Declan P O'Regan
DeepMesh: Mesh-based Cardiac Motion Tracking using Deep Learning
Sep 25, 2023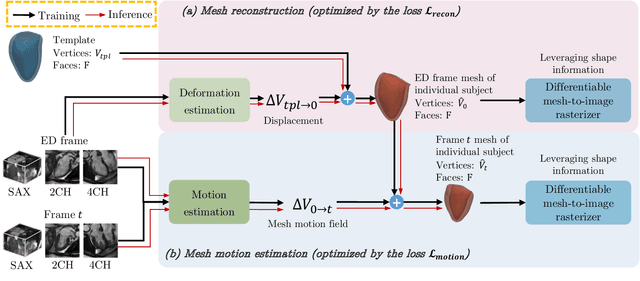
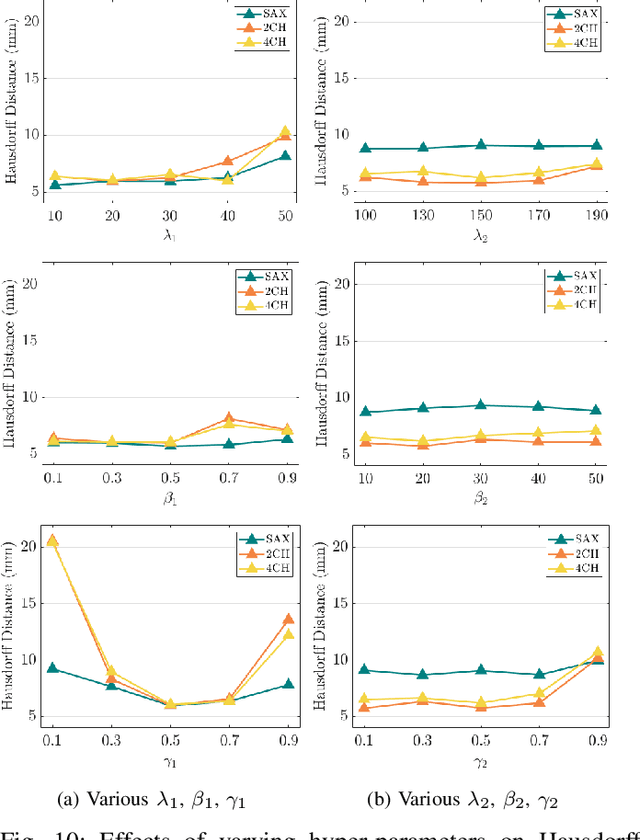
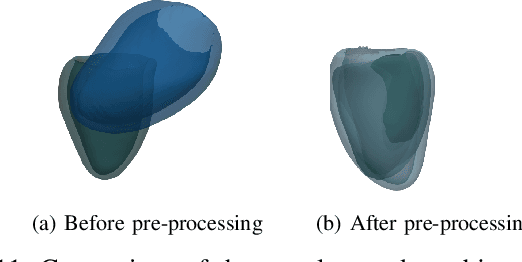
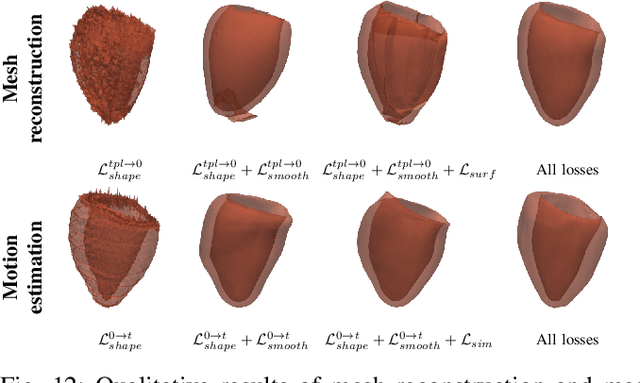
Abstract:3D motion estimation from cine cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) images is important for the assessment of cardiac function and the diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases. Current state-of-the art methods focus on estimating dense pixel-/voxel-wise motion fields in image space, which ignores the fact that motion estimation is only relevant and useful within the anatomical objects of interest, e.g., the heart. In this work, we model the heart as a 3D mesh consisting of epi- and endocardial surfaces. We propose a novel learning framework, DeepMesh, which propagates a template heart mesh to a subject space and estimates the 3D motion of the heart mesh from CMR images for individual subjects. In DeepMesh, the heart mesh of the end-diastolic frame of an individual subject is first reconstructed from the template mesh. Mesh-based 3D motion fields with respect to the end-diastolic frame are then estimated from 2D short- and long-axis CMR images. By developing a differentiable mesh-to-image rasterizer, DeepMesh is able to leverage 2D shape information from multiple anatomical views for 3D mesh reconstruction and mesh motion estimation. The proposed method estimates vertex-wise displacement and thus maintains vertex correspondences between time frames, which is important for the quantitative assessment of cardiac function across different subjects and populations. We evaluate DeepMesh on CMR images acquired from the UK Biobank. We focus on 3D motion estimation of the left ventricle in this work. Experimental results show that the proposed method quantitatively and qualitatively outperforms other image-based and mesh-based cardiac motion tracking methods.
Mesh-based 3D Motion Tracking in Cardiac MRI using Deep Learning
Sep 05, 2022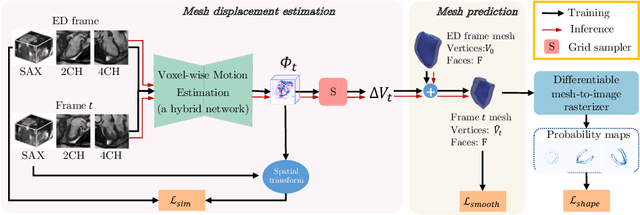
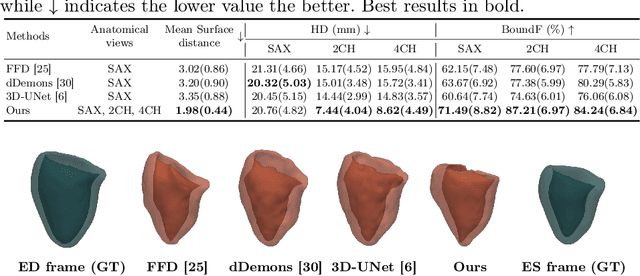
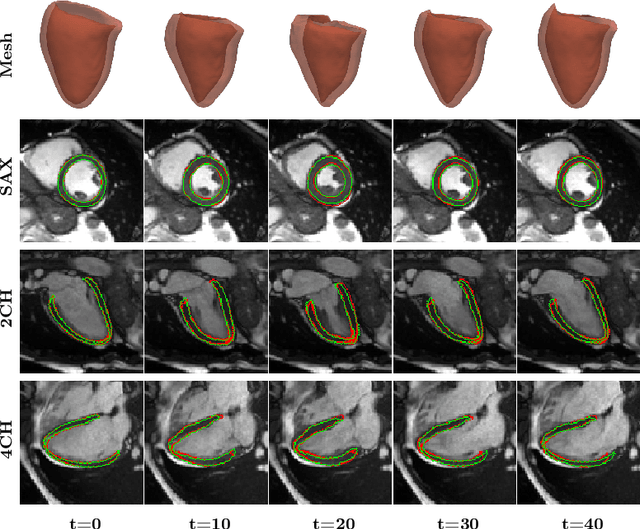

Abstract:3D motion estimation from cine cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) images is important for the assessment of cardiac function and diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases. Most of the previous methods focus on estimating pixel-/voxel-wise motion fields in the full image space, which ignore the fact that motion estimation is mainly relevant and useful within the object of interest, e.g., the heart. In this work, we model the heart as a 3D geometric mesh and propose a novel deep learning-based method that can estimate 3D motion of the heart mesh from 2D short- and long-axis CMR images. By developing a differentiable mesh-to-image rasterizer, the method is able to leverage the anatomical shape information from 2D multi-view CMR images for 3D motion estimation. The differentiability of the rasterizer enables us to train the method end-to-end. One advantage of the proposed method is that by tracking the motion of each vertex, it is able to keep the vertex correspondence of 3D meshes between time frames, which is important for quantitative assessment of the cardiac function on the mesh. We evaluate the proposed method on CMR images acquired from the UK Biobank study. Experimental results show that the proposed method quantitatively and qualitatively outperforms both conventional and learning-based cardiac motion tracking methods.
MulViMotion: Shape-aware 3D Myocardial Motion Tracking from Multi-View Cardiac MRI
Jul 29, 2022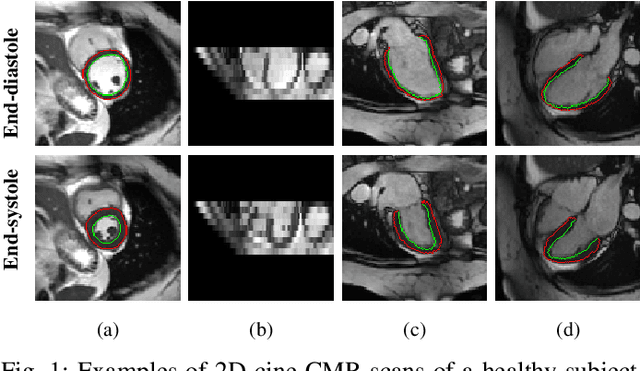
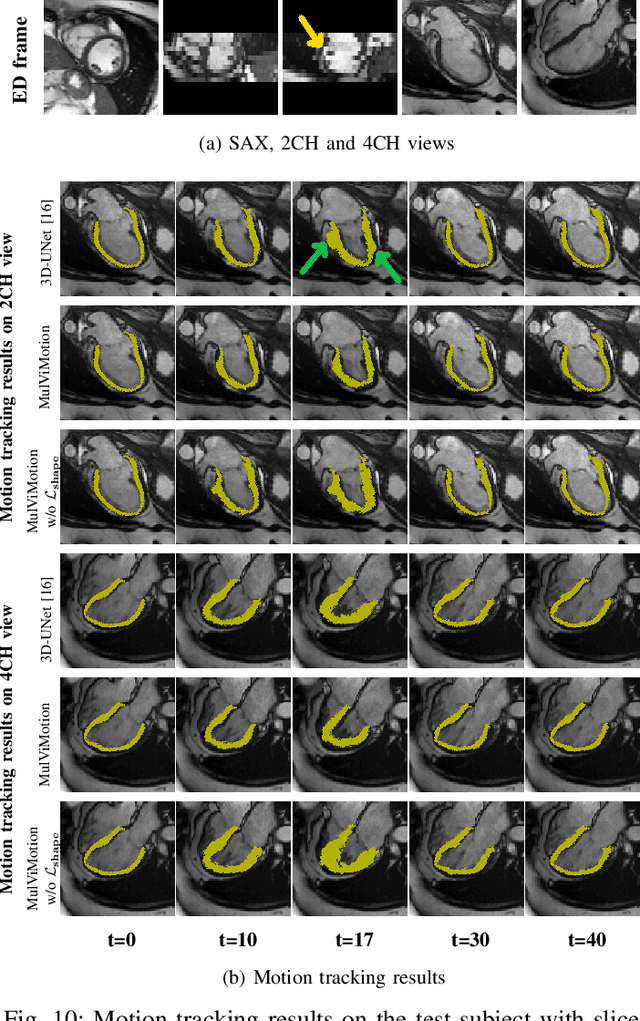
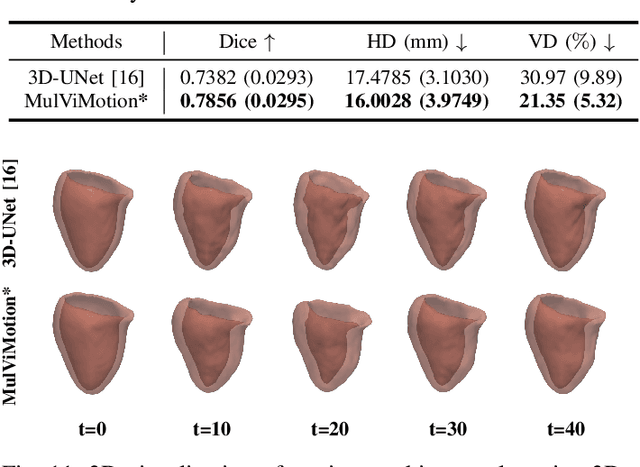
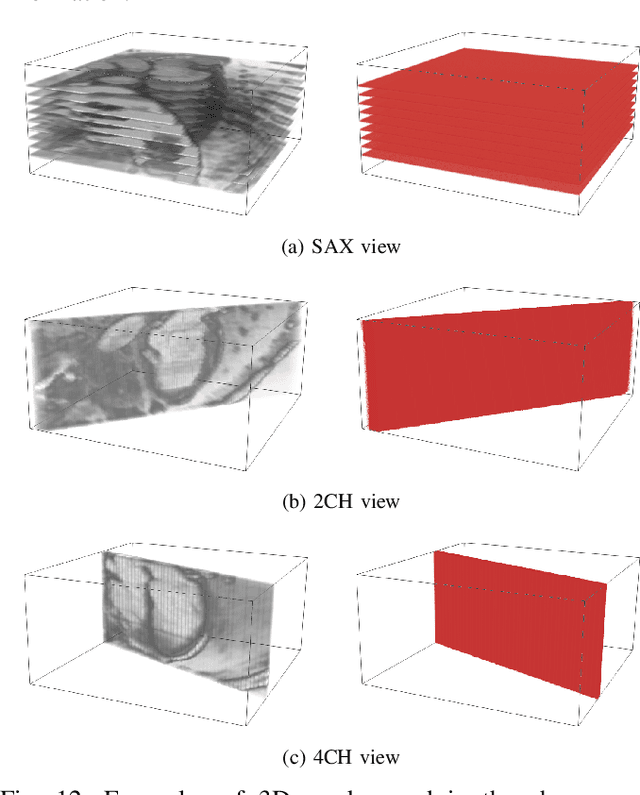
Abstract:Recovering the 3D motion of the heart from cine cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging enables the assessment of regional myocardial function and is important for understanding and analyzing cardiovascular disease. However, 3D cardiac motion estimation is challenging because the acquired cine CMR images are usually 2D slices which limit the accurate estimation of through-plane motion. To address this problem, we propose a novel multi-view motion estimation network (MulViMotion), which integrates 2D cine CMR images acquired in short-axis and long-axis planes to learn a consistent 3D motion field of the heart. In the proposed method, a hybrid 2D/3D network is built to generate dense 3D motion fields by learning fused representations from multi-view images. To ensure that the motion estimation is consistent in 3D, a shape regularization module is introduced during training, where shape information from multi-view images is exploited to provide weak supervision to 3D motion estimation. We extensively evaluate the proposed method on 2D cine CMR images from 580 subjects of the UK Biobank study for 3D motion tracking of the left ventricular myocardium. Experimental results show that the proposed method quantitatively and qualitatively outperforms competing methods.
Joint analysis of clinical risk factors and 4D cardiac motion for survival prediction using a hybrid deep learning network
Oct 07, 2019



Abstract:In this work, a novel approach is proposed for joint analysis of high dimensional time-resolved cardiac motion features obtained from segmented cardiac MRI and low dimensional clinical risk factors to improve survival prediction in heart failure. Different methods are evaluated to find the optimal way to insert conventional covariates into deep prediction networks. Correlation analysis between autoencoder latent codes and covariate features is used to examine how these predictors interact. We believe that similar approaches could also be used to introduce knowledge of genetic variants to such survival networks to improve outcome prediction by jointly analysing cardiac motion traits with inheritable risk factors.
* 4 pages, 2 figures
VS-Net: Variable splitting network for accelerated parallel MRI reconstruction
Jul 19, 2019



Abstract:In this work, we propose a deep learning approach for parallel magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) reconstruction, termed a variable splitting network (VS-Net), for an efficient, high-quality reconstruction of undersampled multi-coil MR data. We formulate the generalized parallel compressed sensing reconstruction as an energy minimization problem, for which a variable splitting optimization method is derived. Based on this formulation we propose a novel, end-to-end trainable deep neural network architecture by unrolling the resulting iterative process of such variable splitting scheme. VS-Net is evaluated on complex valued multi-coil knee images for 4-fold and 6-fold acceleration factors. We show that VS-Net outperforms state-of-the-art deep learning reconstruction algorithms, in terms of reconstruction accuracy and perceptual quality. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/j-duan/VS-Net.
Automatic 3D bi-ventricular segmentation of cardiac images by a shape-constrained multi-task deep learning approach
Aug 28, 2018



Abstract:Deep learning approaches have achieved state-of-the-art performance in cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) image segmentation. However, most approaches have focused on learning image intensity features for segmentation, whereas the incorporation of anatomical shape priors has received less attention. In this paper, we combine a multi-task deep learning approach with atlas propagation to develop a shape-constrained bi-ventricular segmentation pipeline for short-axis CMR volumetric images. The pipeline first employs a fully convolutional network (FCN) that learns segmentation and landmark localisation tasks simultaneously. The architecture of the proposed FCN uses a 2.5D representation, thus combining the computational advantage of 2D FCNs networks and the capability of addressing 3D spatial consistency without compromising segmentation accuracy. Moreover, the refinement step is designed to explicitly enforce a shape constraint and improve segmentation quality. This step is effective for overcoming image artefacts (e.g. due to different breath-hold positions and large slice thickness), which preclude the creation of anatomically meaningful 3D cardiac shapes. The proposed pipeline is fully automated, due to network's ability to infer landmarks, which are then used downstream in the pipeline to initialise atlas propagation. We validate the pipeline on 1831 healthy subjects and 649 subjects with pulmonary hypertension. Extensive numerical experiments on the two datasets demonstrate that our proposed method is robust and capable of producing accurate, high-resolution and anatomically smooth bi-ventricular 3D models, despite the artefacts in input CMR volumes.
Deep nested level sets: Fully automated segmentation of cardiac MR images in patients with pulmonary hypertension
Jul 27, 2018


Abstract:In this paper we introduce a novel and accurate optimisation method for segmentation of cardiac MR (CMR) images in patients with pulmonary hypertension (PH). The proposed method explicitly takes into account the image features learned from a deep neural network. To this end, we estimate simultaneous probability maps over region and edge locations in CMR images using a fully convolutional network. Due to the distinct morphology of the heart in patients with PH, these probability maps can then be incorporated in a single nested level set optimisation framework to achieve multi-region segmentation with high efficiency. The proposed method uses an automatic way for level set initialisation and thus the whole optimisation is fully automated. We demonstrate that the proposed deep nested level set (DNLS) method outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods for CMR segmentation in PH patients.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge