Cristiana de Farias
Active Perception for Tactile Sensing: A Task-Agnostic Attention-Based Approach
May 09, 2025Abstract:Humans make extensive use of haptic exploration to map and identify the properties of the objects that we touch. In robotics, active tactile perception has emerged as an important research domain that complements vision for tasks such as object classification, shape reconstruction, and manipulation. This work introduces TAP (Task-agnostic Active Perception) -- a novel framework that leverages reinforcement learning (RL) and transformer-based architectures to address the challenges posed by partially observable environments. TAP integrates Soft Actor-Critic (SAC) and CrossQ algorithms within a unified optimization objective, jointly training a perception module and decision-making policy. By design, TAP is completely task-agnostic and can, in principle, generalize to any active perception problem. We evaluate TAP across diverse tasks, including toy examples and realistic applications involving haptic exploration of 3D models from the Tactile MNIST benchmark. Experiments demonstrate the efficacy of TAP, achieving high accuracies on the Tactile MNIST haptic digit recognition task and a tactile pose estimation task. These findings underscore the potential of TAP as a versatile and generalizable framework for advancing active tactile perception in robotics.
Geometrically-Aware One-Shot Skill Transfer of Category-Level Objects
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:Robotic manipulation of unfamiliar objects in new environments is challenging and requires extensive training or laborious pre-programming. We propose a new skill transfer framework, which enables a robot to transfer complex object manipulation skills and constraints from a single human demonstration. Our approach addresses the challenge of skill acquisition and task execution by deriving geometric representations from demonstrations focusing on object-centric interactions. By leveraging the Functional Maps (FM) framework, we efficiently map interaction functions between objects and their environments, allowing the robot to replicate task operations across objects of similar topologies or categories, even when they have significantly different shapes. Additionally, our method incorporates a Task-Space Imitation Algorithm (TSIA) which generates smooth, geometrically-aware robot paths to ensure the transferred skills adhere to the demonstrated task constraints. We validate the effectiveness and adaptability of our approach through extensive experiments, demonstrating successful skill transfer and task execution in diverse real-world environments without requiring additional training.
Asservissement visuel 3D direct dans le domaine spectral
Apr 03, 2023Abstract:This paper presents a direct 3D visual servo scheme for the automatic alignment of point clouds (respectively, objects) using visual information in the spectral domain. Specifically, we propose an alignment method for 3D models/point clouds that works by estimating the global transformation between a reference point cloud and a target point cloud using harmonic domain data analysis. A 3D discrete Fourier transform (DFT) in $\mathbb{R}^3$ is used for translation estimation and real spherical harmonics in $SO(3)$ are used for rotation estimation. This approach allows us to derive a decoupled visual servo controller with 6 degrees of freedom. We then show how this approach can be used as a controller for a robotic arm to perform a positioning task. Unlike existing 3D visual servo methods, our method works well with partial point clouds and in cases of large initial transformations between the initial and desired position. Additionally, using spectral data (instead of spatial data) for the transformation estimation makes our method robust to sensor-induced noise and partial occlusions. Our method has been successfully validated experimentally on point clouds obtained with a depth camera mounted on a robotic arm.
3D Spectral Domain Registration-Based Visual Servoing
Mar 28, 2023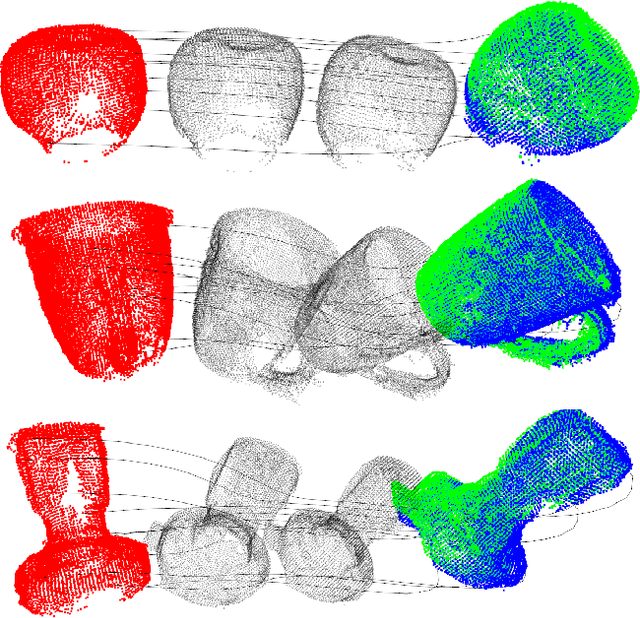
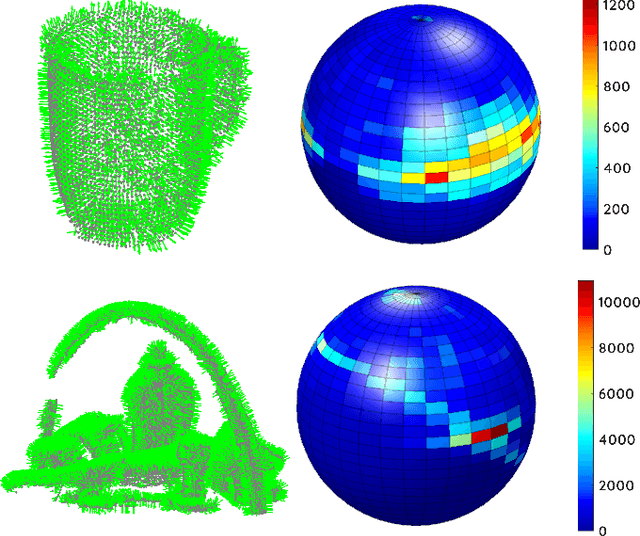
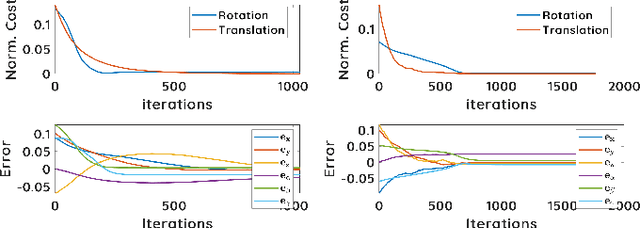
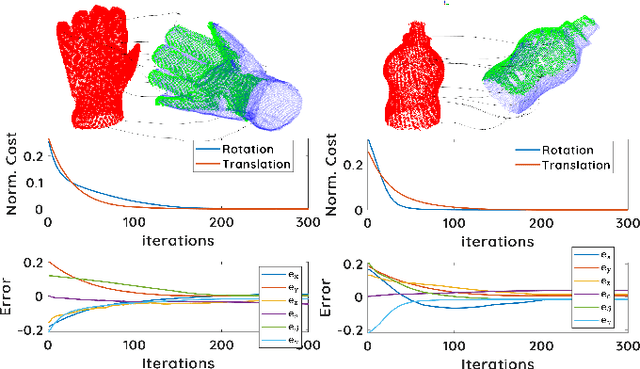
Abstract:This paper presents a spectral domain registration-based visual servoing scheme that works on 3D point clouds. Specifically, we propose a 3D model/point cloud alignment method, which works by finding a global transformation between reference and target point clouds using spectral analysis. A 3D Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) in R3 is used for the translation estimation, and the real spherical harmonics in SO(3) are used for the rotations estimation. Such an approach allows us to derive a decoupled 6 degrees of freedom (DoF) controller, where we use gradient ascent optimisation to minimise translation and rotational costs. We then show how this methodology can be used to regulate a robot arm to perform a positioning task. In contrast to the existing state-of-the-art depth-based visual servoing methods that either require dense depth maps or dense point clouds, our method works well with partial point clouds and can effectively handle larger transformations between the reference and the target positions. Furthermore, the use of spectral data (instead of spatial data) for transformation estimation makes our method robust to sensor-induced noise and partial occlusions. We validate our approach by performing experiments using point clouds acquired by a robot-mounted depth camera. Obtained results demonstrate the effectiveness of our visual servoing approach.
Grasp Transfer for Deformable Objects by Functional Map Correspondence
Mar 01, 2022



Abstract:Handling object deformations for robotic grasping is still a major problem to solve. In this paper, we propose an efficient learning-free solution for this problem where generated grasp hypotheses of a region of an object are adapted to its deformed configurations. To this end, we investigate the applicability of functional map (FM) correspondence, where the shape matching problem is treated as searching for correspondences between geometric functions in a reduced basis. For a user selected region of an object, a ranked list of grasp candidates is generated with local contact moment (LoCoMo) based grasp planner. The proposed FM-based methodology maps these candidates to an instance of the object that has suffered arbitrary level of deformation. The best grasp, by analysing its kinematic feasibility while respecting the original finger configuration as much as possible, is then executed on the object. We have compared the performance of our method with two different state-of-the-art correspondence mapping techniques in terms of grasp stability and region grasping accuracy for 4 different objects with 5 different deformations.
SpectGRASP: Robotic Grasping by Spectral Correlation
Jul 26, 2021
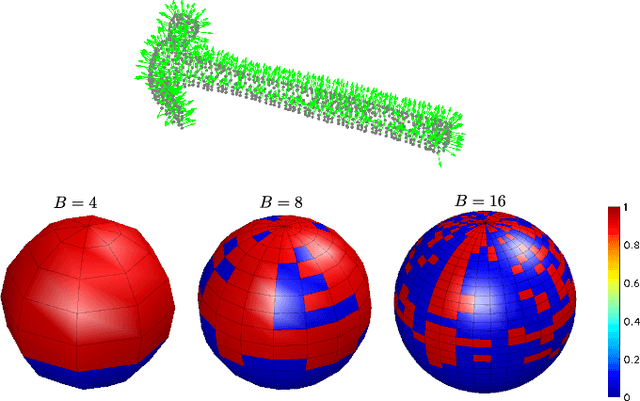


Abstract:This paper presents a spectral correlation-based method (SpectGRASP) for robotic grasping of arbitrarily shaped, unknown objects. Given a point cloud of an object, SpectGRASP extracts contact points on the object's surface matching the hand configuration. It neither requires offline training nor a-priori object models. We propose a novel Binary Extended Gaussian Image (BEGI), which represents the point cloud surface normals of both object and robot fingers as signals on a 2-sphere. Spherical harmonics are then used to estimate the correlation between fingers and object BEGIs. The resulting spectral correlation density function provides a similarity measure of gripper and object surface normals. This is highly efficient in that it is simultaneously evaluated at all possible finger rotations in SO(3). A set of contact points are then extracted for each finger using rotations with high correlation values. We then use our previous work, Local Contact Moment (LoCoMo) similarity metric, to sequentially rank the generated grasps such that the one with maximum likelihood is executed. We evaluate the performance of SpectGRASP by conducting experiments with a 7-axis robot fitted with a parallel-jaw gripper, in a physics simulation environment. Obtained results indicate that the method not only can grasp individual objects, but also can successfully clear randomly organized groups of objects. The SpectGRASP method also outperforms the closest state-of-the-art method in terms of grasp generation time and grasp-efficiency.
Dual Quaternion-Based Visual Servoing for Grasping Moving Objects
Jul 17, 2021



Abstract:This paper presents a new dual quaternion-based formulation for pose-based visual servoing. Extending our previous work on local contact moment (LoCoMo) based grasp planning, we demonstrate grasping of arbitrarily moving objects in 3D space. Instead of using the conventional axis-angle parameterization, dual quaternions allow designing the visual servoing task in a more compact manner and provide robustness to manipulator singularities. Given an object point cloud, LoCoMo generates a ranked list of grasp and pre-grasp poses, which are used as desired poses for visual servoing. Whenever the object moves (tracked by visual marker tracking), the desired pose updates automatically. For this, capitalising on the dual quaternion spatial distance error, we propose a dynamic grasp re-ranking metric to select the best feasible grasp for the moving object. This allows the robot to readily track and grasp arbitrarily moving objects. In addition, we also explore the robot null-space with our controller to avoid joint limits so as to achieve smooth trajectories while following moving objects. We evaluate the performance of the proposed visual servoing by conducting simulation experiments of grasping various objects using a 7-axis robot fitted with a 2-finger gripper. Obtained results demonstrate the efficiency of our proposed visual servoing.
Simultaneous Tactile Exploration and Grasp Refinement for Unknown Objects
Feb 28, 2021
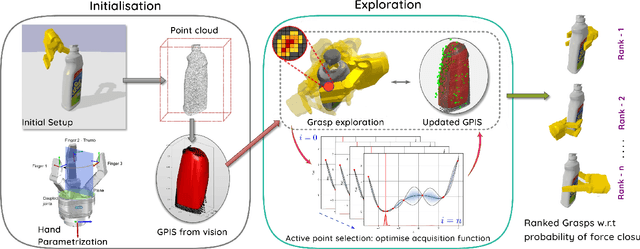

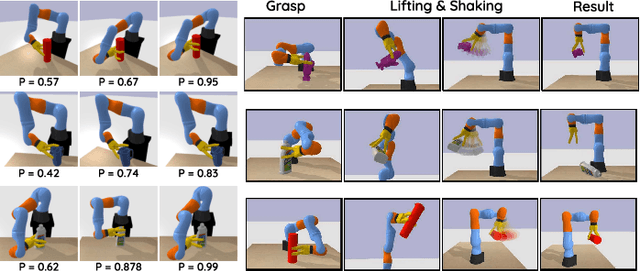
Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of simultaneously exploring an unknown object to model its shape, using tactile sensors on robotic fingers, while also improving finger placement to optimise grasp stability. In many situations, a robot will have only a partial camera view of the near side of an observed object, for which the far side remains occluded. We show how an initial grasp attempt, based on an initial guess of the overall object shape, yields tactile glances of the far side of the object which enable the shape estimate and consequently the successive grasps to be improved. We propose a grasp exploration approach using a probabilistic representation of shape, based on Gaussian Process Implicit Surfaces. This representation enables initial partial vision data to be augmented with additional data from successive tactile glances. This is combined with a probabilistic estimate of grasp quality to refine grasp configurations. When choosing the next set of finger placements, a bi-objective optimisation method is used to mutually maximise grasp quality and improve shape representation during successive grasp attempts. Experimental results show that the proposed approach yields stable grasp configurations more efficiently than a baseline method, while also yielding improved shape estimate of the grasped object.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge