Dylan Sun
Deformable Beta Splatting
Jan 27, 2025



Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has advanced radiance field reconstruction by enabling real-time rendering. However, its reliance on Gaussian kernels for geometry and low-order Spherical Harmonics (SH) for color encoding limits its ability to capture complex geometries and diverse colors. We introduce Deformable Beta Splatting (DBS), a deformable and compact approach that enhances both geometry and color representation. DBS replaces Gaussian kernels with deformable Beta Kernels, which offer bounded support and adaptive frequency control to capture fine geometric details with higher fidelity while achieving better memory efficiency. In addition, we extended the Beta Kernel to color encoding, which facilitates improved representation of diffuse and specular components, yielding superior results compared to SH-based methods. Furthermore, Unlike prior densification techniques that depend on Gaussian properties, we mathematically prove that adjusting regularized opacity alone ensures distribution-preserved Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC), independent of the splatting kernel type. Experimental results demonstrate that DBS achieves state-of-the-art visual quality while utilizing only 45% of the parameters and rendering 1.5x faster than 3DGS-based methods. Notably, for the first time, splatting-based methods outperform state-of-the-art Neural Radiance Fields, highlighting the superior performance and efficiency of DBS for real-time radiance field rendering.
ViT-Lens-2: Gateway to Omni-modal Intelligence
Nov 27, 2023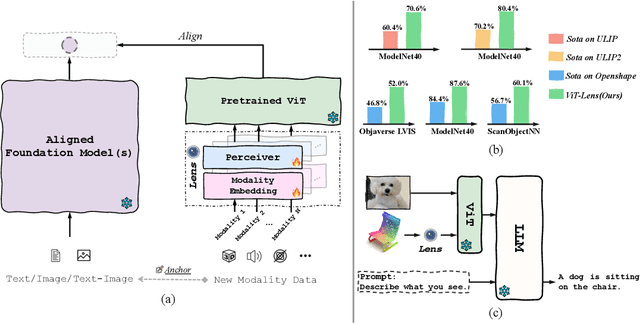
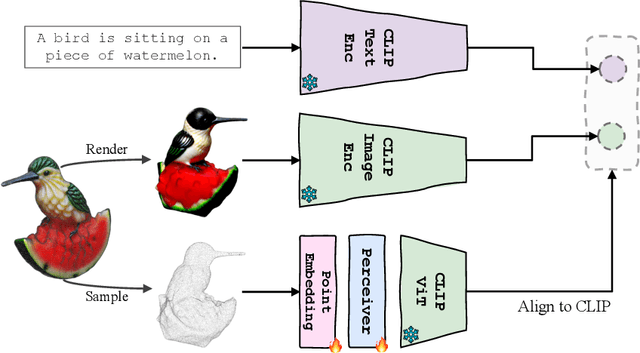
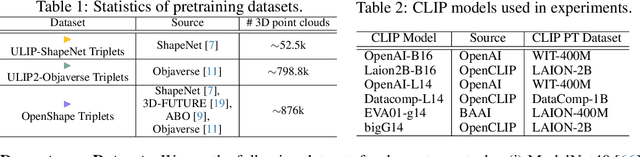
Abstract:Aiming to advance AI agents, large foundation models significantly improve reasoning and instruction execution, yet the current focus on vision and language neglects the potential of perceiving diverse modalities in open-world environments. However, the success of data-driven vision and language models is costly or even infeasible to be reproduced for rare modalities. In this paper, we present ViT-Lens-2 that facilitates efficient omni-modal representation learning by perceiving novel modalities with a pretrained ViT and aligning them to a pre-defined space. Specifically, the modality-specific lens is tuned to project any-modal signals to an intermediate embedding space, which are then processed by a strong ViT with pre-trained visual knowledge. The encoded representations are optimized toward aligning with the modal-independent space, pre-defined by off-the-shelf foundation models. ViT-Lens-2 provides a unified solution for representation learning of increasing modalities with two appealing advantages: (i) Unlocking the great potential of pretrained ViTs to novel modalities effectively with efficient data regime; (ii) Enabling emergent downstream capabilities through modality alignment and shared ViT parameters. We tailor ViT-Lens-2 to learn representations for 3D point cloud, depth, audio, tactile and EEG, and set new state-of-the-art results across various understanding tasks, such as zero-shot classification. By seamlessly integrating ViT-Lens-2 into Multimodal Foundation Models, we enable Any-modality to Text and Image Generation in a zero-shot manner. Code and models are available at https://github.com/TencentARC/ViT-Lens.
ViT-Lens: Towards Omni-modal Representations
Aug 20, 2023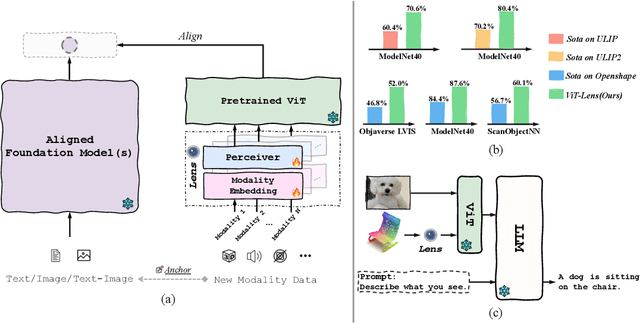
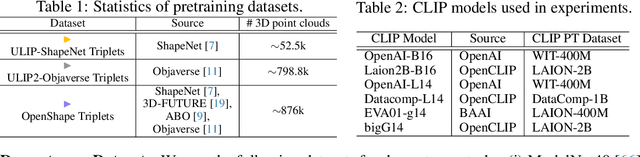
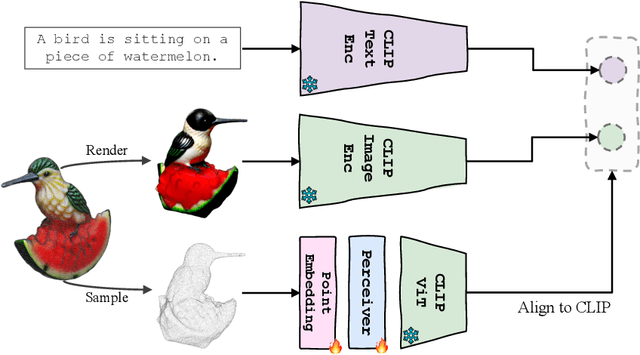
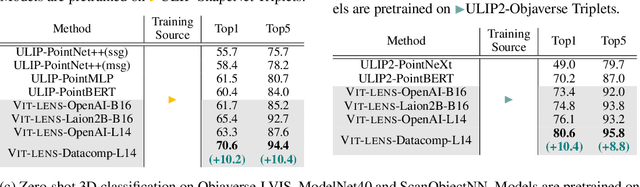
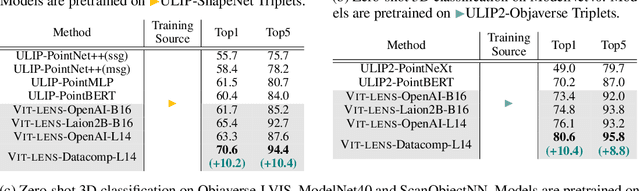
Abstract:Though the success of CLIP-based training recipes in vision-language models, their scalability to more modalities (e.g., 3D, audio, etc.) is limited to large-scale data, which is expensive or even inapplicable for rare modalities. In this paper, we present ViT-Lens that facilitates efficient omni-modal representation learning by perceiving novel modalities with a pretrained ViT and aligning to a pre-defined space. Specifically, the modality-specific lens is tuned to project multimodal signals to the shared embedding space, which are then processed by a strong ViT that carries pre-trained image knowledge. The encoded multimodal representations are optimized toward aligning with the modal-independent space, pre-defined by off-the-shelf foundation models. A well-trained lens with a ViT backbone has the potential to serve as one of these foundation models, supervising the learning of subsequent modalities. ViT-Lens provides a unified solution for representation learning of increasing modalities with two appealing benefits: (i) Exploiting the pretrained ViT across tasks and domains effectively with efficient data regime; (ii) Emergent downstream capabilities of novel modalities are demonstrated due to the modality alignment space. We evaluate ViT-Lens in the context of 3D as an initial verification. In zero-shot 3D classification, ViT-Lens achieves substantial improvements over previous state-of-the-art, showing 52.0% accuracy on Objaverse-LVIS, 87.4% on ModelNet40, and 60.6% on ScanObjectNN. Furthermore, we enable zero-shot 3D question-answering by simply integrating the trained 3D lens into the InstructBLIP model without any adaptation. We will release the results of ViT-Lens on more modalities in the near future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge