Emad Kasaeyan Naeini
Department of Computer Science, University of California, Irvine
Edge-centric Optimization of Multi-modal ML-driven eHealth Applications
Aug 04, 2022



Abstract:Smart eHealth applications deliver personalized and preventive digital healthcare services to clients through remote sensing, continuous monitoring, and data analytics. Smart eHealth applications sense input data from multiple modalities, transmit the data to edge and/or cloud nodes, and process the data with compute intensive machine learning (ML) algorithms. Run-time variations with continuous stream of noisy input data, unreliable network connection, computational requirements of ML algorithms, and choice of compute placement among sensor-edge-cloud layers affect the efficiency of ML-driven eHealth applications. In this chapter, we present edge-centric techniques for optimized compute placement, exploration of accuracy-performance trade-offs, and cross-layered sense-compute co-optimization for ML-driven eHealth applications. We demonstrate the practical use cases of smart eHealth applications in everyday settings, through a sensor-edge-cloud framework for an objective pain assessment case study.
Efficient Personalized Learning for Wearable Health Applications using HyperDimensional Computing
Aug 01, 2022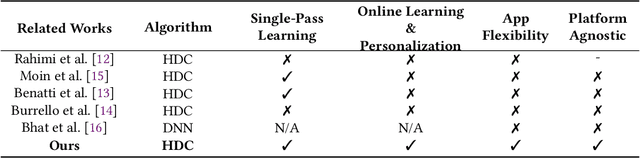

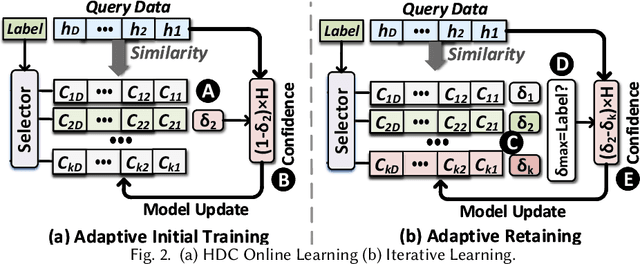
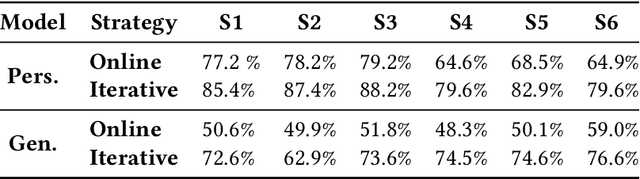
Abstract:Health monitoring applications increasingly rely on machine learning techniques to learn end-user physiological and behavioral patterns in everyday settings. Considering the significant role of wearable devices in monitoring human body parameters, on-device learning can be utilized to build personalized models for behavioral and physiological patterns, and provide data privacy for users at the same time. However, resource constraints on most of these wearable devices prevent the ability to perform online learning on them. To address this issue, it is required to rethink the machine learning models from the algorithmic perspective to be suitable to run on wearable devices. Hyperdimensional computing (HDC) offers a well-suited on-device learning solution for resource-constrained devices and provides support for privacy-preserving personalization. Our HDC-based method offers flexibility, high efficiency, resilience, and performance while enabling on-device personalization and privacy protection. We evaluate the efficacy of our approach using three case studies and show that our system improves the energy efficiency of training by up to $45.8\times$ compared with the state-of-the-art Deep Neural Network (DNN) algorithms while offering a comparable accuracy.
AMSER: Adaptive Multi-modal Sensing for Energy Efficient and Resilient eHealth Systems
Dec 13, 2021



Abstract:eHealth systems deliver critical digital healthcare and wellness services for users by continuously monitoring physiological and contextual data. eHealth applications use multi-modal machine learning kernels to analyze data from different sensor modalities and automate decision-making. Noisy inputs and motion artifacts during sensory data acquisition affect the i) prediction accuracy and resilience of eHealth services and ii) energy efficiency in processing garbage data. Monitoring raw sensory inputs to identify and drop data and features from noisy modalities can improve prediction accuracy and energy efficiency. We propose a closed-loop monitoring and control framework for multi-modal eHealth applications, AMSER, that can mitigate garbage-in garbage-out by i) monitoring input modalities, ii) analyzing raw input to selectively drop noisy data and features, and iii) choosing appropriate machine learning models that fit the configured data and feature vector - to improve prediction accuracy and energy efficiency. We evaluate our AMSER approach using multi-modal eHealth applications of pain assessment and stress monitoring over different levels and types of noisy components incurred via different sensor modalities. Our approach achieves up to 22\% improvement in prediction accuracy and 5.6$\times$ energy consumption reduction in the sensing phase against the state-of-the-art multi-modal monitoring application.
GNN4IP: Graph Neural Network for Hardware Intellectual Property Piracy Detection
Jul 19, 2021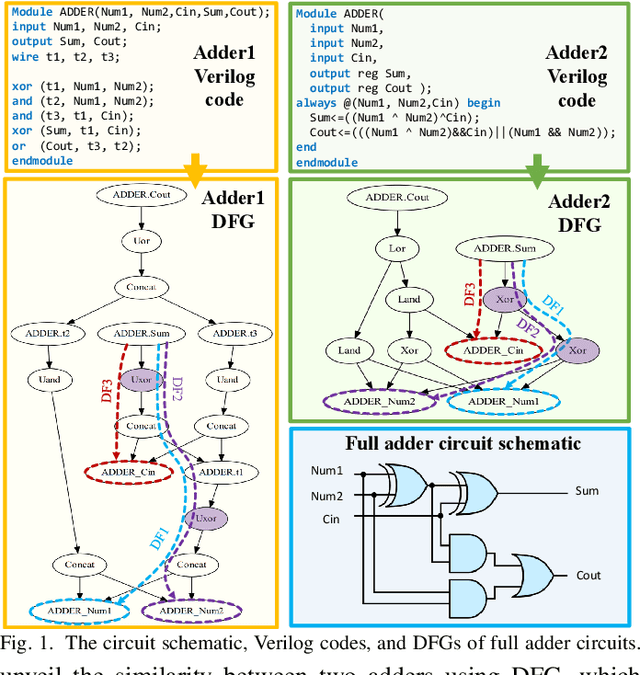
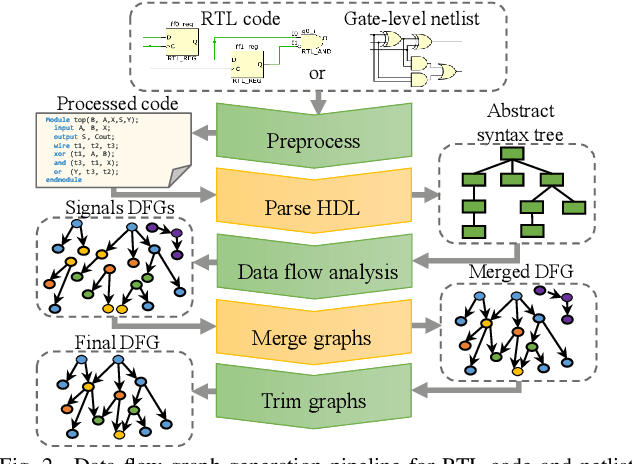
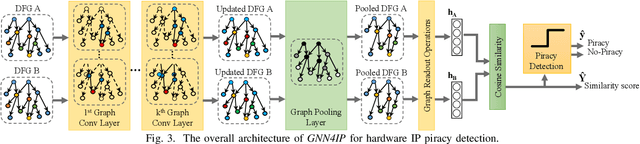
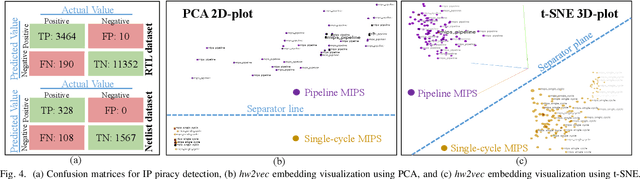
Abstract:Aggressive time-to-market constraints and enormous hardware design and fabrication costs have pushed the semiconductor industry toward hardware Intellectual Properties (IP) core design. However, the globalization of the integrated circuits (IC) supply chain exposes IP providers to theft and illegal redistribution of IPs. Watermarking and fingerprinting are proposed to detect IP piracy. Nevertheless, they come with additional hardware overhead and cannot guarantee IP security as advanced attacks are reported to remove the watermark, forge, or bypass it. In this work, we propose a novel methodology, GNN4IP, to assess similarities between circuits and detect IP piracy. We model the hardware design as a graph and construct a graph neural network model to learn its behavior using the comprehensive dataset of register transfer level codes and gate-level netlists that we have gathered. GNN4IP detects IP piracy with 96% accuracy in our dataset and recognizes the original IP in its obfuscated version with 100% accuracy.
GSR Analysis for Stress: Development and Validation of an Open Source Tool for Noisy Naturalistic GSR Data
May 09, 2020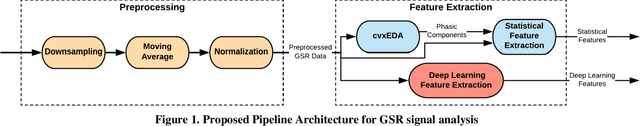
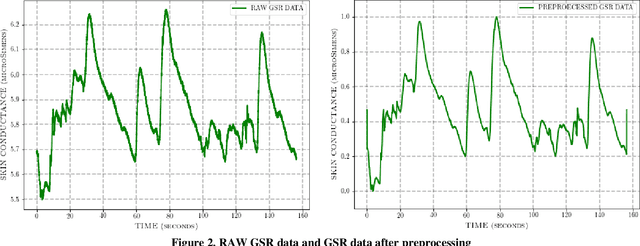
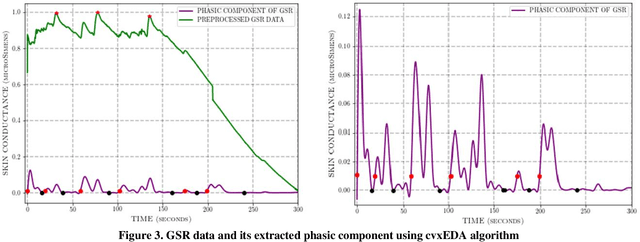
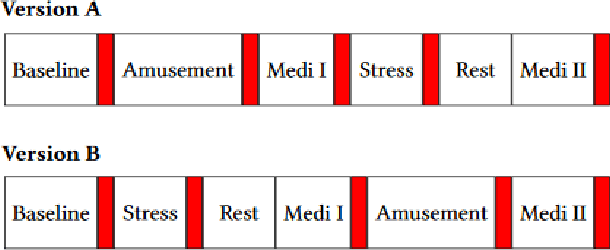
Abstract:The stress detection problem is receiving great attention in related research communities. This is due to its essential part in behavioral studies for many serious health problems and physical illnesses. There are different methods and algorithms for stress detection using different physiological signals. Previous studies have already shown that Galvanic Skin Response (GSR), also known as Electrodermal Activity (EDA), is one of the leading indicators for stress. However, the GSR signal itself is not trivial to analyze. Different features are extracted from GSR signals to detect stress in people like the number of peaks, max peak amplitude, etc. In this paper, we are proposing an open-source tool for GSR analysis, which uses deep learning algorithms alongside statistical algorithms to extract GSR features for stress detection. Then we use different machine learning algorithms and Wearable Stress and Affect Detection (WESAD) dataset to evaluate our results. The results show that we are capable of detecting stress with the accuracy of 92 percent using 10-fold cross-validation and using the features extracted from our tool.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge