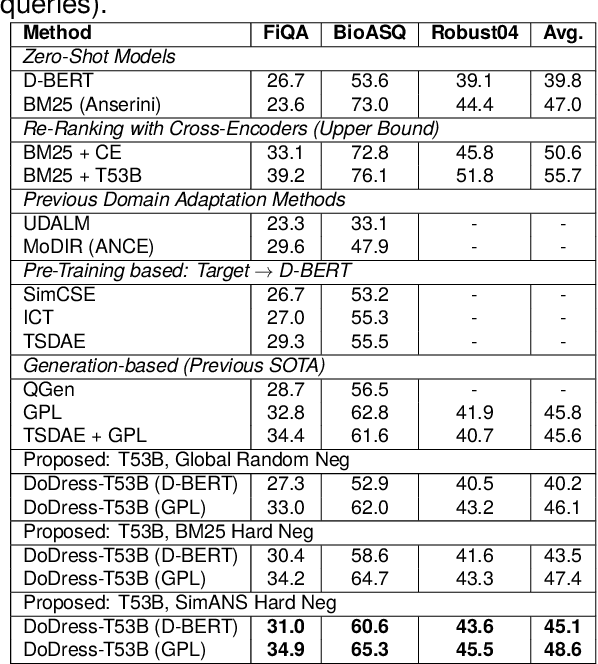
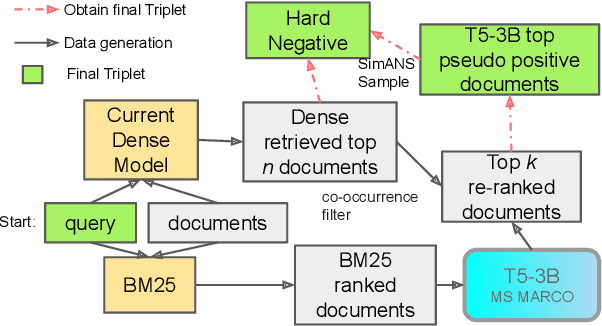
Abstract:Recent studies have demonstrated that the ability of dense retrieval models to generalize to target domains with different distributions is limited, which contrasts with the results obtained with interaction-based models. Prior attempts to mitigate this challenge involved leveraging adversarial learning and query generation approaches, but both approaches nevertheless resulted in limited improvements. In this paper, we propose to combine the query-generation approach with a self-supervision approach in which pseudo-relevance labels are automatically generated on the target domain. To accomplish this, a T5-3B model is utilized for pseudo-positive labeling, and meticulous hard negatives are chosen. We also apply this strategy on conversational dense retrieval model for conversational search. A similar pseudo-labeling approach is used, but with the addition of a query-rewriting module to rewrite conversational queries for subsequent labeling. This proposed approach enables a model's domain adaptation with real queries and documents from the target dataset. Experiments on standard dense retrieval and conversational dense retrieval models both demonstrate improvements on baseline models when they are fine-tuned on the pseudo-relevance labeled data.
On the Fly Detection of Root Causes from Observed Data with Application to IT Systems
Feb 09, 2024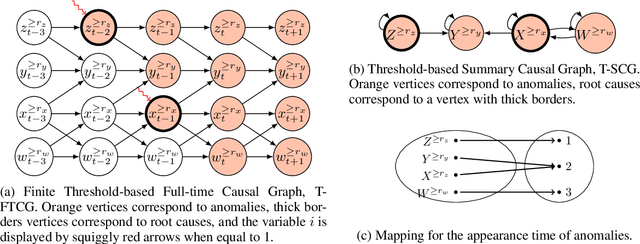
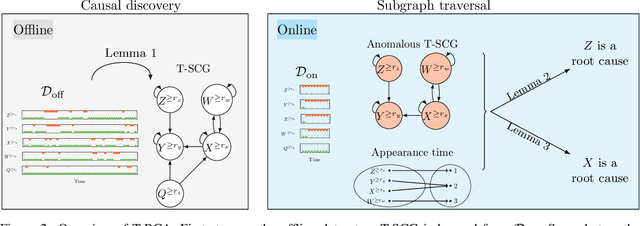
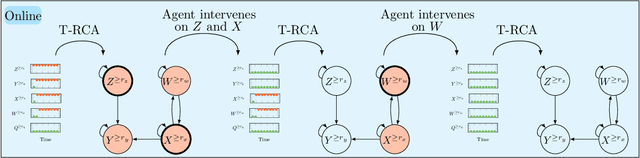
Abstract:This paper introduces a new structural causal model tailored for representing threshold-based IT systems and presents a new algorithm designed to rapidly detect root causes of anomalies in such systems. When root causes are not causally related, the method is proven to be correct; while an extension is proposed based on the intervention of an agent to relax this assumption. Our algorithm and its agent-based extension leverage causal discovery from offline data and engage in subgraph traversal when encountering new anomalies in online data. Our extensive experiments demonstrate the superior performance of our methods, even when applied to data generated from alternative structural causal models or real IT monitoring data.
Identifiability of total effects from abstractions of time series causal graphs
Nov 02, 2023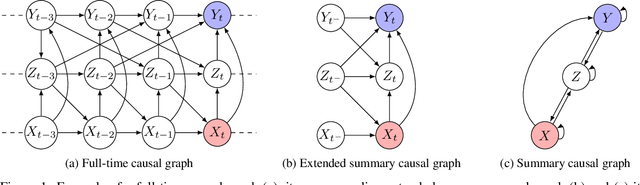
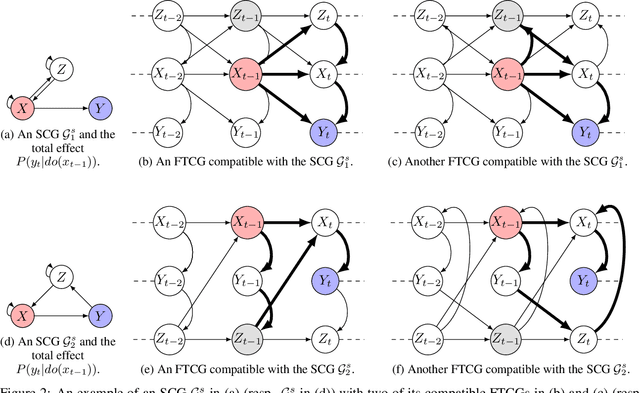
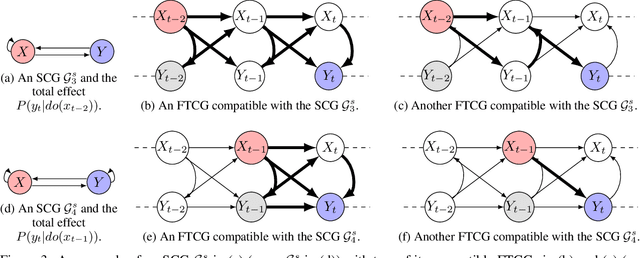
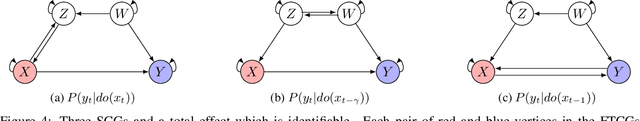
Abstract:We study the problem of identifiability of the total effect of an intervention from observational time series only given an abstraction of the causal graph of the system. Specifically, we consider two types of abstractions: the extended summary causal graph which conflates all lagged causal relations but distinguishes between lagged and instantaneous relations; and the summary causal graph which does not give any indication about the lag between causal relations. We show that the total effect is always identifiable in extended summary causal graphs and we provide necessary and sufficient graphical conditions for identifiability in summary causal graphs. Furthermore, we provide adjustment sets allowing to estimate the total effect whenever it is identifiable.
Case Studies of Causal Discovery from IT Monitoring Time Series
Jul 28, 2023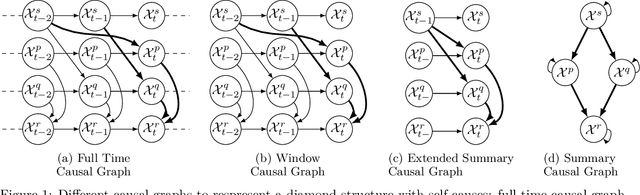
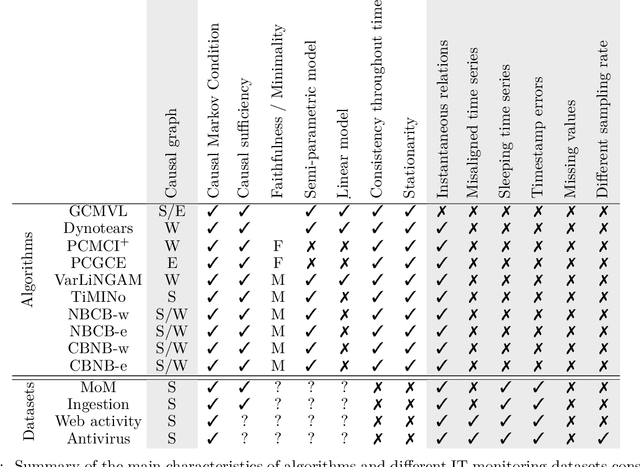
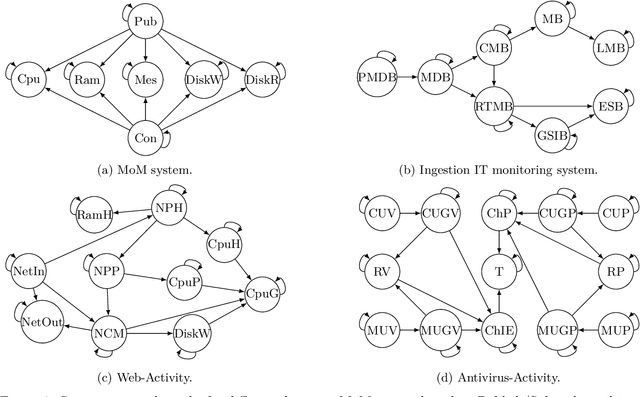
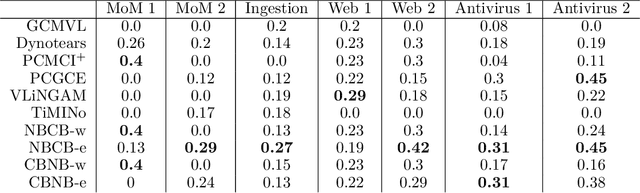
Abstract:Information technology (IT) systems are vital for modern businesses, handling data storage, communication, and process automation. Monitoring these systems is crucial for their proper functioning and efficiency, as it allows collecting extensive observational time series data for analysis. The interest in causal discovery is growing in IT monitoring systems as knowing causal relations between different components of the IT system helps in reducing downtime, enhancing system performance and identifying root causes of anomalies and incidents. It also allows proactive prediction of future issues through historical data analysis. Despite its potential benefits, applying causal discovery algorithms on IT monitoring data poses challenges, due to the complexity of the data. For instance, IT monitoring data often contains misaligned time series, sleeping time series, timestamp errors and missing values. This paper presents case studies on applying causal discovery algorithms to different IT monitoring datasets, highlighting benefits and ongoing challenges.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge