Engin Erzin
Learning Annotation Consensus for Continuous Emotion Recognition
May 27, 2025Abstract:In affective computing, datasets often contain multiple annotations from different annotators, which may lack full agreement. Typically, these annotations are merged into a single gold standard label, potentially losing valuable inter-rater variability. We propose a multi-annotator training approach for continuous emotion recognition (CER) that seeks a consensus across all annotators rather than relying on a single reference label. Our method employs a consensus network to aggregate annotations into a unified representation, guiding the main arousal-valence predictor to better reflect collective inputs. Tested on the RECOLA and COGNIMUSE datasets, our approach outperforms traditional methods that unify annotations into a single label. This underscores the benefits of fully leveraging multi-annotator data in emotion recognition and highlights its applicability across various fields where annotations are abundant yet inconsistent.
Efficient and Safe Contact-rich pHRI via Subtask Detection and Motion Estimation using Deep Learning
Jul 19, 2024



Abstract:This paper proposes an adaptive admittance controller for improving efficiency and safety in physical human-robot interaction (pHRI) tasks in small-batch manufacturing that involve contact with stiff environments, such as drilling, polishing, cutting, etc. We aim to minimize human effort and task completion time while maximizing precision and stability during the contact of the machine tool attached to the robot's end-effector with the workpiece. To this end, a two-layered learning-based human intention recognition mechanism is proposed, utilizing only the kinematic and kinetic data from the robot and two force sensors. A ``subtask detector" recognizes the human intent by estimating which phase of the task is being performed, e.g., \textit{Idle}, \textit{Tool-Attachment}, \textit{Driving}, and \textit{Contact}. Simultaneously, a ``motion estimator" continuously quantifies intent more precisely during the \textit{Driving} to predict when \textit{Contact} will begin. The controller is adapted online according to the subtask while allowing early adaptation before the \textit{Contact} to maximize precision and safety and prevent potential instabilities. Three sets of pHRI experiments were performed with multiple subjects under various conditions. Spring compression experiments were performed in virtual environments to train the data-driven models and validate the proposed adaptive system, and drilling experiments were performed in the physical world to test the proposed methods' efficacy in real-life scenarios. Experimental results show subtask classification accuracy of 84\% and motion estimation R\textsuperscript{2} score of 0.96. Furthermore, 57\% lower human effort was achieved during \textit{Driving} as well as 53\% lower oscillation amplitude at \textit{Contact} as a result of the proposed system.
Role of Audio in Audio-Visual Video Summarization
Dec 02, 2022



Abstract:Video summarization attracts attention for efficient video representation, retrieval, and browsing to ease volume and traffic surge problems. Although video summarization mostly uses the visual channel for compaction, the benefits of audio-visual modeling appeared in recent literature. The information coming from the audio channel can be a result of audio-visual correlation in the video content. In this study, we propose a new audio-visual video summarization framework integrating four ways of audio-visual information fusion with GRU-based and attention-based networks. Furthermore, we investigate a new explainability methodology using audio-visual canonical correlation analysis (CCA) to better understand and explain the role of audio in the video summarization task. Experimental evaluations on the TVSum dataset attain F1 score and Kendall-tau score improvements for the audio-visual video summarization. Furthermore, splitting video content on TVSum and COGNIMUSE datasets based on audio-visual CCA as positively and negatively correlated videos yields a strong performance improvement over the positively correlated videos for audio-only and audio-visual video summarization.
HuBERT-TR: Reviving Turkish Automatic Speech Recognition with Self-supervised Speech Representation Learning
Oct 13, 2022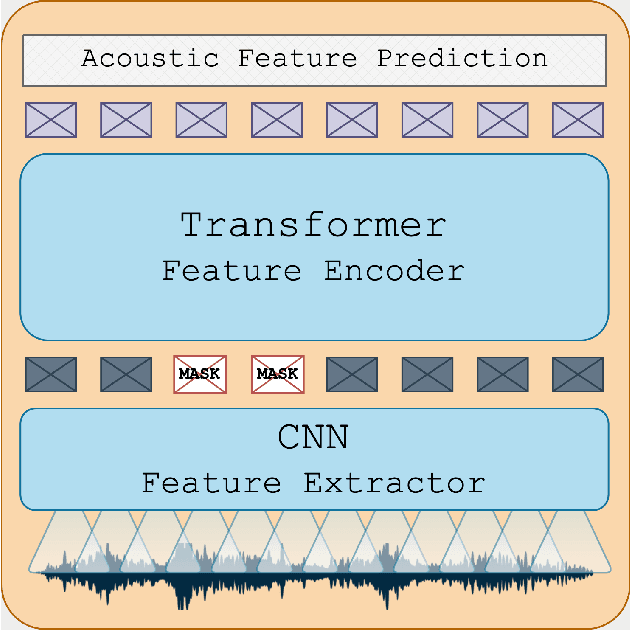
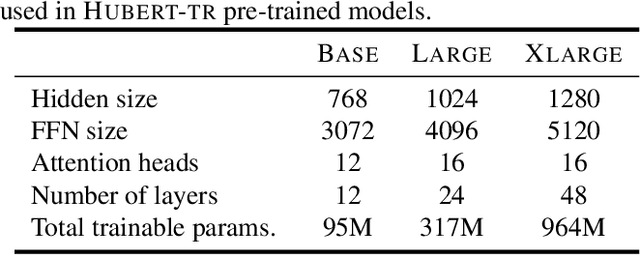
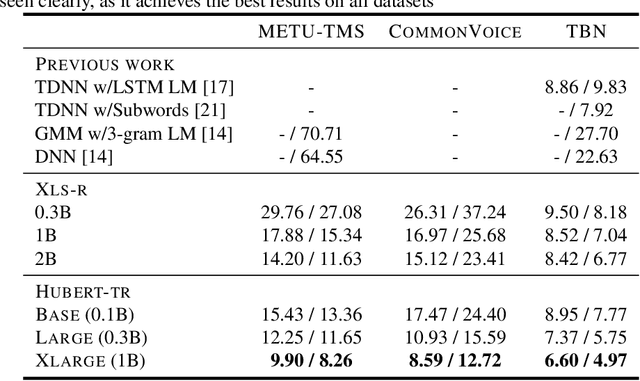
Abstract:While the Turkish language is listed among low-resource languages, literature on Turkish automatic speech recognition (ASR) is relatively old. In this paper, we present HuBERT-TR, a speech representation model for Turkish based on HuBERT. HuBERT-TR achieves state-of-the-art results on several Turkish ASR datasets. We investigate pre-training HuBERT for Turkish with large-scale data curated from online resources. We pre-train HuBERT-TR using over 6,500 hours of speech data curated from YouTube that includes extensive variability in terms of quality and genre. We show that pre-trained models within a multi-lingual setup are inferior to language-specific models, where our Turkish model HuBERT-TR base performs better than its x10 times larger multi-lingual counterpart XLS-R-1B. Moreover, we study the effect of scaling on ASR performance by scaling our models up to 1B parameters. Our best model yields a state-of-the-art word error rate of 4.97% on the Turkish Broadcast News dataset. Models are available at huggingface.co/asafaya .
Affective Burst Detection from Speech using Kernel-fusion Dilated Convolutional Neural Networks
Oct 08, 2021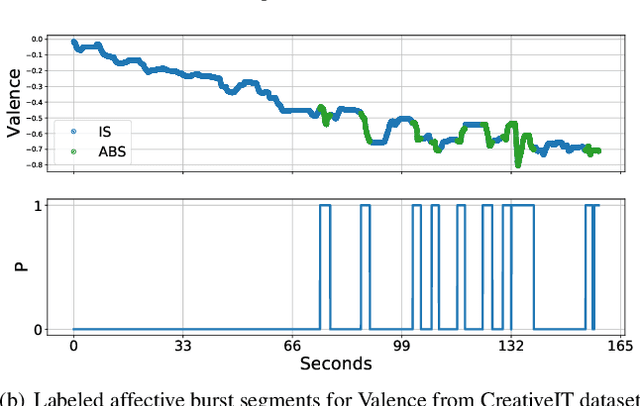
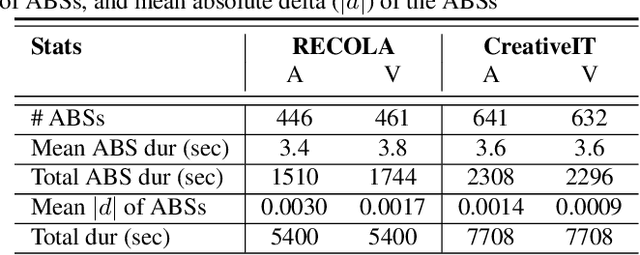
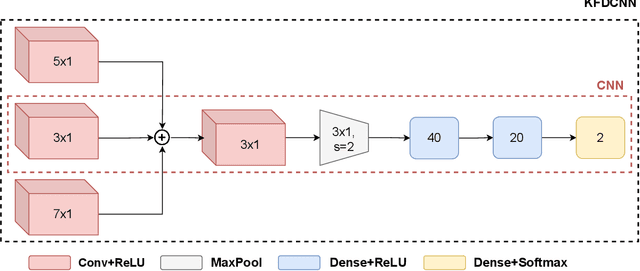
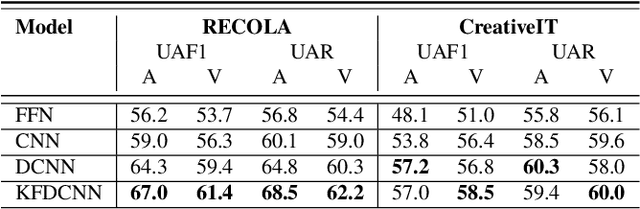
Abstract:As speech-interfaces are getting richer and widespread, speech emotion recognition promises more attractive applications. In the continuous emotion recognition (CER) problem, tracking changes across affective states is an important and desired capability. Although CER studies widely use correlation metrics in evaluations, these metrics do not always capture all the high-intensity changes in the affective domain. In this paper, we define a novel affective burst detection problem to accurately capture high-intensity changes of the affective attributes. For this problem, we formulate a two-class classification approach to isolate affective burst regions over the affective state contour. The proposed classifier is a kernel-fusion dilated convolutional neural network (KFDCNN) architecture driven by speech spectral features to segment the affective attribute contour into idle and burst sections. Experimental evaluations are performed on the RECOLA and CreativeIT datasets. The proposed KFDCNN is observed to outperform baseline feedforward neural networks on both datasets.
Use of Affective Visual Information for Summarization of Human-Centric Videos
Jul 08, 2021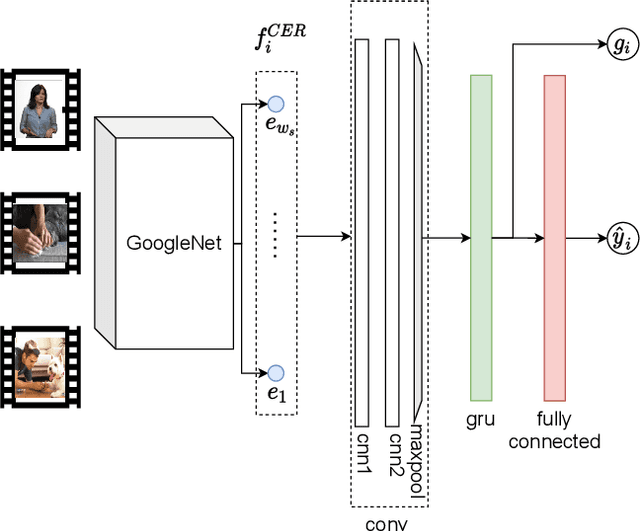

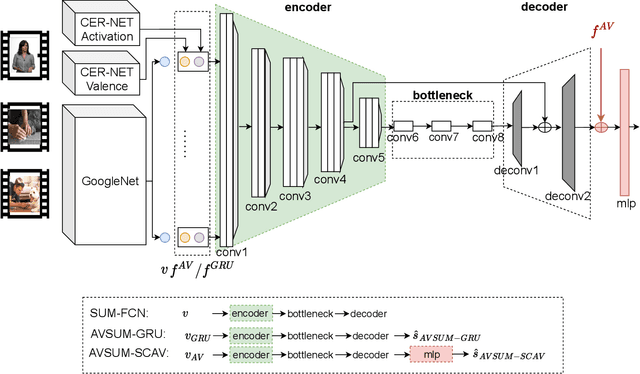
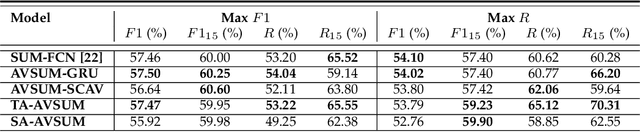
Abstract:Increasing volume of user-generated human-centric video content and their applications, such as video retrieval and browsing, require compact representations that are addressed by the video summarization literature. Current supervised studies formulate video summarization as a sequence-to-sequence learning problem and the existing solutions often neglect the surge of human-centric view, which inherently contains affective content. In this study, we investigate the affective-information enriched supervised video summarization task for human-centric videos. First, we train a visual input-driven state-of-the-art continuous emotion recognition model (CER-NET) on the RECOLA dataset to estimate emotional attributes. Then, we integrate the estimated emotional attributes and the high-level representations from the CER-NET with the visual information to define the proposed affective video summarization architectures (AVSUM). In addition, we investigate the use of attention to improve the AVSUM architectures and propose two new architectures based on temporal attention (TA-AVSUM) and spatial attention (SA-AVSUM). We conduct video summarization experiments on the TvSum database. The proposed AVSUM-GRU architecture with an early fusion of high level GRU embeddings and the temporal attention based TA-AVSUM architecture attain competitive video summarization performances by bringing strong performance improvements for the human-centric videos compared to the state-of-the-art in terms of F-score and self-defined face recall metrics.
AffectON: Incorporating Affect Into Dialog Generation
Dec 12, 2020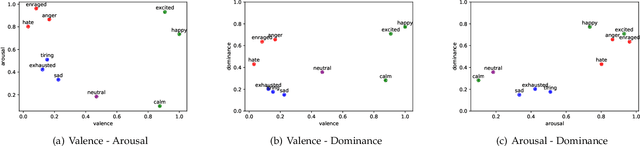
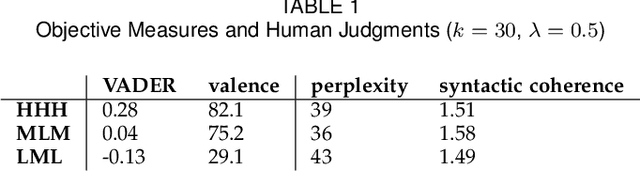


Abstract:Due to its expressivity, natural language is paramount for explicit and implicit affective state communication among humans. The same linguistic inquiry (e.g., How are you?) might induce responses with different affects depending on the affective state of the conversational partner(s) and the context of the conversation. Yet, most dialog systems do not consider affect as constitutive aspect of response generation. In this paper, we introduce AffectON, an approach for generating affective responses during inference. For generating language in a targeted affect, our approach leverages a probabilistic language model and an affective space. AffectON is language model agnostic, since it can work with probabilities generated by any language model (e.g., sequence-to-sequence models, neural language models, n-grams). Hence, it can be employed for both affective dialog and affective language generation. We experimented with affective dialog generation and evaluated the generated text objectively and subjectively. For the subjective part of the evaluation, we designed a custom user interface for rating and provided recommendations for the design of such interfaces. The results, both subjective and objective demonstrate that our approach is successful in pulling the generated language toward the targeted affect, with little sacrifice in syntactic coherence.
Batch Recurrent Q-Learning for Backchannel Generation Towards Engaging Agents
Aug 06, 2019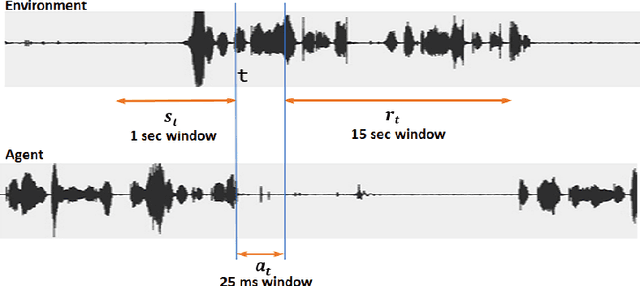
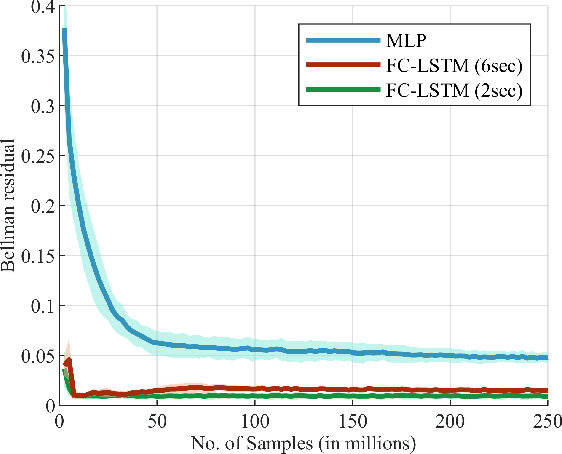
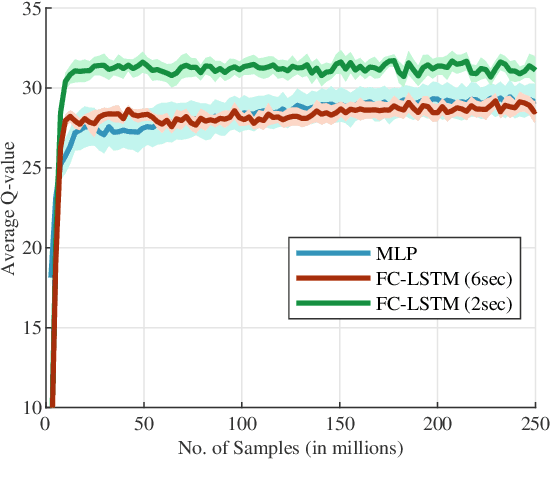
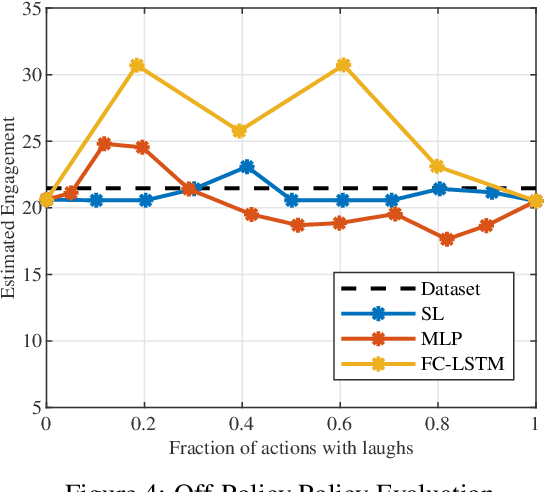
Abstract:The ability to generate appropriate verbal and non-verbal backchannels by an agent during human-robot interaction greatly enhances the interaction experience. Backchannels are particularly important in applications like tutoring and counseling, which require constant attention and engagement of the user. We present here a method for training a robot for backchannel generation during a human-robot interaction within the reinforcement learning (RL) framework, with the goal of maintaining high engagement level. Since online learning by interaction with a human is highly time-consuming and impractical, we take advantage of the recorded human-to-human dataset and approach our problem as a batch reinforcement learning problem. The dataset is utilized as a batch data acquired by some behavior policy. We perform experiments with laughs as a backchannel and train an agent with value-based techniques. In particular, we demonstrate the effectiveness of recurrent layers in the approximate value function for this problem, that boosts the performance in partially observable environments. With off-policy policy evaluation, it is shown that the RL agents are expected to produce more engagement than an agent trained from imitation learning.
Speech Driven Backchannel Generation using Deep Q-Network for Enhancing Engagement in Human-Robot Interaction
Aug 05, 2019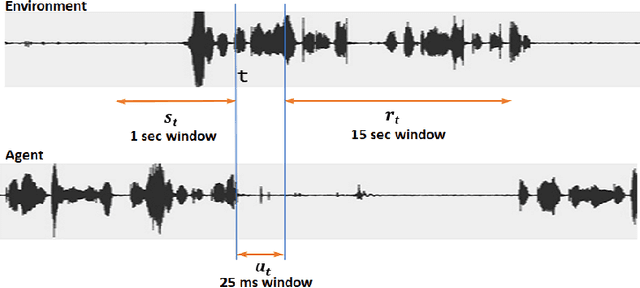
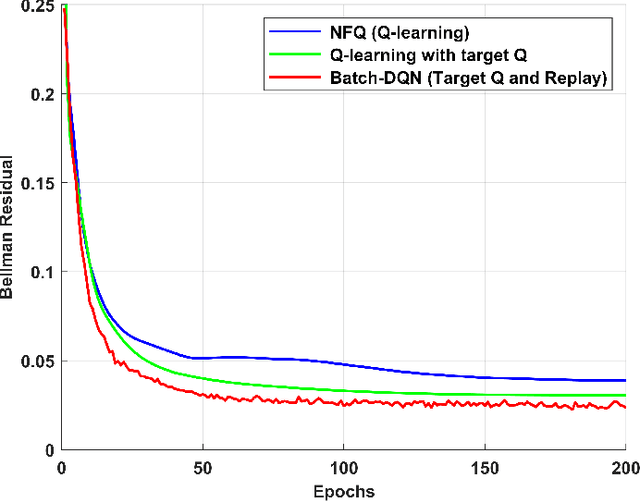
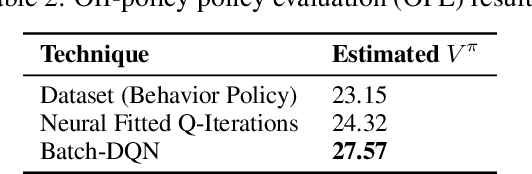
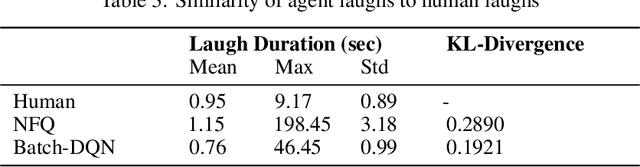
Abstract:We present a novel method for training a social robot to generate backchannels during human-robot interaction. We address the problem within an off-policy reinforcement learning framework, and show how a robot may learn to produce non-verbal backchannels like laughs, when trained to maximize the engagement and attention of the user. A major contribution of this work is the formulation of the problem as a Markov decision process (MDP) with states defined by the speech activity of the user and rewards generated by quantified engagement levels. The problem that we address falls into the class of applications where unlimited interaction with the environment is not possible (our environment being a human) because it may be time-consuming, costly, impracticable or even dangerous in case a bad policy is executed. Therefore, we introduce deep Q-network (DQN) in a batch reinforcement learning framework, where an optimal policy is learned from a batch data collected using a more controlled policy. We suggest the use of human-to-human dyadic interaction datasets as a batch of trajectories to train an agent for engaging interactions. Our experiments demonstrate the potential of our method to train a robot for engaging behaviors in an offline manner.
Inter Genre Similarity Modelling For Automatic Music Genre Classification
Jul 18, 2009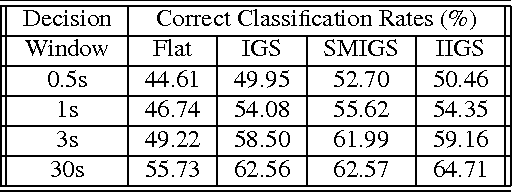
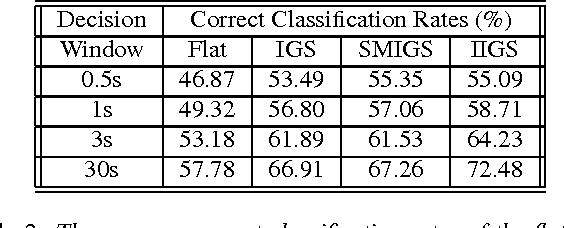
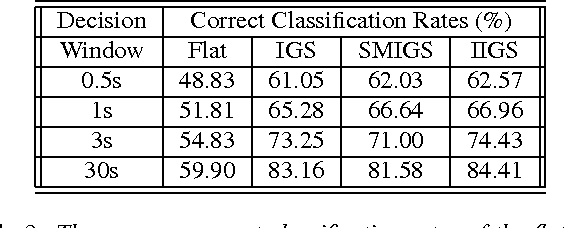
Abstract:Music genre classification is an essential tool for music information retrieval systems and it has been finding critical applications in various media platforms. Two important problems of the automatic music genre classification are feature extraction and classifier design. This paper investigates inter-genre similarity modelling (IGS) to improve the performance of automatic music genre classification. Inter-genre similarity information is extracted over the mis-classified feature population. Once the inter-genre similarity is modelled, elimination of the inter-genre similarity reduces the inter-genre confusion and improves the identification rates. Inter-genre similarity modelling is further improved with iterative IGS modelling(IIGS) and score modelling for IGS elimination(SMIGS). Experimental results with promising classification improvements are provided.
* Dafx 2006 submission
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge