Emad M. Boctor
Enabling Mammography with Co-Robotic Ultrasound
Dec 16, 2023Abstract:Ultrasound (US) imaging is a vital adjunct to mammography in breast cancer screening and diagnosis, but its reliance on hand-held transducers often lacks repeatability and heavily depends on sonographers' skills. Integrating US systems from different vendors further complicates clinical standards and workflows. This research introduces a co-robotic US platform for repeatable, accurate, and vendor-independent breast US image acquisition. The platform can autonomously perform 3D volume scans or swiftly acquire real-time 2D images of suspicious lesions. Utilizing a Universal Robot UR5 with an RGB camera, a force sensor, and an L7-4 linear array transducer, the system achieves autonomous navigation, motion control, and image acquisition. The calibrations, including camera-mammogram, robot-camera, and robot-US, were rigorously conducted and validated. Governed by a PID force control, the robot-held transducer maintains a constant contact force with the compression plate during the scan for safety and patient comfort. The framework was validated on a lesion-mimicking phantom. Our results indicate that the developed co-robotic US platform promises to enhance the precision and repeatability of breast cancer screening and diagnosis. Additionally, the platform offers straightforward integration into most mammographic devices to ensure vendor-independence.
Automatic Search for Photoacoustic Marker Using Automated Transrectal Ultrasound
Jul 20, 2023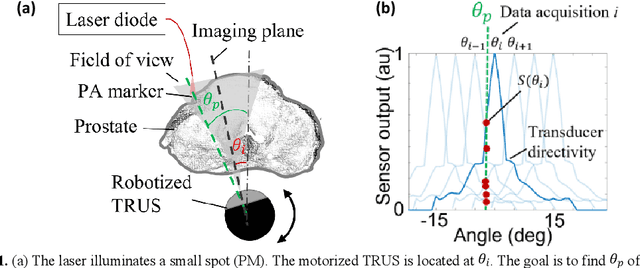
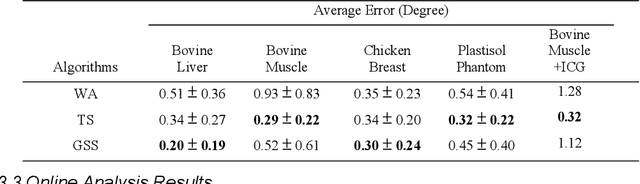
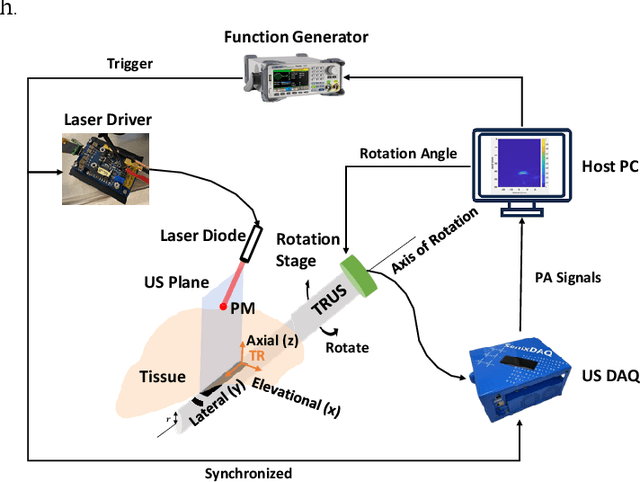
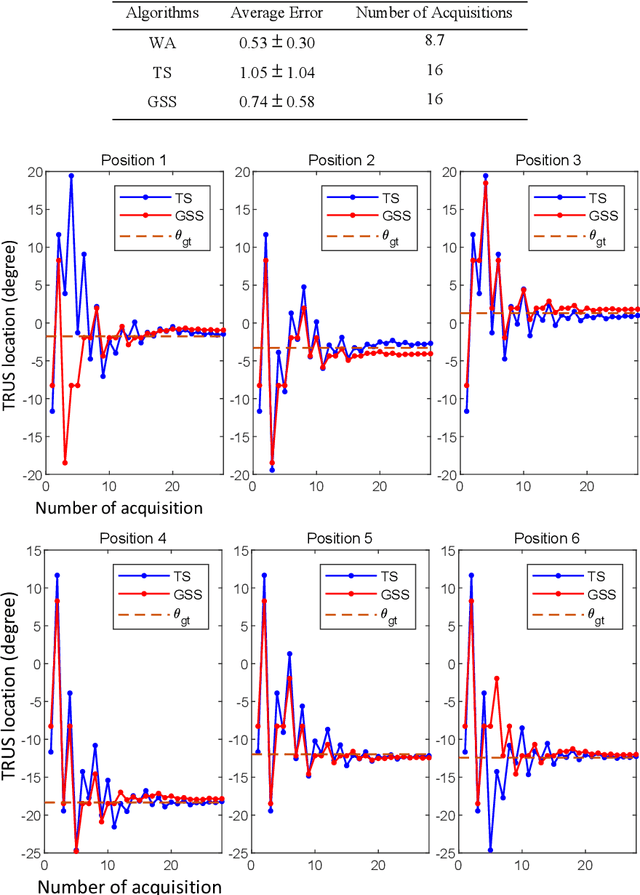
Abstract:Real-time transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) image guidance during robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy has the potential to enhance surgery outcomes. Whether conventional or photoacoustic TRUS is used, the robotic system and the TRUS must be registered to each other. Accurate registration can be performed using photoacoustic (PA markers). However, this requires a manual search by an assistant [19]. This paper introduces the first automatic search for PA markers using a transrectal ultrasound robot. This effectively reduces the challenges associated with the da Vinci-TRUS registration. This paper investigated the performance of three search algorithms in simulation and experiment: Weighted Average (WA), Golden Section Search (GSS), and Ternary Search (TS). For validation, a surgical prostate scenario was mimicked and various ex vivo tissues were tested. As a result, the WA algorithm can achieve 0.53 degree average error after 9 data acquisitions, while the TS and GSS algorithm can achieve 0.29 degree and 0.48 degree average errors after 28 data acquisitions.
Arc-to-line frame registration method for ultrasound and photoacoustic image-guided intraoperative robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy
Jun 21, 2023



Abstract:Purpose: To achieve effective robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy, the integration of transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) imaging system which is the most widely used imaging modelity in prostate imaging is essential. However, manual manipulation of the ultrasound transducer during the procedure will significantly interfere with the surgery. Therefore, we propose an image co-registration algorithm based on a photoacoustic marker method, where the ultrasound / photoacoustic (US/PA) images can be registered to the endoscopic camera images to ultimately enable the TRUS transducer to automatically track the surgical instrument Methods: An optimization-based algorithm is proposed to co-register the images from the two different imaging modalities. The principles of light propagation and an uncertainty in PM detection were assumed in this algorithm to improve the stability and accuracy of the algorithm. The algorithm is validated using the previously developed US/PA image-guided system with a da Vinci surgical robot. Results: The target-registration-error (TRE) is measured to evaluate the proposed algorithm. In both simulation and experimental demonstration, the proposed algorithm achieved a sub-centimeter accuracy which is acceptable in practical clinics. The result is also comparable with our previous approach, and the proposed method can be implemented with a normal white light stereo camera and doesn't require highly accurate localization of the PM. Conclusion: The proposed frame registration algorithm enabled a simple yet efficient integration of commercial US/PA imaging system into laparoscopic surgical setting by leveraging the characteristic properties of acoustic wave propagation and laser excitation, contributing to automated US/PA image-guided surgical intervention applications.
Single Frame Laser Diode Photoacoustic Imaging: Denoising and Reconstruction
Dec 16, 2022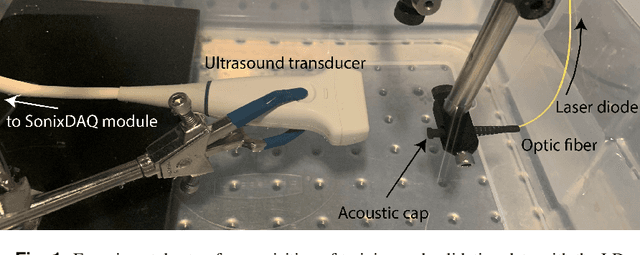
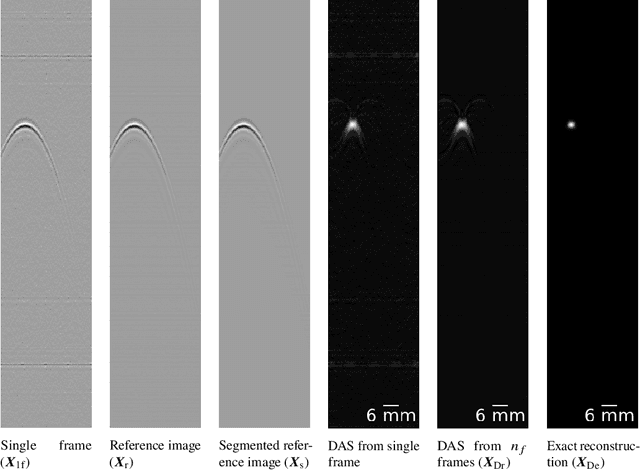
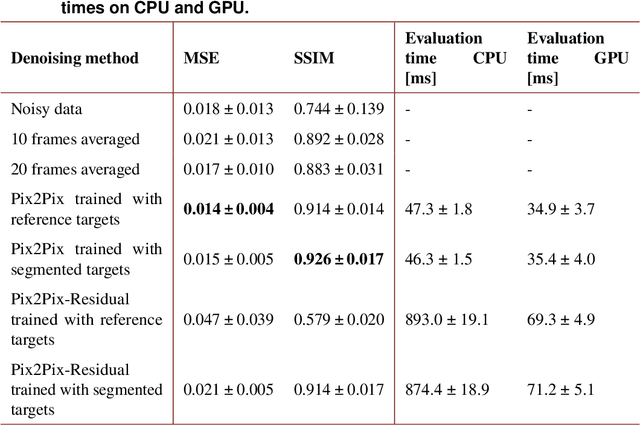

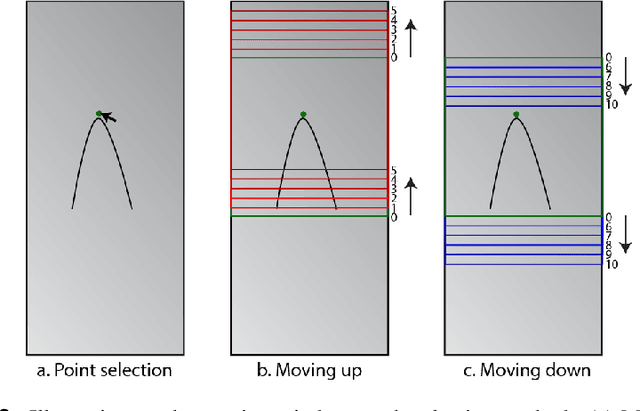
Abstract:A new development in photoacoustic (PA) imaging has been the use of compact, portable and low-cost laser diodes (LDs), but LD-based PA imaging suffers from low signal intensity recorded by the conventional transducers. A common method to improve signal strength is temporal averaging, which reduces frame rate and increases laser exposure to patients. To tackle this problem, we propose a deep learning method that will denoise the PA images before beamforming with a very few frames, even one. We also present a deep learning method to automatically reconstruct point sources from noisy pre-beamformed data. Finally, we employ a strategy of combined denoising and reconstruction, which can supplement the reconstruction algorithm for very low signal-to-noise ratio inputs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge