Chuck Rosenberg
OmniSearchSage: Multi-Task Multi-Entity Embeddings for Pinterest Search
Apr 25, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we present OmniSearchSage, a versatile and scalable system for understanding search queries, pins, and products for Pinterest search. We jointly learn a unified query embedding coupled with pin and product embeddings, leading to an improvement of $>8\%$ relevance, $>7\%$ engagement, and $>5\%$ ads CTR in Pinterest's production search system. The main contributors to these gains are improved content understanding, better multi-task learning, and real-time serving. We enrich our entity representations using diverse text derived from image captions from a generative LLM, historical engagement, and user-curated boards. Our multitask learning setup produces a single search query embedding in the same space as pin and product embeddings and compatible with pre-existing pin and product embeddings. We show the value of each feature through ablation studies, and show the effectiveness of a unified model compared to standalone counterparts. Finally, we share how these embeddings have been deployed across the Pinterest search stack, from retrieval to ranking, scaling to serve $300k$ requests per second at low latency. Our implementation of this work is available at https://github.com/pinterest/atg-research/tree/main/omnisearchsage.
Hierarchical Temporal Convolutional Networks for Dynamic Recommender Systems
Apr 10, 2019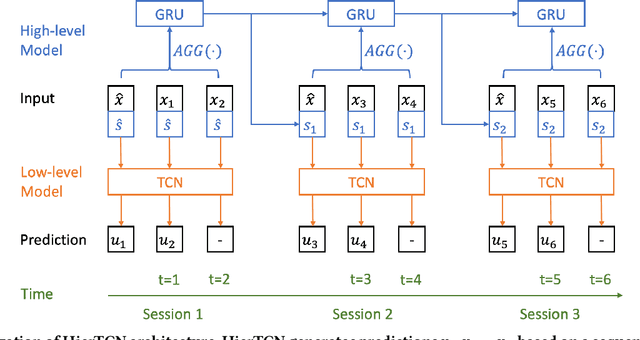
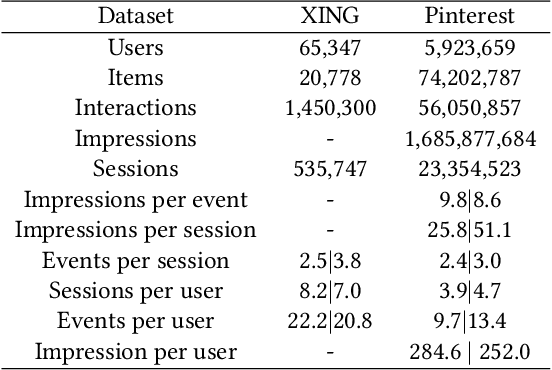
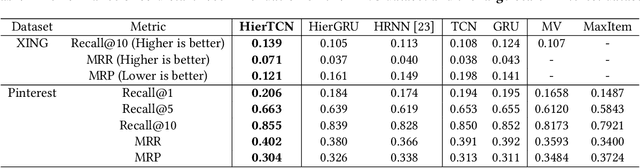
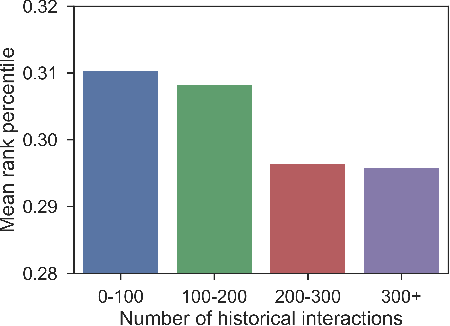
Abstract:Recommender systems that can learn from cross-session data to dynamically predict the next item a user will choose are crucial for online platforms. However, existing approaches often use out-of-the-box sequence models which are limited by speed and memory consumption, are often infeasible for production environments, and usually do not incorporate cross-session information, which is crucial for effective recommendations. Here we propose Hierarchical Temporal Convolutional Networks (HierTCN), a hierarchical deep learning architecture that makes dynamic recommendations based on users' sequential multi-session interactions with items. HierTCN is designed for web-scale systems with billions of items and hundreds of millions of users. It consists of two levels of models: The high-level model uses Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) to aggregate users' evolving long-term interests across different sessions, while the low-level model is implemented with Temporal Convolutional Networks (TCN), utilizing both the long-term interests and the short-term interactions within sessions to predict the next interaction. We conduct extensive experiments on a public XING dataset and a large-scale Pinterest dataset that contains 6 million users with 1.6 billion interactions. We show that HierTCN is 2.5x faster than RNN-based models and uses 90% less data memory compared to TCN-based models. We further develop an effective data caching scheme and a queue-based mini-batch generator, enabling our model to be trained within 24 hours on a single GPU. Our model consistently outperforms state-of-the-art dynamic recommendation methods, with up to 18% improvement in recall and 10% in mean reciprocal rank.
Learning Fine-grained Image Similarity with Deep Ranking
Apr 17, 2014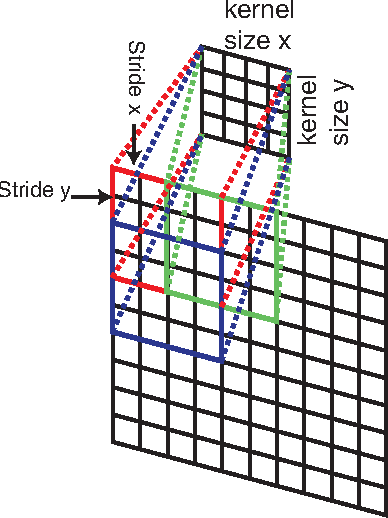
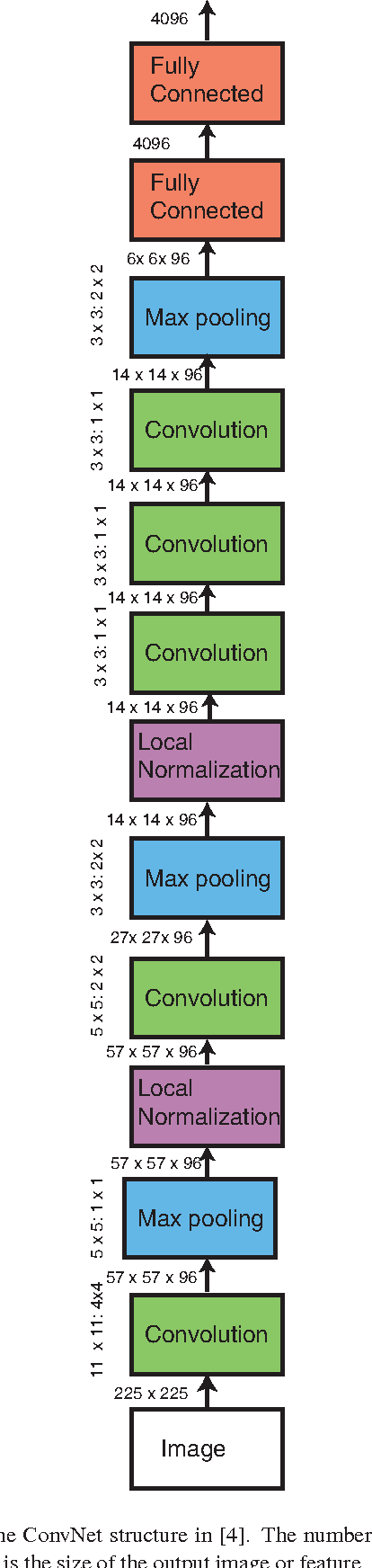

Abstract:Learning fine-grained image similarity is a challenging task. It needs to capture between-class and within-class image differences. This paper proposes a deep ranking model that employs deep learning techniques to learn similarity metric directly from images.It has higher learning capability than models based on hand-crafted features. A novel multiscale network structure has been developed to describe the images effectively. An efficient triplet sampling algorithm is proposed to learn the model with distributed asynchronized stochastic gradient. Extensive experiments show that the proposed algorithm outperforms models based on hand-crafted visual features and deep classification models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge