David Lowe
InvisMark: Invisible and Robust Watermarking for AI-generated Image Provenance
Nov 19, 2024
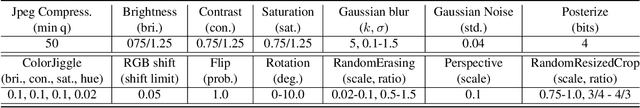


Abstract:The proliferation of AI-generated images has intensified the need for robust content authentication methods. We present InvisMark, a novel watermarking technique designed for high-resolution AI-generated images. Our approach leverages advanced neural network architectures and training strategies to embed imperceptible yet highly robust watermarks. InvisMark achieves state-of-the-art performance in imperceptibility (PSNR$\sim$51, SSIM $\sim$ 0.998) while maintaining over 97\% bit accuracy across various image manipulations. Notably, we demonstrate the successful encoding of 256-bit watermarks, significantly expanding payload capacity while preserving image quality. This enables the embedding of UUIDs with error correction codes, achieving near-perfect decoding success rates even under challenging image distortions. We also address potential vulnerabilities against advanced attacks and propose mitigation strategies. By combining high imperceptibility, extended payload capacity, and resilience to manipulations, InvisMark provides a robust foundation for ensuring media provenance in an era of increasingly sophisticated AI-generated content. Source code of this paper is available at: https://github.com/microsoft/InvisMark.
Topical Phrase Extraction from Clinical Reports by Incorporating both Local and Global Context
Nov 22, 2019



Abstract:Making sense of words often requires to simultaneously examine the surrounding context of a term as well as the global themes characterizing the overall corpus. Several topic models have already exploited word embeddings to recognize local context, however, it has been weakly combined with the global context during the topic inference. This paper proposes to extract topical phrases corroborating the word embedding information with the global context detected by Latent Semantic Analysis, and then combine them by means of the P\'{o}lya urn model. To highlight the effectiveness of this combined approach the model was assessed analyzing clinical reports, a challenging scenario characterized by technical jargon and a limited word statistics available. Results show it outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches in terms of both topic coherence and computational cost.
Analysis of Multibeam SONAR Data using Dissimilarity Representations
Feb 19, 2014


Abstract:This paper considers the problem of low-dimensional visualisation of very high dimensional information sources for the purpose of situation awareness in the maritime environment. In response to the requirement for human decision support aids to reduce information overload (and specifically, data amenable to inter-point relative similarity measures) appropriate to the below-water maritime domain, we are investigating a preliminary prototype topographic visualisation model. The focus of the current paper is on the mathematical problem of exploiting a relative dissimilarity representation of signals in a visual informatics mapping model, driven by real-world sonar systems. An independent source model is used to analyse the sonar beams from which a simple probabilistic input model to represent uncertainty is mapped to a latent visualisation space where data uncertainty can be accommodated. The use of euclidean and non-euclidean measures are used and the motivation for future use of non-euclidean measures is made. Concepts are illustrated using a simulated 64 beam weak SNR dataset with realistic sonar targets.
Semantic Robot Vision Challenge: Current State and Future Directions
Aug 19, 2009Abstract:The Semantic Robot Vision Competition provided an excellent opportunity for our research lab to integrate our many ideas under one umbrella, inspiring both collaboration and new research. The task, visual search for an unknown object, is relevant to both the vision and robotics communities. Moreover, since the interplay of robotics and vision is sometimes ignored, the competition provides a venue to integrate two communities. In this paper, we outline a number of modifications to the competition to both improve the state-of-the-art and increase participation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge