Chuqiao Li
FrankenMotion: Part-level Human Motion Generation and Composition
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Human motion generation from text prompts has made remarkable progress in recent years. However, existing methods primarily rely on either sequence-level or action-level descriptions due to the absence of fine-grained, part-level motion annotations. This limits their controllability over individual body parts. In this work, we construct a high-quality motion dataset with atomic, temporally-aware part-level text annotations, leveraging the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs). Unlike prior datasets that either provide synchronized part captions with fixed time segments or rely solely on global sequence labels, our dataset captures asynchronous and semantically distinct part movements at fine temporal resolution. Based on this dataset, we introduce a diffusion-based part-aware motion generation framework, namely FrankenMotion, where each body part is guided by its own temporally-structured textual prompt. This is, to our knowledge, the first work to provide atomic, temporally-aware part-level motion annotations and have a model that allows motion generation with both spatial (body part) and temporal (atomic action) control. Experiments demonstrate that FrankenMotion outperforms all previous baseline models adapted and retrained for our setting, and our model can compose motions unseen during training. Our code and dataset will be publicly available upon publication.
Physics-based Human Pose Estimation from a Single Moving RGB Camera
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Most monocular and physics-based human pose tracking methods, while achieving state-of-the-art results, suffer from artifacts when the scene does not have a strictly flat ground plane or when the camera is moving. Moreover, these methods are often evaluated on in-the-wild real world videos without ground-truth data or on synthetic datasets, which fail to model the real world light transport, camera motion, and pose-induced appearance and geometry changes. To tackle these two problems, we introduce MoviCam, the first non-synthetic dataset containing ground-truth camera trajectories of a dynamically moving monocular RGB camera, scene geometry, and 3D human motion with human-scene contact labels. Additionally, we propose PhysDynPose, a physics-based method that incorporates scene geometry and physical constraints for more accurate human motion tracking in case of camera motion and non-flat scenes. More precisely, we use a state-of-the-art kinematics estimator to obtain the human pose and a robust SLAM method to capture the dynamic camera trajectory, enabling the recovery of the human pose in the world frame. We then refine the kinematic pose estimate using our scene-aware physics optimizer. From our new benchmark, we found that even state-of-the-art methods struggle with this inherently challenging setting, i.e. a moving camera and non-planar environments, while our method robustly estimates both human and camera poses in world coordinates.
Unimotion: Unifying 3D Human Motion Synthesis and Understanding
Sep 24, 2024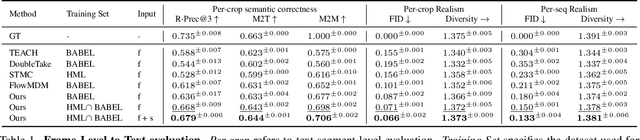
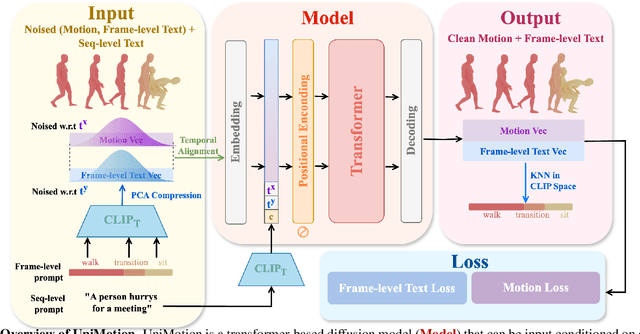
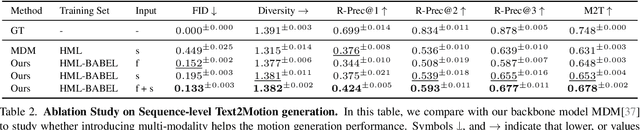
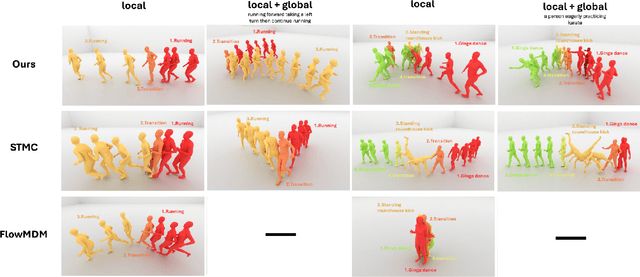
Abstract:We introduce Unimotion, the first unified multi-task human motion model capable of both flexible motion control and frame-level motion understanding. While existing works control avatar motion with global text conditioning, or with fine-grained per frame scripts, none can do both at once. In addition, none of the existing works can output frame-level text paired with the generated poses. In contrast, Unimotion allows to control motion with global text, or local frame-level text, or both at once, providing more flexible control for users. Importantly, Unimotion is the first model which by design outputs local text paired with the generated poses, allowing users to know what motion happens and when, which is necessary for a wide range of applications. We show Unimotion opens up new applications: 1.) Hierarchical control, allowing users to specify motion at different levels of detail, 2.) Obtaining motion text descriptions for existing MoCap data or YouTube videos 3.) Allowing for editability, generating motion from text, and editing the motion via text edits. Moreover, Unimotion attains state-of-the-art results for the frame-level text-to-motion task on the established HumanML3D dataset. The pre-trained model and code are available available on our project page at https://coral79.github.io/Unimotion/.
A Continual Deepfake Detection Benchmark: Dataset, Methods, and Essentials
May 14, 2022



Abstract:There have been emerging a number of benchmarks and techniques for the detection of deepfakes. However, very few works study the detection of incrementally appearing deepfakes in the real-world scenarios. To simulate the wild scenes, this paper suggests a continual deepfake detection benchmark (CDDB) over a new collection of deepfakes from both known and unknown generative models. The suggested CDDB designs multiple evaluations on the detection over easy, hard, and long sequence of deepfake tasks, with a set of appropriate measures. In addition, we exploit multiple approaches to adapt multiclass incremental learning methods, commonly used in the continual visual recognition, to the continual deepfake detection problem. We evaluate several methods, including the adapted ones, on the proposed CDDB. Within the proposed benchmark, we explore some commonly known essentials of standard continual learning. Our study provides new insights on these essentials in the context of continual deepfake detection. The suggested CDDB is clearly more challenging than the existing benchmarks, which thus offers a suitable evaluation avenue to the future research. Our benchmark dataset and the source code will be made publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge