Berkay Kopru
Teacher-Student Learning based Low Complexity Relay Selection in Wireless Powered Communications
Feb 03, 2024Abstract:Radio Frequency Energy Harvesting (RF-EH) networks are key enablers of massive Internet-of-things by providing controllable and long-distance energy transfer to energy-limited devices. Relays, helping either energy or information transfer, have been demonstrated to significantly improve the performance of these networks. This paper studies the joint relay selection, scheduling, and power control problem in multiple-source-multiple-relay RF-EH networks under nonlinear EH conditions. We first obtain the optimal solution to the scheduling and power control problem for the given relay selection. Then, the relay selection problem is formulated as a classification problem, for which two convolutional neural network (CNN) based architectures are proposed. While the first architecture employs conventional 2D convolution blocks and benefits from skip connections between layers; the second architecture replaces them with inception blocks, to decrease trainable parameter size without sacrificing accuracy for memory-constrained applications. To decrease the runtime complexity further, teacher-student learning is employed such that the teacher network is larger, and the student is a smaller size CNN-based architecture distilling the teacher's knowledge. A novel dichotomous search-based algorithm is employed to determine the best architecture for the student network. Our simulation results demonstrate that the proposed solutions provide lower complexity than the state-of-art iterative approaches without compromising optimality.
Role of Audio in Audio-Visual Video Summarization
Dec 02, 2022



Abstract:Video summarization attracts attention for efficient video representation, retrieval, and browsing to ease volume and traffic surge problems. Although video summarization mostly uses the visual channel for compaction, the benefits of audio-visual modeling appeared in recent literature. The information coming from the audio channel can be a result of audio-visual correlation in the video content. In this study, we propose a new audio-visual video summarization framework integrating four ways of audio-visual information fusion with GRU-based and attention-based networks. Furthermore, we investigate a new explainability methodology using audio-visual canonical correlation analysis (CCA) to better understand and explain the role of audio in the video summarization task. Experimental evaluations on the TVSum dataset attain F1 score and Kendall-tau score improvements for the audio-visual video summarization. Furthermore, splitting video content on TVSum and COGNIMUSE datasets based on audio-visual CCA as positively and negatively correlated videos yields a strong performance improvement over the positively correlated videos for audio-only and audio-visual video summarization.
Affective Burst Detection from Speech using Kernel-fusion Dilated Convolutional Neural Networks
Oct 08, 2021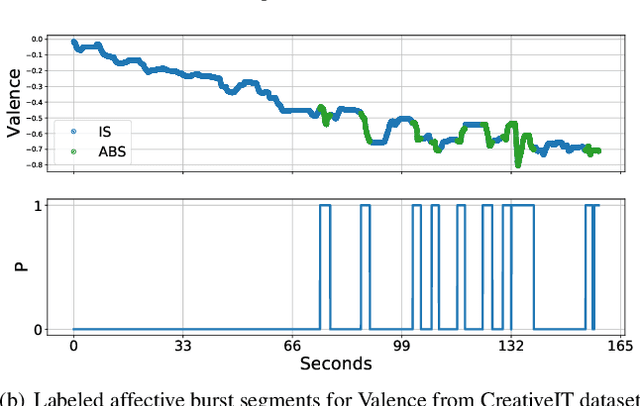
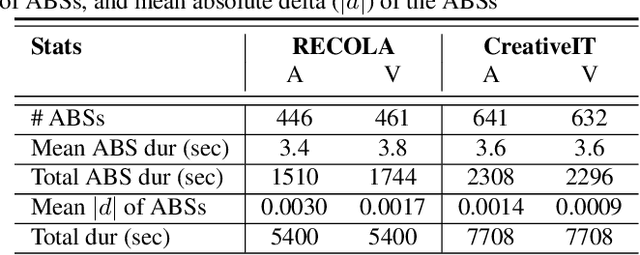
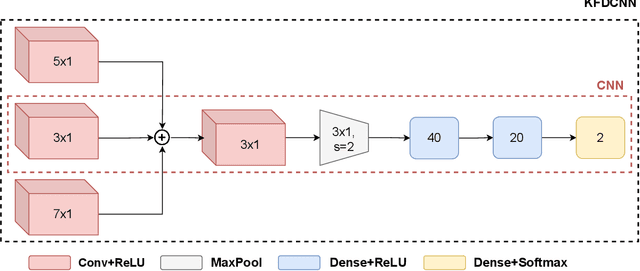
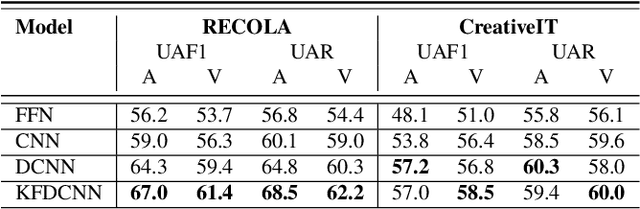
Abstract:As speech-interfaces are getting richer and widespread, speech emotion recognition promises more attractive applications. In the continuous emotion recognition (CER) problem, tracking changes across affective states is an important and desired capability. Although CER studies widely use correlation metrics in evaluations, these metrics do not always capture all the high-intensity changes in the affective domain. In this paper, we define a novel affective burst detection problem to accurately capture high-intensity changes of the affective attributes. For this problem, we formulate a two-class classification approach to isolate affective burst regions over the affective state contour. The proposed classifier is a kernel-fusion dilated convolutional neural network (KFDCNN) architecture driven by speech spectral features to segment the affective attribute contour into idle and burst sections. Experimental evaluations are performed on the RECOLA and CreativeIT datasets. The proposed KFDCNN is observed to outperform baseline feedforward neural networks on both datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge