Dimitrina Zlatkova
A Neighbourhood Framework for Resource-Lean Content Flagging
Mar 31, 2021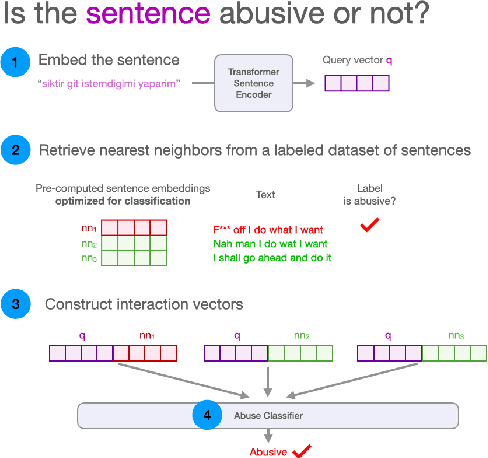
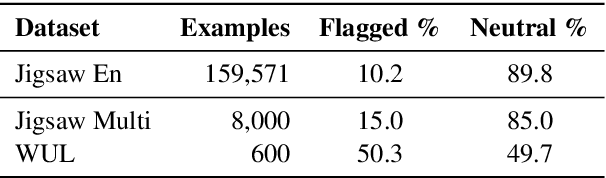
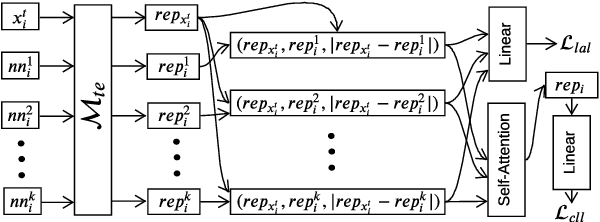
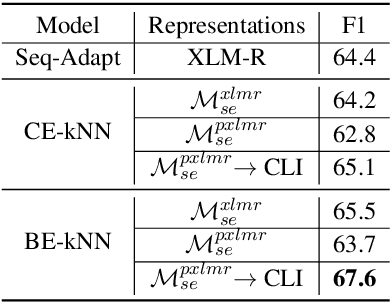
Abstract:We propose a novel interpretable framework for cross-lingual content flagging, which significantly outperforms prior work both in terms of predictive performance and average inference time. The framework is based on a nearest-neighbour architecture and is interpretable by design. Moreover, it can easily adapt to new instances without the need to retrain it from scratch. Unlike prior work, (i) we encode not only the texts, but also the labels in the neighbourhood space (which yields better accuracy), and (ii) we use a bi-encoder instead of a cross-encoder (which saves computation time). Our evaluation results on ten different datasets for abusive language detection in eight languages shows sizable improvements over the state of the art, as well as a speed-up at inference time.
Detecting Abusive Language on Online Platforms: A Critical Analysis
Feb 27, 2021
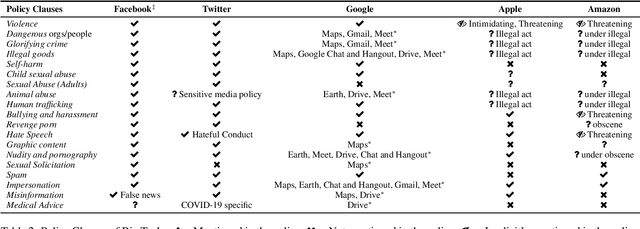
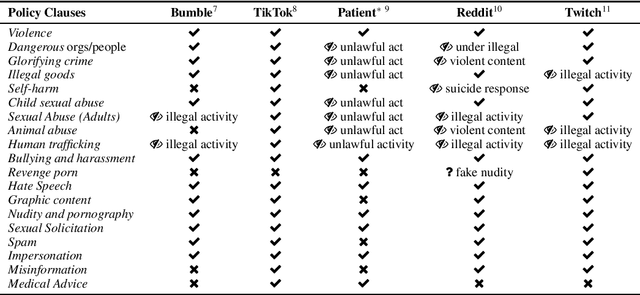

Abstract:Abusive language on online platforms is a major societal problem, often leading to important societal problems such as the marginalisation of underrepresented minorities. There are many different forms of abusive language such as hate speech, profanity, and cyber-bullying, and online platforms seek to moderate it in order to limit societal harm, to comply with legislation, and to create a more inclusive environment for their users. Within the field of Natural Language Processing, researchers have developed different methods for automatically detecting abusive language, often focusing on specific subproblems or on narrow communities, as what is considered abusive language very much differs by context. We argue that there is currently a dichotomy between what types of abusive language online platforms seek to curb, and what research efforts there are to automatically detect abusive language. We thus survey existing methods as well as content moderation policies by online platforms in this light, and we suggest directions for future work.
EXAMS: A Multi-Subject High School Examinations Dataset for Cross-Lingual and Multilingual Question Answering
Nov 05, 2020



Abstract:We propose EXAMS -- a new benchmark dataset for cross-lingual and multilingual question answering for high school examinations. We collected more than 24,000 high-quality high school exam questions in 16 languages, covering 8 language families and 24 school subjects from Natural Sciences and Social Sciences, among others. EXAMS offers a fine-grained evaluation framework across multiple languages and subjects, which allows precise analysis and comparison of various models. We perform various experiments with existing top-performing multilingual pre-trained models and we show that EXAMS offers multiple challenges that require multilingual knowledge and reasoning in multiple domains. We hope that EXAMS will enable researchers to explore challenging reasoning and knowledge transfer methods and pre-trained models for school question answering in various languages which was not possible before. The data, code, pre-trained models, and evaluation are available at https://github.com/mhardalov/exams-qa.
Fact-Checking Meets Fauxtography: Verifying Claims About Images
Aug 30, 2019



Abstract:The recent explosion of false claims in social media and on the Web in general has given rise to a lot of manual fact-checking initiatives. Unfortunately, the number of claims that need to be fact-checked is several orders of magnitude larger than what humans can handle manually. Thus, there has been a lot of research aiming at automating the process. Interestingly, previous work has largely ignored the growing number of claims about images. This is despite the fact that visual imagery is more influential than text and naturally appears alongside fake news. Here we aim at bridging this gap. In particular, we create a new dataset for this problem, and we explore a variety of features modeling the claim, the image, and the relationship between the claim and the image. The evaluation results show sizable improvements over the baseline. We release our dataset, hoping to enable further research on fact-checking claims about images.
* Claims about Images; Fauxtography; Fact-Checking; Veracity; Fake News
Recursive Style Breach Detection with Multifaceted Ensemble Learning
Jun 17, 2019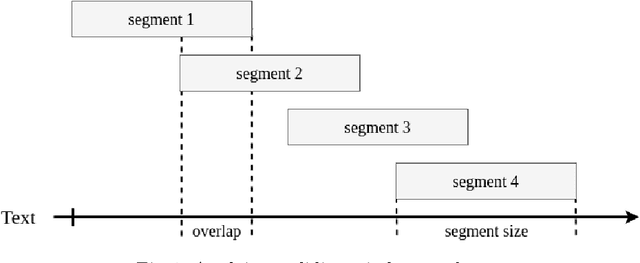

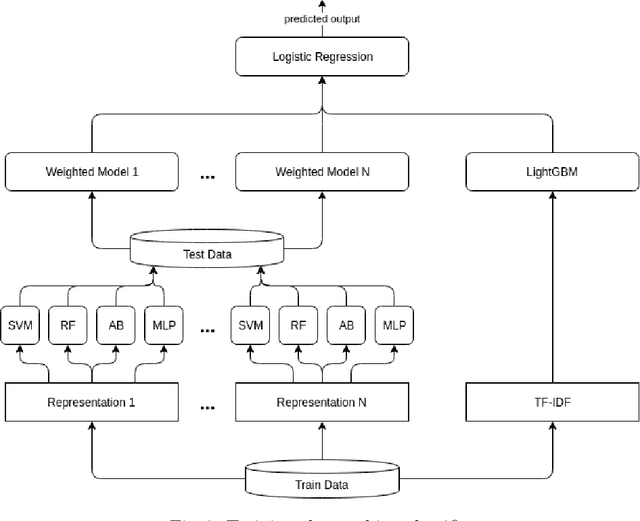
Abstract:We present a supervised approach for style change detection, which aims at predicting whether there are changes in the style in a given text document, as well as at finding the exact positions where such changes occur. In particular, we combine a TF.IDF representation of the document with features specifically engineered for the task, and we make predictions via an ensemble of diverse classifiers including SVM, Random Forest, AdaBoost, MLP, and LightGBM. Whenever the model detects that style change is present, we apply it recursively, looking to find the specific positions of the change. Our approach powered the winning system for the PAN@CLEF 2018 task on Style Change Detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge