Cong Tran
LiveNeRF: Efficient Face Replacement Through Neural Radiance Fields Integration
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Face replacement technology enables significant advancements in entertainment, education, and communication applications, including dubbing, virtual avatars, and cross-cultural content adaptation. Our LiveNeRF framework addresses critical limitations of existing methods by achieving real-time performance (33 FPS) with superior visual quality, enabling practical deployment in live streaming, video conferencing, and interactive media. The technology particularly benefits content creators, educators, and individuals with speech impairments through accessible avatar communication. While acknowledging potential misuse in unauthorized deepfake creation, we advocate for responsible deployment with user consent verification and integration with detection systems to ensure positive societal impact while minimizing risks.
A4O: All Trigger for One sample
Jan 13, 2025Abstract:Backdoor attacks have become a critical threat to deep neural networks (DNNs), drawing many research interests. However, most of the studied attacks employ a single type of trigger. Consequently, proposed backdoor defenders often rely on the assumption that triggers would appear in a unified way. In this paper, we show that this naive assumption can create a loophole, allowing more sophisticated backdoor attacks to bypass. We design a novel backdoor attack mechanism that incorporates multiple types of backdoor triggers, focusing on stealthiness and effectiveness. Our journey begins with the intriguing observation that the performance of a backdoor attack in deep learning models, as well as its detectability and removability, are all proportional to the magnitude of the trigger. Based on this correlation, we propose reducing the magnitude of each trigger type and combining them to achieve a strong backdoor relying on the combined trigger while still staying safely under the radar of defenders. Extensive experiments on three standard datasets demonstrate that our method can achieve high attack success rates (ASRs) while consistently bypassing state-of-the-art defenses.
REM: A Scalable Reinforced Multi-Expert Framework for Multiplex Influence Maximization
Jan 01, 2025



Abstract:In social online platforms, identifying influential seed users to maximize influence spread is a crucial as it can greatly diminish the cost and efforts required for information dissemination. While effective, traditional methods for Multiplex Influence Maximization (MIM) have reached their performance limits, prompting the emergence of learning-based approaches. These novel methods aim for better generalization and scalability for more sizable graphs but face significant challenges, such as (1) inability to handle unknown diffusion patterns and (2) reliance on high-quality training samples. To address these issues, we propose the Reinforced Expert Maximization framework (REM). REM leverages a Propagation Mixture of Experts technique to encode dynamic propagation of large multiplex networks effectively in order to generate enhanced influence propagation. Noticeably, REM treats a generative model as a policy to autonomously generate different seed sets and learn how to improve them from a Reinforcement Learning perspective. Extensive experiments on several real-world datasets demonstrate that REM surpasses state-of-the-art methods in terms of influence spread, scalability, and inference time in influence maximization tasks.
Innovative Silicosis and Pneumonia Classification: Leveraging Graph Transformer Post-hoc Modeling and Ensemble Techniques
Dec 31, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a comprehensive study on the classification and detection of Silicosis-related lung inflammation. Our main contributions include 1) the creation of a newly curated chest X-ray (CXR) image dataset named SVBCX that is tailored to the nuances of lung inflammation caused by distinct agents, providing a valuable resource for silicosis and pneumonia research community; and 2) we propose a novel deep-learning architecture that integrates graph transformer networks alongside a traditional deep neural network module for the effective classification of silicosis and pneumonia. Additionally, we employ the Balanced Cross-Entropy (BalCE) as a loss function to ensure more uniform learning across different classes, enhancing the model's ability to discern subtle differences in lung conditions. The proposed model architecture and loss function selection aim to improve the accuracy and reliability of inflammation detection, particularly in the context of Silicosis. Furthermore, our research explores the efficacy of an ensemble approach that combines the strengths of diverse model architectures. Experimental results on the constructed dataset demonstrate promising outcomes, showcasing substantial enhancements compared to baseline models. The ensemble of models achieves a macro-F1 score of 0.9749 and AUC ROC scores exceeding 0.99 for each class, underscoring the effectiveness of our approach in accurate and robust lung inflammation classification.
Enhancing Fine-grained Image Classification through Attentive Batch Training
Dec 27, 2024Abstract:Fine-grained image classification, which is a challenging task in computer vision, requires precise differentiation among visually similar object categories. In this paper, we propose 1) a novel module called Residual Relationship Attention (RRA) that leverages the relationships between images within each training batch to effectively integrate visual feature vectors of batch images and 2) a novel technique called Relationship Position Encoding (RPE), which encodes the positions of relationships between original images in a batch and effectively preserves the relationship information between images within the batch. Additionally, we design a novel framework, namely Relationship Batch Integration (RBI), which utilizes RRA in conjunction with RPE, allowing the discernment of vital visual features that may remain elusive when examining a singular image representative of a particular class. Through extensive experiments, our proposed method demonstrates significant improvements in the accuracy of different fine-grained classifiers, with an average increase of $(+2.78\%)$ and $(+3.83\%)$ on the CUB200-2011 and Stanford Dog datasets, respectively, while achieving a state-of-the-art results $(95.79\%)$ on the Stanford Dog dataset. Despite not achieving the same level of improvement as in fine-grained image classification, our method still demonstrates its prowess in leveraging general image classification by attaining a state-of-the-art result of $(93.71\%)$ on the Tiny-Imagenet dataset. Furthermore, our method serves as a plug-in refinement module and can be easily integrated into different networks.
Federated Few-shot Learning for Cough Classification with Edge Devices
Sep 03, 2023Abstract:Automatically classifying cough sounds is one of the most critical tasks for the diagnosis and treatment of respiratory diseases. However, collecting a huge amount of labeled cough dataset is challenging mainly due to high laborious expenses, data scarcity, and privacy concerns. In this work, our aim is to develop a framework that can effectively perform cough classification even in situations when enormous cough data is not available, while also addressing privacy concerns. Specifically, we formulate a new problem to tackle these challenges and adopt few-shot learning and federated learning to design a novel framework, termed F2LCough, for solving the newly formulated problem. We illustrate the superiority of our method compared with other approaches on COVID-19 Thermal Face & Cough dataset, in which F2LCough achieves an average F1-Score of 86%. Our results show the feasibility of few-shot learning combined with federated learning to build a classification model of cough sounds. This new methodology is able to classify cough sounds in data-scarce situations and maintain privacy properties. The outcomes of this work can be a fundamental framework for building support systems for the detection and diagnosis of cough-related diseases.
UnsMOT: Unified Framework for Unsupervised Multi-Object Tracking with Geometric Topology Guidance
Sep 03, 2023Abstract:Object detection has long been a topic of high interest in computer vision literature. Motivated by the fact that annotating data for the multi-object tracking (MOT) problem is immensely expensive, recent studies have turned their attention to the unsupervised learning setting. In this paper, we push forward the state-of-the-art performance of unsupervised MOT methods by proposing UnsMOT, a novel framework that explicitly combines the appearance and motion features of objects with geometric information to provide more accurate tracking. Specifically, we first extract the appearance and motion features using CNN and RNN models, respectively. Then, we construct a graph of objects based on their relative distances in a frame, which is fed into a GNN model together with CNN features to output geometric embedding of objects optimized using an unsupervised loss function. Finally, associations between objects are found by matching not only similar extracted features but also geometric embedding of detections and tracklets. Experimental results show remarkable performance in terms of HOTA, IDF1, and MOTA metrics in comparison with state-of-the-art methods.
Node Feature Augmentation Vitaminizes Network Alignment
Apr 25, 2023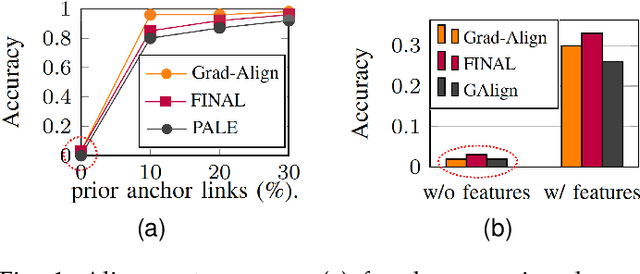
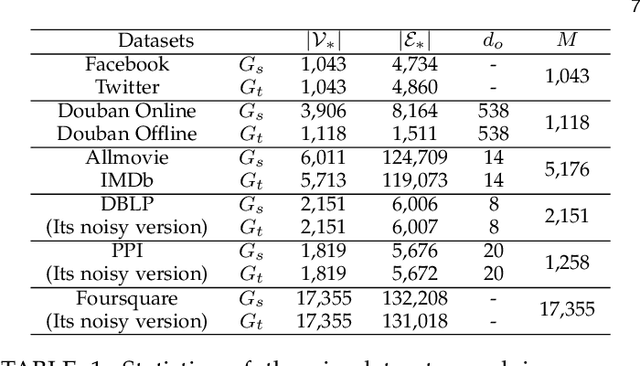
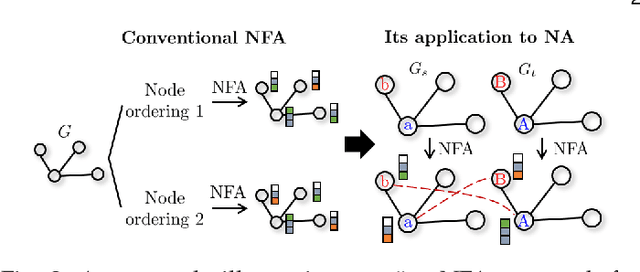
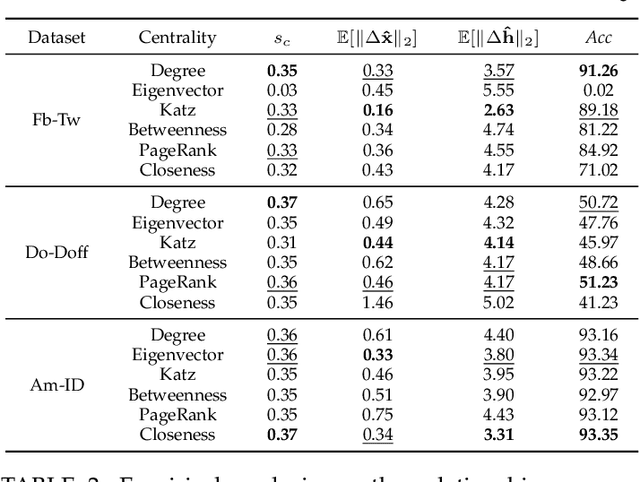
Abstract:Network alignment (NA) is the task of discovering node correspondences across multiple networks using topological and/or feature information of given networks. Although NA methods have achieved remarkable success in a myriad of scenarios, their effectiveness is not without additional information such as prior anchor links and/or node features, which may not always be available due to privacy concerns or access restrictions. To tackle this practical challenge, we propose Grad-Align+, a novel NA method built upon a recent state-of-the-art NA method, the so-called Grad-Align, that gradually discovers only a part of node pairs until all node pairs are found. In designing Grad-Align+, we account for how to augment node features in the sense of performing the NA task and how to design our NA method by maximally exploiting the augmented node features. To achieve this goal, we develop Grad-Align+ consisting of three key components: 1) centrality-based node feature augmentation (CNFA), 2) graph neural network (GNN)-aided embedding similarity calculation alongside the augmented node features, and 3) gradual NA with similarity calculation using the information of aligned cross-network neighbor-pairs (ACNs). Through comprehensive experiments, we demonstrate that Grad-Align+ exhibits (a) the superiority over benchmark NA methods by a large margin, (b) empirical validations as well as our theoretical findings to see the effectiveness of CNFA, (c) the influence of each component, (d) the robustness to network noises, and (e) the computational efficiency.
Graph Neural Network-Aided Exploratory Learning for Community Detection with Unknown Topology
Apr 10, 2023

Abstract:In social networks, the discovery of community structures has received considerable attention as a fundamental problem in various network analysis tasks. However, due to privacy concerns or access restrictions, the network structure is often unknown, thereby rendering established community detection approaches ineffective without costly network topology acquisition. To tackle this challenge, we present META-CODE, a novel end-to-end solution for detecting overlapping communities in networks with unknown topology via exploratory learning aided by easy-to-collect node metadata. Specifically, META-CODE consists of three iterative steps in addition to the initial network inference step: 1) node-level community-affiliation embeddings based on graph neural networks (GNNs) trained by our new reconstruction loss, 2) network exploration via community affiliation-based node queries, and 3) network inference using an edge connectivity-based Siamese neural network model from the explored network. Through comprehensive evaluations using five real-world datasets, we demonstrate that META-CODE exhibits (a) its superiority over benchmark community detection methods, (b) empirical evaluations as well as theoretical findings to see the effectiveness of our node query, (c) the influence of each module, and (d) its computational efficiency.
Grad-Align+: Empowering Gradual Network Alignment Using Attribute Augmentation
Aug 24, 2022
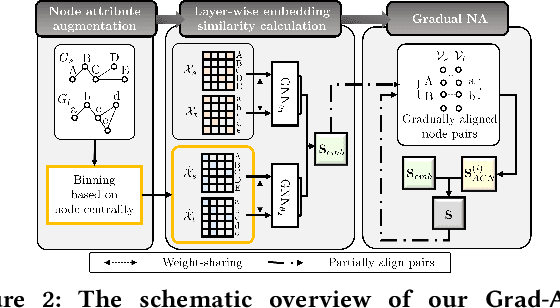
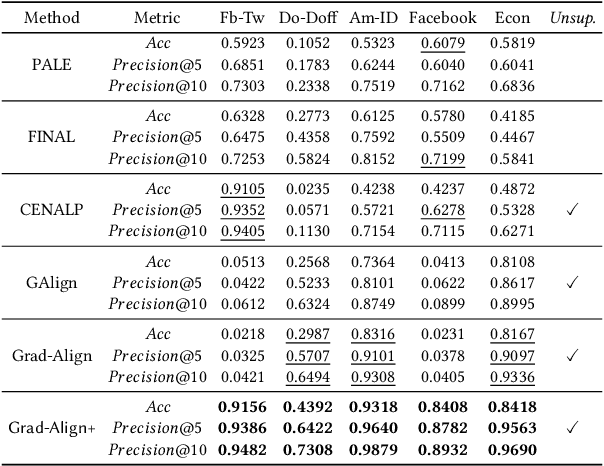
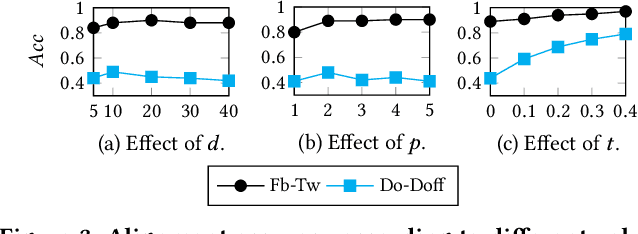
Abstract:Network alignment (NA) is the task of discovering node correspondences across different networks. Although NA methods have achieved remarkable success in a myriad of scenarios, their satisfactory performance is not without prior anchor link information and/or node attributes, which may not always be available. In this paper, we propose Grad-Align+, a novel NA method using node attribute augmentation that is quite robust to the absence of such additional information. Grad-Align+ is built upon a recent state-of-the-art NA method, the so-called Grad-Align, that gradually discovers only a part of node pairs until all node pairs are found. Specifically, Grad-Align+ is composed of the following key components: 1) augmenting node attributes based on nodes' centrality measures, 2) calculating an embedding similarity matrix extracted from a graph neural network into which the augmented node attributes are fed, and 3) gradually discovering node pairs by calculating similarities between cross-network nodes with respect to the aligned cross-network neighbor-pair. Experimental results demonstrate that Grad-Align+ exhibits (a) superiority over benchmark NA methods, (b) empirical validation of our theoretical findings, and (c) the effectiveness of our attribute augmentation module.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge