Ameya Bhatawdekar
Natural Language Commanding via Program Synthesis
Jun 06, 2023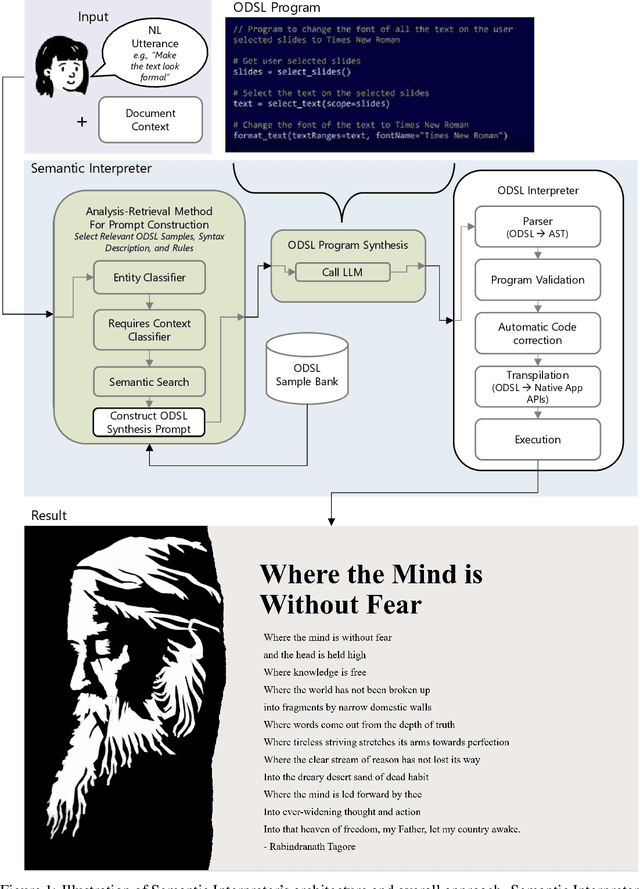

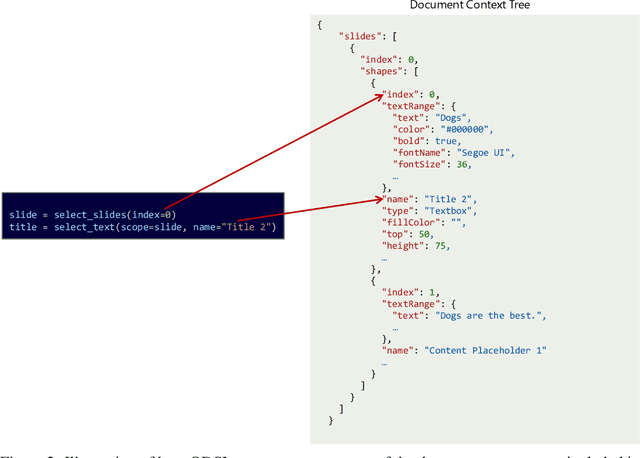

Abstract:We present Semantic Interpreter, a natural language-friendly AI system for productivity software such as Microsoft Office that leverages large language models (LLMs) to execute user intent across application features. While LLMs are excellent at understanding user intent expressed as natural language, they are not sufficient for fulfilling application-specific user intent that requires more than text-to-text transformations. We therefore introduce the Office Domain Specific Language (ODSL), a concise, high-level language specialized for performing actions in and interacting with entities in Office applications. Semantic Interpreter leverages an Analysis-Retrieval prompt construction method with LLMs for program synthesis, translating natural language user utterances to ODSL programs that can be transpiled to application APIs and then executed. We focus our discussion primarily on a research exploration for Microsoft PowerPoint.
Detecting Abusive Language on Online Platforms: A Critical Analysis
Feb 27, 2021
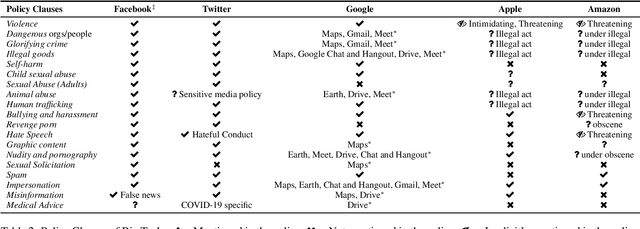
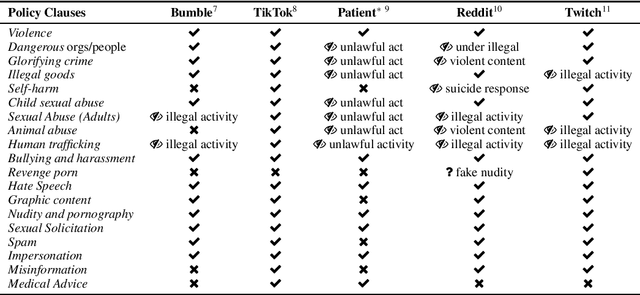

Abstract:Abusive language on online platforms is a major societal problem, often leading to important societal problems such as the marginalisation of underrepresented minorities. There are many different forms of abusive language such as hate speech, profanity, and cyber-bullying, and online platforms seek to moderate it in order to limit societal harm, to comply with legislation, and to create a more inclusive environment for their users. Within the field of Natural Language Processing, researchers have developed different methods for automatically detecting abusive language, often focusing on specific subproblems or on narrow communities, as what is considered abusive language very much differs by context. We argue that there is currently a dichotomy between what types of abusive language online platforms seek to curb, and what research efforts there are to automatically detect abusive language. We thus survey existing methods as well as content moderation policies by online platforms in this light, and we suggest directions for future work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge