Ed Lin
Adapting Large Language Model with Speech for Fully Formatted End-to-End Speech Recognition
Aug 03, 2023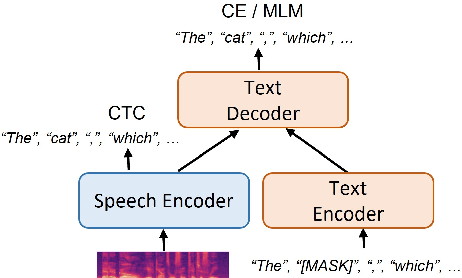
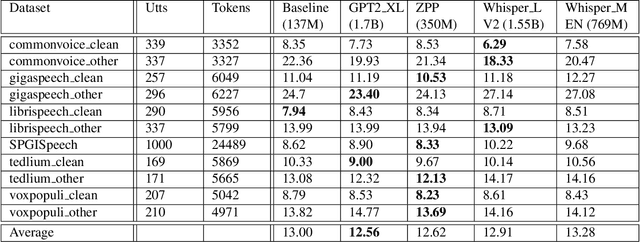
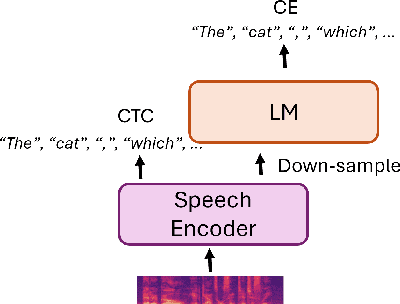
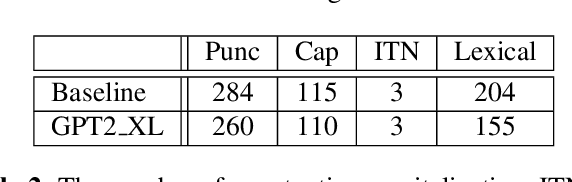
Abstract:Most end-to-end (E2E) speech recognition models are composed of encoder and decoder blocks that perform acoustic and language modeling functions. Pretrained large language models (LLMs) have the potential to improve the performance of E2E ASR. However, integrating a pretrained language model into an E2E speech recognition model has shown limited benefits due to the mismatches between text-based LLMs and those used in E2E ASR. In this paper, we explore an alternative approach by adapting a pretrained LLMs to speech. Our experiments on fully-formatted E2E ASR transcription tasks across various domains demonstrate that our approach can effectively leverage the strengths of pretrained LLMs to produce more readable ASR transcriptions. Our model, which is based on the pretrained large language models with either an encoder-decoder or decoder-only structure, surpasses strong ASR models such as Whisper, in terms of recognition error rate, considering formats like punctuation and capitalization as well.
FastCorrect: Fast Error Correction with Edit Alignment for Automatic Speech Recognition
Jun 03, 2021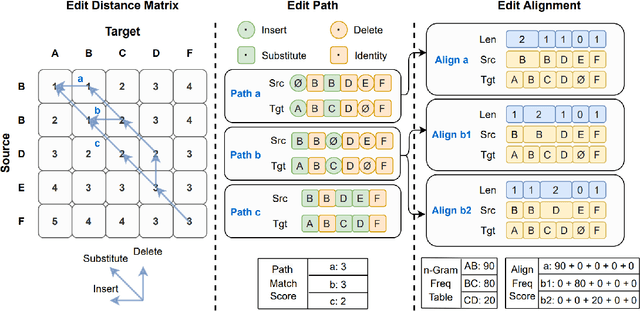
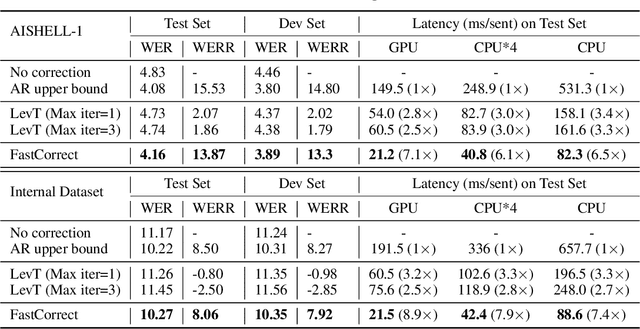
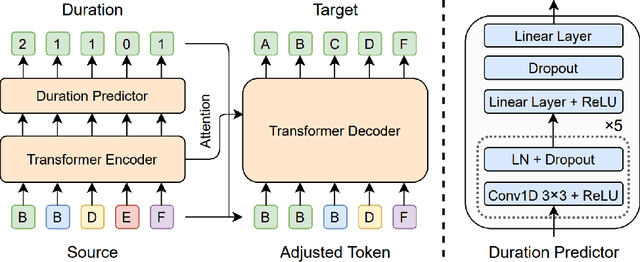
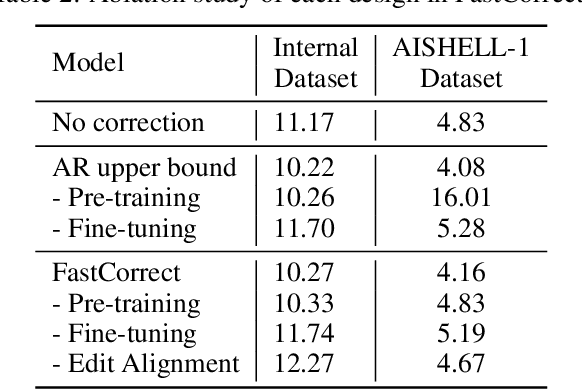
Abstract:Error correction techniques have been used to refine the output sentences from automatic speech recognition (ASR) models and achieve a lower word error rate (WER) than original ASR outputs. Previous works usually use a sequence-to-sequence model to correct an ASR output sentence autoregressively, which causes large latency and cannot be deployed in online ASR services. A straightforward solution to reduce latency, inspired by non-autoregressive (NAR) neural machine translation, is to use an NAR sequence generation model for ASR error correction, which, however, comes at the cost of significantly increased ASR error rate. In this paper, observing distinctive error patterns and correction operations (i.e., insertion, deletion, and substitution) in ASR, we propose FastCorrect, a novel NAR error correction model based on edit alignment. In training, FastCorrect aligns each source token from an ASR output sentence to the target tokens from the corresponding ground-truth sentence based on the edit distance between the source and target sentences, and extracts the number of target tokens corresponding to each source token during edition/correction, which is then used to train a length predictor and to adjust the source tokens to match the length of the target sentence for parallel generation. In inference, the token number predicted by the length predictor is used to adjust the source tokens for target sequence generation. Experiments on the public AISHELL-1 dataset and an internal industrial-scale ASR dataset show the effectiveness of FastCorrect for ASR error correction: 1) it speeds up the inference by 6-9 times and maintains the accuracy (8-14% WER reduction) compared with the autoregressive correction model; and 2) it outperforms the popular NAR models adopted in neural machine translation and text edition by a large margin.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge