Dongseok Lee
Toward a Robust and Generalizable Metamaterial Foundation Model
Jul 03, 2025Abstract:Advances in material functionalities drive innovations across various fields, where metamaterials-defined by structure rather than composition-are leading the way. Despite the rise of artificial intelligence (AI)-driven design strategies, their impact is limited by task-specific retraining, poor out-of-distribution(OOD) generalization, and the need for separate models for forward and inverse design. To address these limitations, we introduce the Metamaterial Foundation Model (MetaFO), a Bayesian transformer-based foundation model inspired by large language models. MetaFO learns the underlying mechanics of metamaterials, enabling probabilistic, zero-shot predictions across diverse, unseen combinations of material properties and structural responses. It also excels in nonlinear inverse design, even under OOD conditions. By treating metamaterials as an operator that maps material properties to structural responses, MetaFO uncovers intricate structure-property relationships and significantly expands the design space. This scalable and generalizable framework marks a paradigm shift in AI-driven metamaterial discovery, paving the way for next-generation innovations.
MaD-Scientist: AI-based Scientist solving Convection-Diffusion-Reaction Equations Using Massive PINN-Based Prior Data
Oct 09, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs), like ChatGPT, have shown that even trained with noisy prior data, they can generalize effectively to new tasks through in-context learning (ICL) and pre-training techniques. Motivated by this, we explore whether a similar approach can be applied to scientific foundation models (SFMs). Our methodology is structured as follows: (i) we collect low-cost physics-informed neural network (PINN)-based approximated prior data in the form of solutions to partial differential equations (PDEs) constructed through an arbitrary linear combination of mathematical dictionaries; (ii) we utilize Transformer architectures with self and cross-attention mechanisms to predict PDE solutions without knowledge of the governing equations in a zero-shot setting; (iii) we provide experimental evidence on the one-dimensional convection-diffusion-reaction equation, which demonstrate that pre-training remains robust even with approximated prior data, with only marginal impacts on test accuracy. Notably, this finding opens the path to pre-training SFMs with realistic, low-cost data instead of (or in conjunction with) numerical high-cost data. These results support the conjecture that SFMs can improve in a manner similar to LLMs, where fully cleaning the vast set of sentences crawled from the Internet is nearly impossible.
Cooperative Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Framework for Scalping Trading
Mar 31, 2019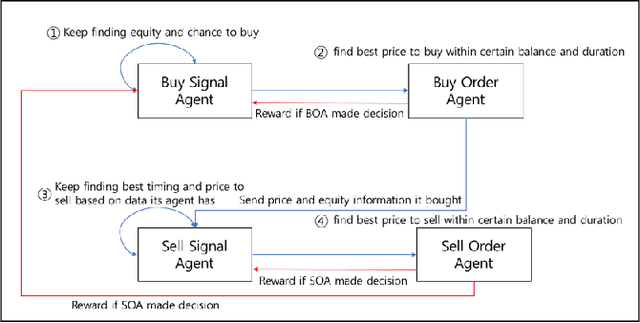
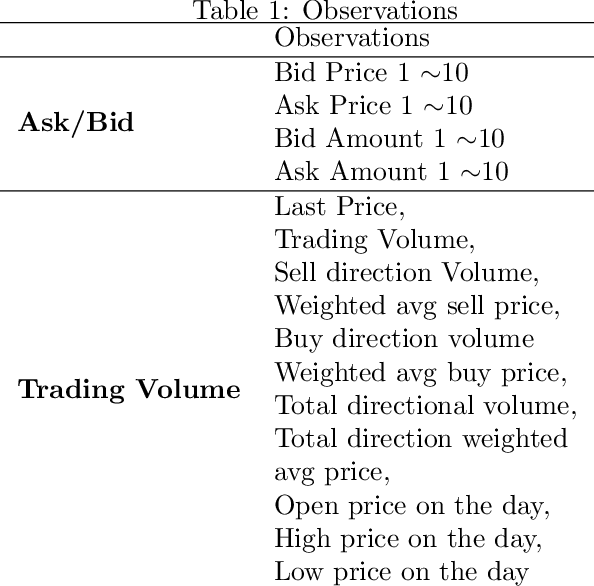

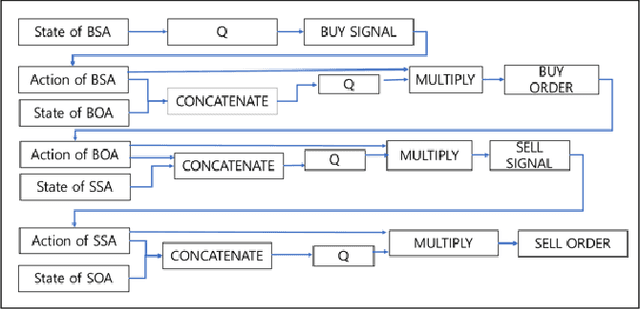
Abstract:We explore deep Reinforcement Learning(RL) algorithms for scalping trading and knew that there is no appropriate trading gym and agent examples. Thus we propose gym and agent like Open AI gym in finance. Not only that, we introduce new RL framework based on our hybrid algorithm which leverages between supervised learning and RL algorithm and uses meaningful observations such order book and settlement data from experience watching scalpers trading. That is very crucial information for traders behavior to be decided. To feed these data into our model, we use spatio-temporal convolution layer, called Conv3D for order book data and temporal CNN, called Conv1D for settlement data. Those are preprocessed by episode filter we developed. Agent consists of four sub agents divided to clarify their own goal to make best decision. Also, we adopted value and policy based algorithm to our framework. With these features, we could make agent mimic scalpers as much as possible. In many fields, RL algorithm has already begun to transcend human capabilities in many domains. This approach could be a starting point to beat human in the financial stock market, too and be a good reference for anyone who wants to design RL algorithm in real world domain. Finally, weexperiment our framework and gave you experiment progress.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge