Chuandong Liu
Holistic Large-Scale Scene Reconstruction via Mixed Gaussian Splatting
May 29, 2025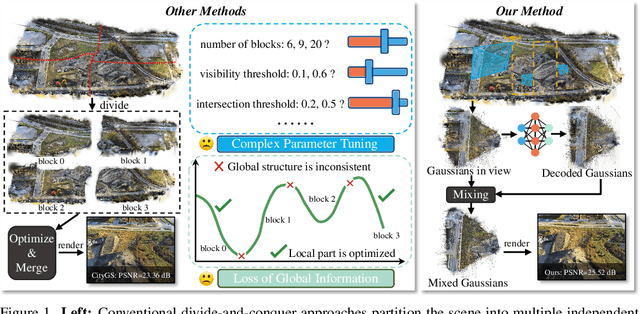
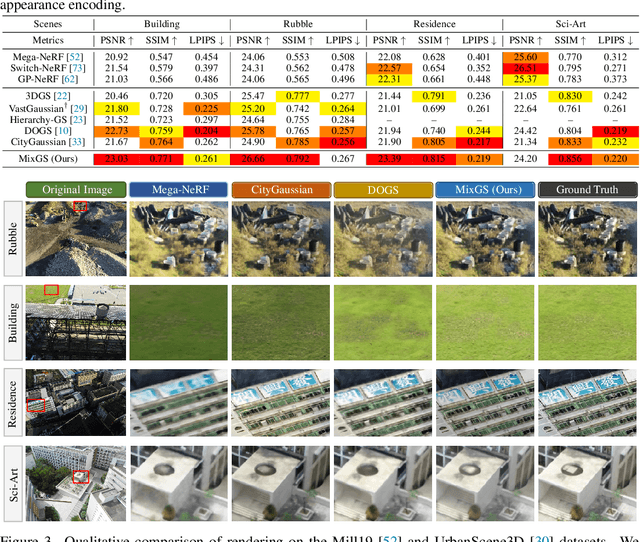
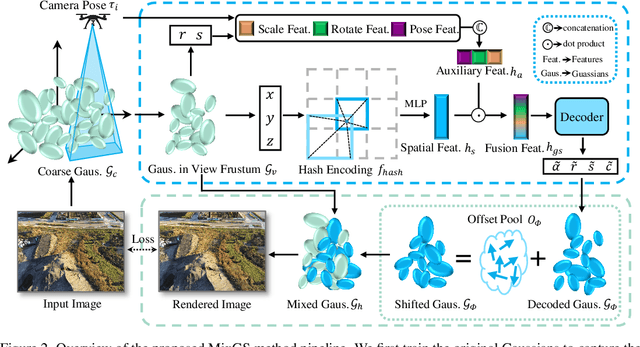
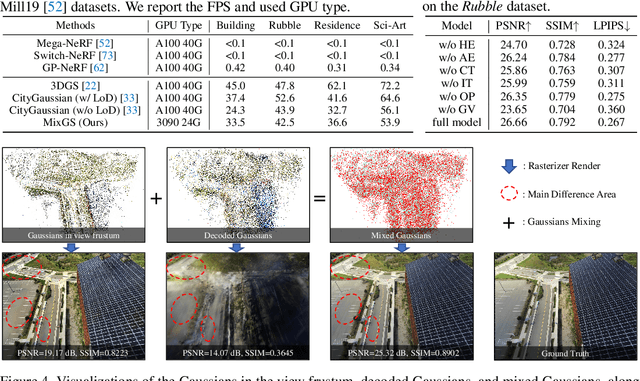
Abstract:Recent advances in 3D Gaussian Splatting have shown remarkable potential for novel view synthesis. However, most existing large-scale scene reconstruction methods rely on the divide-and-conquer paradigm, which often leads to the loss of global scene information and requires complex parameter tuning due to scene partitioning and local optimization. To address these limitations, we propose MixGS, a novel holistic optimization framework for large-scale 3D scene reconstruction. MixGS models the entire scene holistically by integrating camera pose and Gaussian attributes into a view-aware representation, which is decoded into fine-detailed Gaussians. Furthermore, a novel mixing operation combines decoded and original Gaussians to jointly preserve global coherence and local fidelity. Extensive experiments on large-scale scenes demonstrate that MixGS achieves state-of-the-art rendering quality and competitive speed, while significantly reducing computational requirements, enabling large-scale scene reconstruction training on a single 24GB VRAM GPU. The code will be released at https://github.com/azhuantou/MixGS.
Exploring Scene Coherence for Semi-Supervised 3D Semantic Segmentation
Aug 21, 2024



Abstract:Semi-supervised semantic segmentation, which efficiently addresses the limitation of acquiring dense annotations, is essential for 3D scene understanding. Most methods leverage the teacher model to generate pseudo labels, and then guide the learning of the student model on unlabeled scenes. However, they focus only on points with pseudo labels while directly overlooking points without pseudo labels, namely intra-scene inconsistency, leading to semantic ambiguity. Moreover, inter-scene correlation between labeled and unlabeled scenes contribute to transferring rich annotation information, yet this has not been explored for the semi-supervised tasks. To address these two problems, we propose to explore scene coherence for semi-supervised 3D semantic segmentation, dubbed CoScene. Inspired by the unstructured and unordered nature of the point clouds, our CoScene adopts the straightforward point erasure strategy to ensure the intra-scene consistency. Moreover, patch-based data augmentation is proposed to enhance the inter-scene information transfer between labeled and unlabeled scenes at both scene and instance levels. Extensive experimental results on SemanticKITTI and nuScenes show that our approach outperforms existing methods.
Are Dense Labels Always Necessary for 3D Object Detection from Point Cloud?
Mar 05, 2024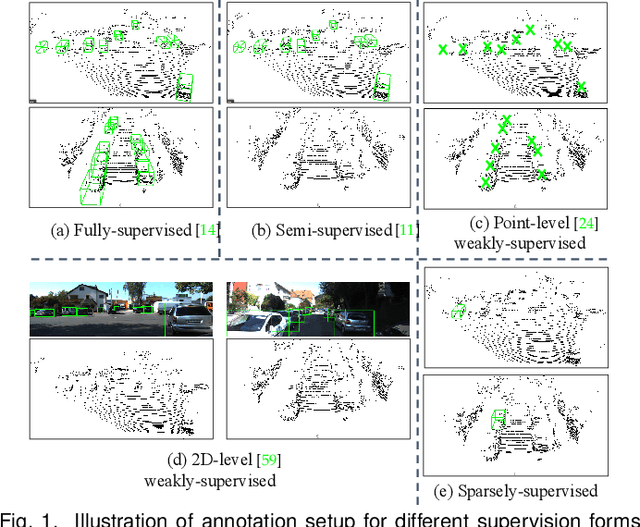



Abstract:Current state-of-the-art (SOTA) 3D object detection methods often require a large amount of 3D bounding box annotations for training. However, collecting such large-scale densely-supervised datasets is notoriously costly. To reduce the cumbersome data annotation process, we propose a novel sparsely-annotated framework, in which we just annotate one 3D object per scene. Such a sparse annotation strategy could significantly reduce the heavy annotation burden, while inexact and incomplete sparse supervision may severely deteriorate the detection performance. To address this issue, we develop the SS3D++ method that alternatively improves 3D detector training and confident fully-annotated scene generation in a unified learning scheme. Using sparse annotations as seeds, we progressively generate confident fully-annotated scenes based on designing a missing-annotated instance mining module and reliable background mining module. Our proposed method produces competitive results when compared with SOTA weakly-supervised methods using the same or even more annotation costs. Besides, compared with SOTA fully-supervised methods, we achieve on-par or even better performance on the KITTI dataset with about 5x less annotation cost, and 90% of their performance on the Waymo dataset with about 15x less annotation cost. The additional unlabeled training scenes could further boost the performance. The code will be available at https://github.com/gaocq/SS3D2.
Hierarchical Supervision and Shuffle Data Augmentation for 3D Semi-Supervised Object Detection
Apr 04, 2023



Abstract:State-of-the-art 3D object detectors are usually trained on large-scale datasets with high-quality 3D annotations. However, such 3D annotations are often expensive and time-consuming, which may not be practical for real applications. A natural remedy is to adopt semi-supervised learning (SSL) by leveraging a limited amount of labeled samples and abundant unlabeled samples. Current pseudolabeling-based SSL object detection methods mainly adopt a teacher-student framework, with a single fixed threshold strategy to generate supervision signals, which inevitably brings confused supervision when guiding the student network training. Besides, the data augmentation of the point cloud in the typical teacher-student framework is too weak, and only contains basic down sampling and flip-and-shift (i.e., rotate and scaling), which hinders the effective learning of feature information. Hence, we address these issues by introducing a novel approach of Hierarchical Supervision and Shuffle Data Augmentation (HSSDA), which is a simple yet effective teacher-student framework. The teacher network generates more reasonable supervision for the student network by designing a dynamic dual-threshold strategy. Besides, the shuffle data augmentation strategy is designed to strengthen the feature representation ability of the student network. Extensive experiments show that HSSDA consistently outperforms the recent state-of-the-art methods on different datasets. The code will be released at https://github.com/azhuantou/HSSDA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge