Daniel DeAlcala
Membership Inference Test: Auditing Training Data in Object Classification Models
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:In this research, we analyze the performance of Membership Inference Tests (MINT), focusing on determining whether given data were utilized during the training phase, specifically in the domain of object recognition. Within the area of object recognition, we propose and develop architectures tailored for MINT models. These architectures aim to optimize performance and efficiency in data utilization, offering a tailored solution to tackle the complexities inherent in the object recognition domain. We conducted experiments involving an object detection model, an embedding extractor, and a MINT module. These experiments were performed in three public databases, totaling over 174K images. The proposed architecture leverages convolutional layers to capture and model the activation patterns present in the data during the training process. Through our analysis, we are able to identify given data used for testing and training, achieving precision rates ranging between 70% and 80%, contingent upon the depth of the detection module layer chosen for input to the MINT module. Additionally, our studies entail an analysis of the factors influencing the MINT Module, delving into the contributing elements behind more transparent training processes.
Active Membership Inference Test (aMINT): Enhancing Model Auditability with Multi-Task Learning
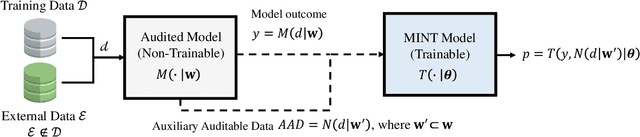
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:Active Membership Inference Test (aMINT) is a method designed to detect whether given data were used during the training of machine learning models. In Active MINT, we propose a novel multitask learning process that involves training simultaneously two models: the original or Audited Model, and a secondary model, referred to as the MINT Model, responsible for identifying the data used for training the Audited Model. This novel multi-task learning approach has been designed to incorporate the auditability of the model as an optimization objective during the training process of neural networks. The proposed approach incorporates intermediate activation maps as inputs to the MINT layers, which are trained to enhance the detection of training data. We present results using a wide range of neural networks, from lighter architectures such as MobileNet to more complex ones such as Vision Transformers, evaluated in 5 public benchmarks. Our proposed Active MINT achieves over 80% accuracy in detecting if given data was used for training, significantly outperforming previous approaches in the literature. Our aMINT and related methodological developments contribute to increasing transparency in AI models, facilitating stronger safeguards in AI deployments to achieve proper security, privacy, and copyright protection.
MINT-Demo: Membership Inference Test Demonstrator
Mar 11, 2025



Abstract:We present the Membership Inference Test Demonstrator, to emphasize the need for more transparent machine learning training processes. MINT is a technique for experimentally determining whether certain data has been used during the training of machine learning models. We conduct experiments with popular face recognition models and 5 public databases containing over 22M images. Promising results, up to 89% accuracy are achieved, suggesting that it is possible to recognize if an AI model has been trained with specific data. Finally, we present a MINT platform as demonstrator of this technology aimed to promote transparency in AI training.
Is my Data in your AI Model? Membership Inference Test with Application to Face Images
Feb 14, 2024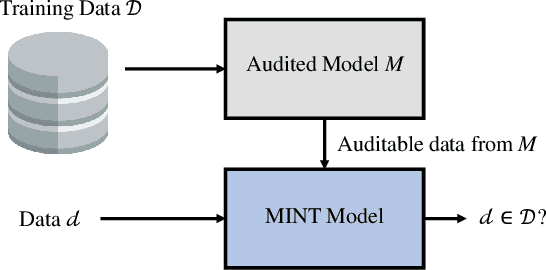


Abstract:This paper introduces the Membership Inference Test (MINT), a novel approach that aims to empirically assess if specific data was used during the training of Artificial Intelligence (AI) models. Specifically, we propose two novel MINT architectures designed to learn the distinct activation patterns that emerge when an audited model is exposed to data used during its training process. The first architecture is based on a Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) network and the second one is based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). The proposed MINT architectures are evaluated on a challenging face recognition task, considering three state-of-the-art face recognition models. Experiments are carried out using six publicly available databases, comprising over 22 million face images in total. Also, different experimental scenarios are considered depending on the context available of the AI model to test. Promising results, up to 90% accuracy, are achieved using our proposed MINT approach, suggesting that it is possible to recognize if an AI model has been trained with specific data.
Measuring Bias in AI Models with Application to Face Biometrics: An Statistical Approach
Apr 26, 2023



Abstract:The new regulatory framework proposal on Artificial Intelligence (AI) published by the European Commission establishes a new risk-based legal approach. The proposal highlights the need to develop adequate risk assessments for the different uses of AI. This risk assessment should address, among others, the detection and mitigation of bias in AI. In this work we analyze statistical approaches to measure biases in automatic decision-making systems. We focus our experiments in face recognition technologies. We propose a novel way to measure the biases in machine learning models using a statistical approach based on the N-Sigma method. N-Sigma is a popular statistical approach used to validate hypotheses in general science such as physics and social areas and its application to machine learning is yet unexplored. In this work we study how to apply this methodology to develop new risk assessment frameworks based on bias analysis and we discuss the main advantages and drawbacks with respect to other popular statistical tests.
Statistical Keystroke Synthesis for Improved Bot Detection
Jul 28, 2022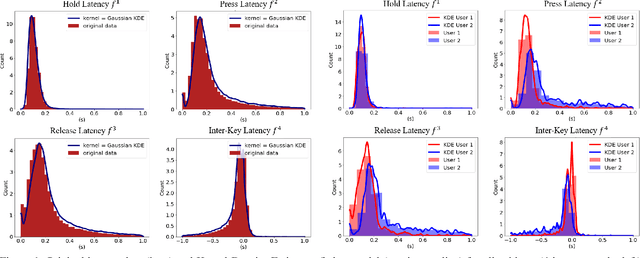

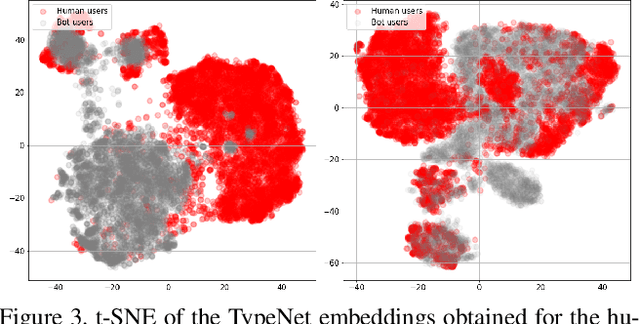
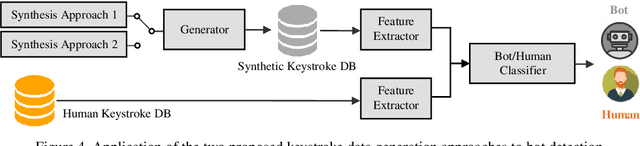
Abstract:This work proposes two statistical approaches for the synthesis of keystroke biometric data based on Universal and User-dependent Models. Both approaches are validated on the bot detection task, using the keystroke synthetic data to better train the systems. Our experiments include a dataset with 136 million keystroke events from 168,000 subjects. We have analyzed the performance of the two synthesis approaches through qualitative and quantitative experiments. Different bot detectors are considered based on two supervised classifiers (Support Vector Machine and Long Short-Term Memory network) and a learning framework including human and generated samples. Our results prove that the proposed statistical approaches are able to generate realistic human-like synthetic keystroke samples. Also, the classification results suggest that in scenarios with large labeled data, these synthetic samples can be detected with high accuracy. However, in few-shot learning scenarios it represents an important challenge.
ALEBk: Feasibility Study of Attention Level Estimation via Blink Detection applied to e-Learning
Dec 16, 2021



Abstract:This work presents a feasibility study of remote attention level estimation based on eye blink frequency. We first propose an eye blink detection system based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), very competitive with respect to related works. Using this detector, we experimentally evaluate the relationship between the eye blink rate and the attention level of students captured during online sessions. The experimental framework is carried out using a public multimodal database for eye blink detection and attention level estimation called mEBAL, which comprises data from 38 students and multiples acquisition sensors, in particular, i) an electroencephalogram (EEG) band which provides the time signals coming from the student's cognitive information, and ii) RGB and NIR cameras to capture the students face gestures. The results achieved suggest an inverse correlation between the eye blink frequency and the attention level. This relation is used in our proposed method called ALEBk for estimating the attention level as the inverse of the eye blink frequency. Our results open a new research line to introduce this technology for attention level estimation on future e-learning platforms, among other applications of this kind of behavioral biometrics based on face analysis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge