David Hysom
Merlin: Enabling Machine Learning-Ready HPC Ensembles
Dec 05, 2019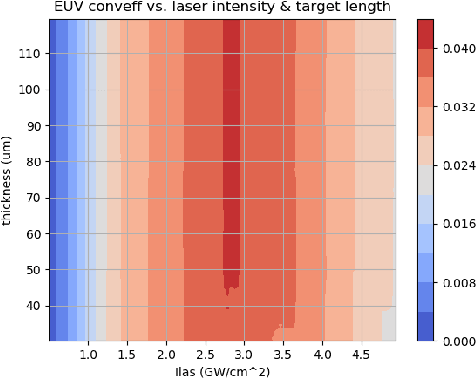
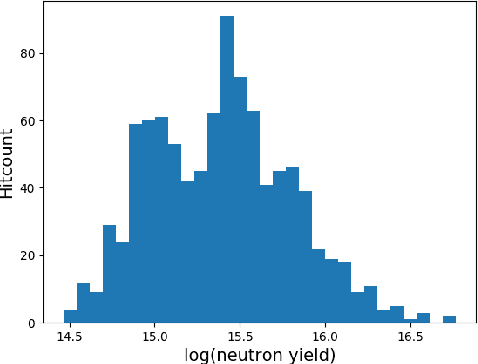
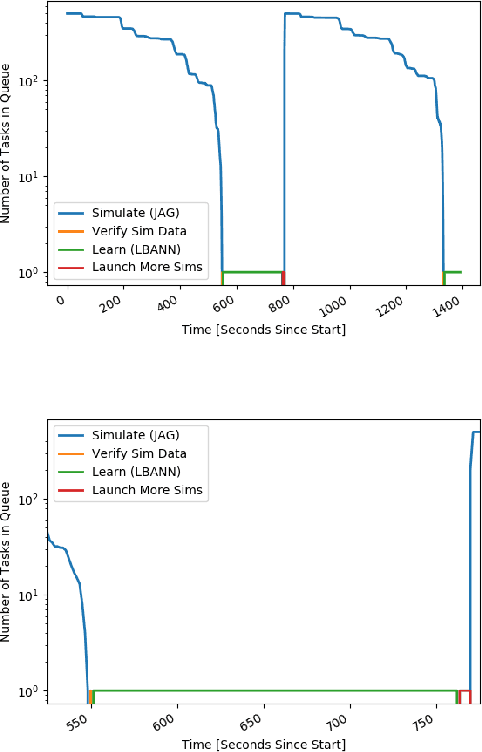
Abstract:With the growing complexity of computational and experimental facilities, many scientific researchers are turning to machine learning (ML) techniques to analyze large scale ensemble data. With complexities such as multi-component workflows, heterogeneous machine architectures, parallel file systems, and batch scheduling, care must be taken to facilitate this analysis in a high performance computing (HPC) environment. In this paper, we present Merlin, a workflow framework to enable large ML-friendly ensembles of scientific HPC simulations. By augmenting traditional HPC with distributed compute technologies, Merlin aims to lower the barrier for scientific subject matter experts to incorporate ML into their analysis. In addition to its design and some examples, we describe how Merlin was deployed on the Sierra Supercomputer at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory to create an unprecedented benchmark inertial confinement fusion dataset of approximately 100 million individual simulations and over 24 terabytes of multi-modal physics-based scalar, vector and hyperspectral image data.
Parallelizing Training of Deep Generative Models on Massive Scientific Datasets
Oct 05, 2019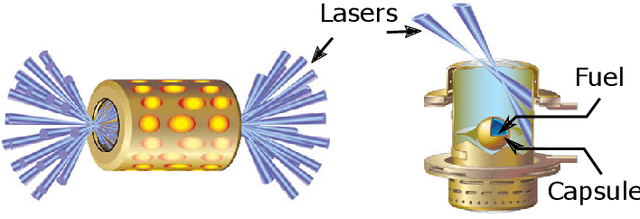
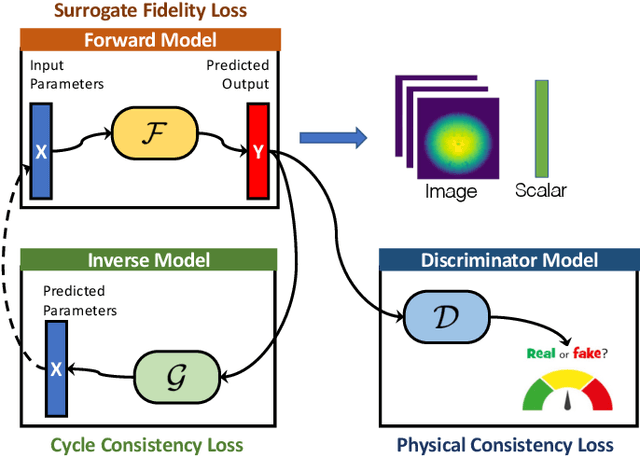
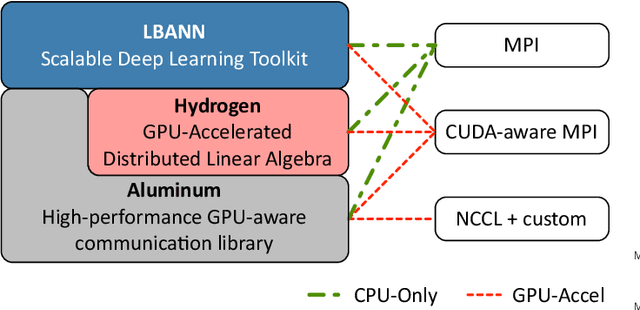
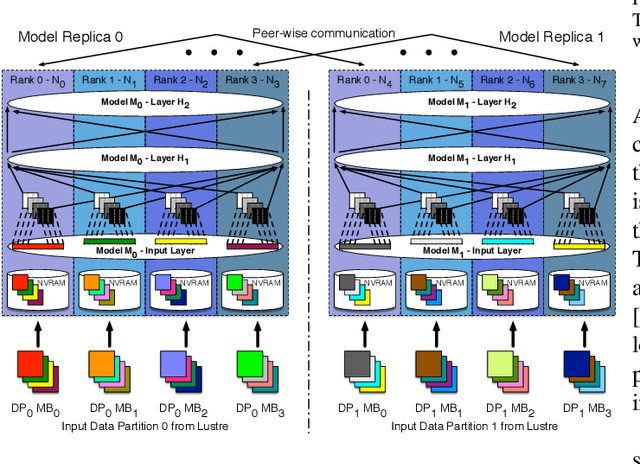
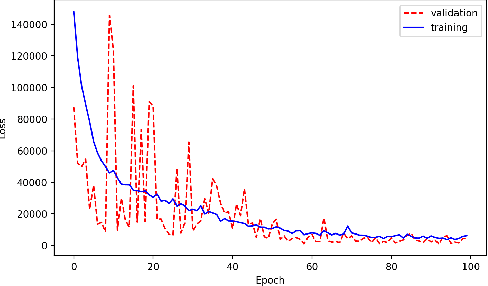
Abstract:Training deep neural networks on large scientific data is a challenging task that requires enormous compute power, especially if no pre-trained models exist to initialize the process. We present a novel tournament method to train traditional as well as generative adversarial networks built on LBANN, a scalable deep learning framework optimized for HPC systems. LBANN combines multiple levels of parallelism and exploits some of the worlds largest supercomputers. We demonstrate our framework by creating a complex predictive model based on multi-variate data from high-energy-density physics containing hundreds of millions of images and hundreds of millions of scalar values derived from tens of millions of simulations of inertial confinement fusion. Our approach combines an HPC workflow and extends LBANN with optimized data ingestion and the new tournament-style training algorithm to produce a scalable neural network architecture using a CORAL-class supercomputer. Experimental results show that 64 trainers (1024 GPUs) achieve a speedup of 70.2 over a single trainer (16 GPUs) baseline, and an effective 109% parallel efficiency.
Scalable Topological Data Analysis and Visualization for Evaluating Data-Driven Models in Scientific Applications
Jul 19, 2019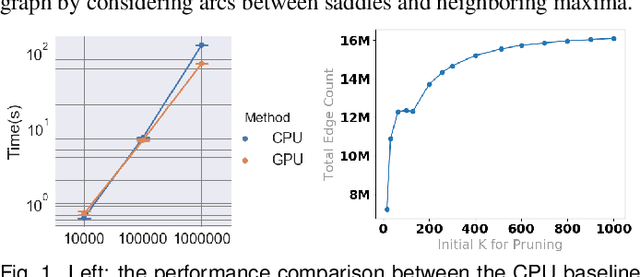
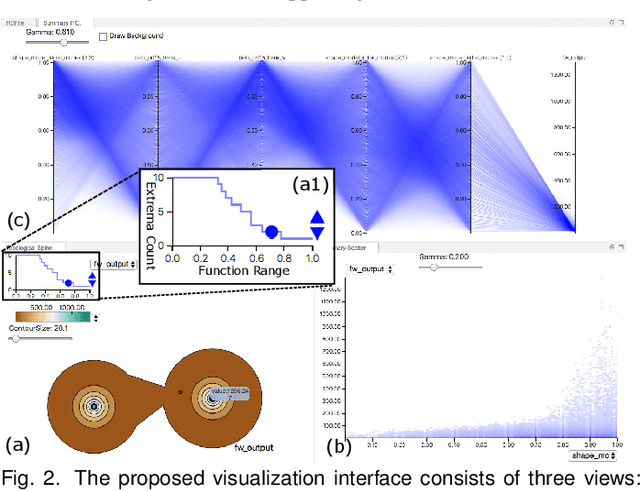
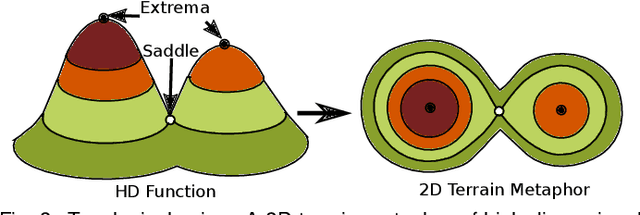
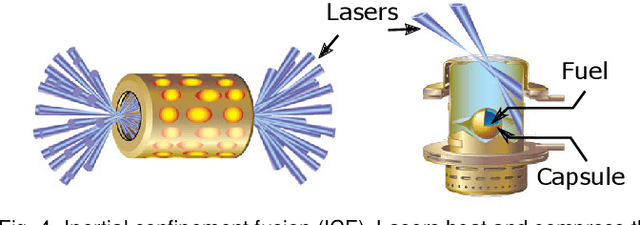
Abstract:With the rapid adoption of machine learning techniques for large-scale applications in science and engineering comes the convergence of two grand challenges in visualization. First, the utilization of black box models (e.g., deep neural networks) calls for advanced techniques in exploring and interpreting model behaviors. Second, the rapid growth in computing has produced enormous datasets that require techniques that can handle millions or more samples. Although some solutions to these interpretability challenges have been proposed, they typically do not scale beyond thousands of samples, nor do they provide the high-level intuition scientists are looking for. Here, we present the first scalable solution to explore and analyze high-dimensional functions often encountered in the scientific data analysis pipeline. By combining a new streaming neighborhood graph construction, the corresponding topology computation, and a novel data aggregation scheme, namely topology aware datacubes, we enable interactive exploration of both the topological and the geometric aspect of high-dimensional data. Following two use cases from high-energy-density (HED) physics and computational biology, we demonstrate how these capabilities have led to crucial new insights in both applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge