Deeni Fatiha
Gemini: A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models
Dec 19, 2023Abstract:This report introduces a new family of multimodal models, Gemini, that exhibit remarkable capabilities across image, audio, video, and text understanding. The Gemini family consists of Ultra, Pro, and Nano sizes, suitable for applications ranging from complex reasoning tasks to on-device memory-constrained use-cases. Evaluation on a broad range of benchmarks shows that our most-capable Gemini Ultra model advances the state of the art in 30 of 32 of these benchmarks - notably being the first model to achieve human-expert performance on the well-studied exam benchmark MMLU, and improving the state of the art in every one of the 20 multimodal benchmarks we examined. We believe that the new capabilities of Gemini models in cross-modal reasoning and language understanding will enable a wide variety of use cases and we discuss our approach toward deploying them responsibly to users.
Controlling Commercial Cooling Systems Using Reinforcement Learning
Nov 11, 2022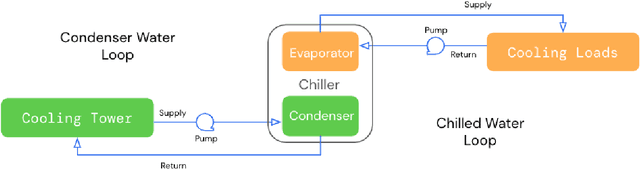
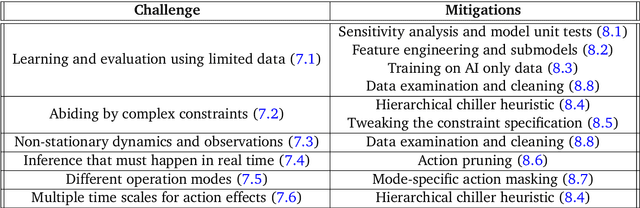
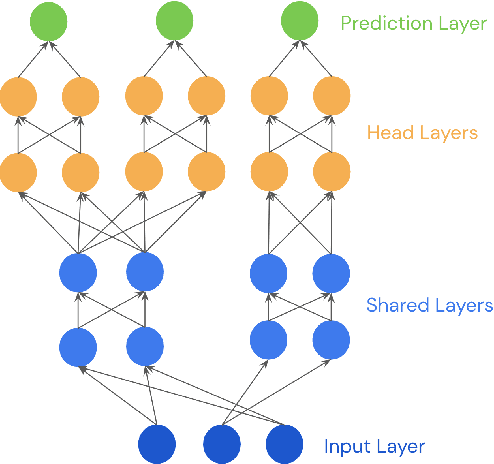
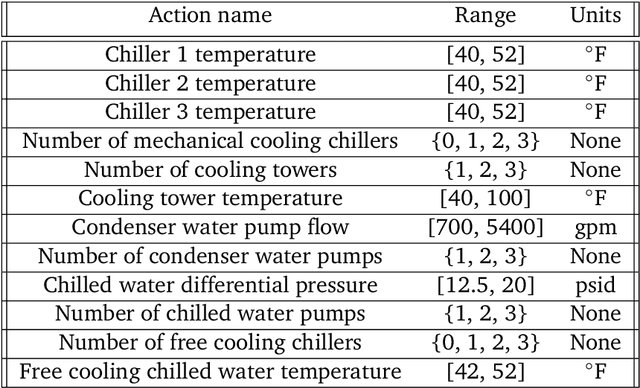
Abstract:This paper is a technical overview of DeepMind and Google's recent work on reinforcement learning for controlling commercial cooling systems. Building on expertise that began with cooling Google's data centers more efficiently, we recently conducted live experiments on two real-world facilities in partnership with Trane Technologies, a building management system provider. These live experiments had a variety of challenges in areas such as evaluation, learning from offline data, and constraint satisfaction. Our paper describes these challenges in the hope that awareness of them will benefit future applied RL work. We also describe the way we adapted our RL system to deal with these challenges, resulting in energy savings of approximately 9% and 13% respectively at the two live experiment sites.
Studying oppressive cityscapes of Bangladesh
Dec 10, 2018



Abstract:In a densely populated city like Dhaka (Bangladesh), a growing number of high-rise buildings is an inevitable reality. However, they pose mental health risks for citizens in terms of detachment from natural light, sky view, greenery, and environmental landscapes. The housing economy and rent structure in different areas may or may not take account of such environmental factors. In this paper, we build a computer vision based pipeline to study factors like sky visibility, greenery in the sidewalks, and dominant colors present in streets from a pedestrian's perspective. We show that people in lower economy classes may suffer from lower sky visibility, whereas people in higher economy classes may suffer from lack of greenery in their environment, both of which could be possibly addressed by implementing rent restructuring schemes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge