Christos Sardianos
Exploring Machine Learning Algorithms for Infection Detection Using GC-IMS Data: A Preliminary Study
Apr 24, 2024



Abstract:The developing field of enhanced diagnostic techniques in the diagnosis of infectious diseases, constitutes a crucial domain in modern healthcare. By utilizing Gas Chromatography-Ion Mobility Spectrometry (GC-IMS) data and incorporating machine learning algorithms into one platform, our research aims to tackle the ongoing issue of precise infection identification. Inspired by these difficulties, our goals consist of creating a strong data analytics process, enhancing machine learning (ML) models, and performing thorough validation for clinical applications. Our research contributes to the emerging field of advanced diagnostic technologies by integrating Gas Chromatography-Ion Mobility Spectrometry (GC-IMS) data and machine learning algorithms within a unified Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) platform. Preliminary trials demonstrate encouraging levels of accuracy when employing various ML algorithms to differentiate between infected and non-infected samples. Continuing endeavors are currently concentrated on enhancing the effectiveness of the model, investigating techniques to clarify its functioning, and incorporating many types of data to further support the early detection of diseases.
Multimodal Explainable Artificial Intelligence: A Comprehensive Review of Methodological Advances and Future Research Directions
Jun 09, 2023



Abstract:The current study focuses on systematically analyzing the recent advances in the field of Multimodal eXplainable Artificial Intelligence (MXAI). In particular, the relevant primary prediction tasks and publicly available datasets are initially described. Subsequently, a structured presentation of the MXAI methods of the literature is provided, taking into account the following criteria: a) The number of the involved modalities, b) The stage at which explanations are produced, and c) The type of the adopted methodology (i.e. mathematical formalism). Then, the metrics used for MXAI evaluation are discussed. Finally, a comprehensive analysis of current challenges and future research directions is provided.
AI-as-a-Service Toolkit for Human-Centered Intelligence in Autonomous Driving
Feb 09, 2022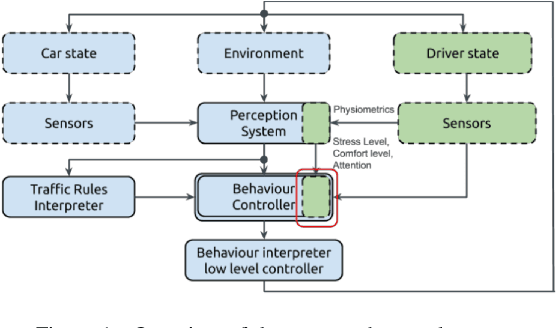
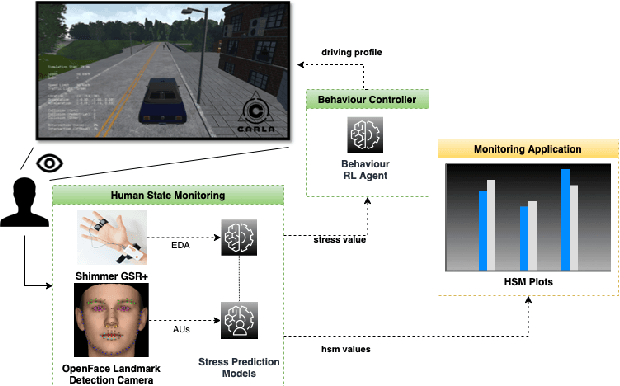
Abstract:This paper presents a proof-of-concept implementation of the AI-as-a-Service toolkit developed within the H2020 TEACHING project and designed to implement an autonomous driving personalization system according to the output of an automatic driver's stress recognition algorithm, both of them realizing a Cyber-Physical System of Systems. In addition, we implemented a data-gathering subsystem to collect data from different sensors, i.e., wearables and cameras, to automatize stress recognition. The system was attached for testing to a driving simulation software, CARLA, which allows testing the approach's feasibility with minimum cost and without putting at risk drivers and passengers. At the core of the relative subsystems, different learning algorithms were implemented using Deep Neural Networks, Recurrent Neural Networks, and Reinforcement Learning.
Blockchain-based Recommender Systems: Applications, Challenges and Future Opportunities
Nov 22, 2021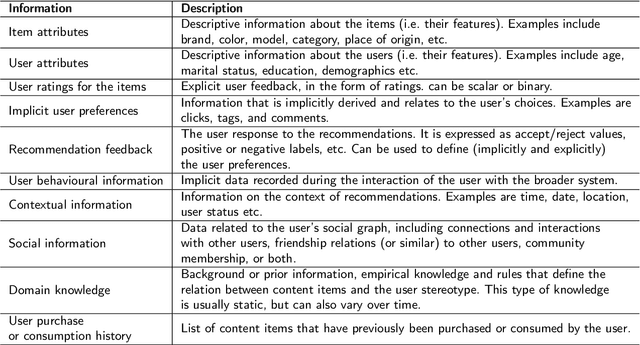
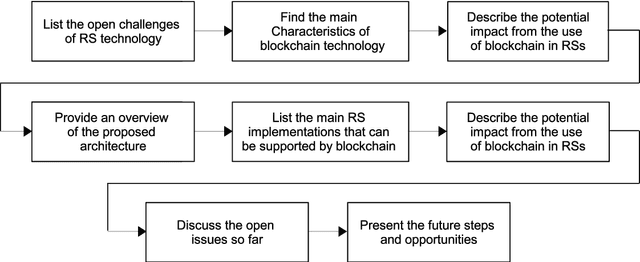
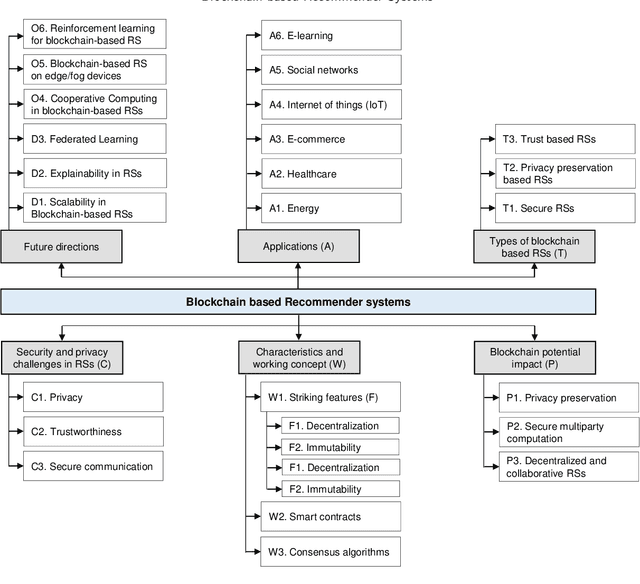
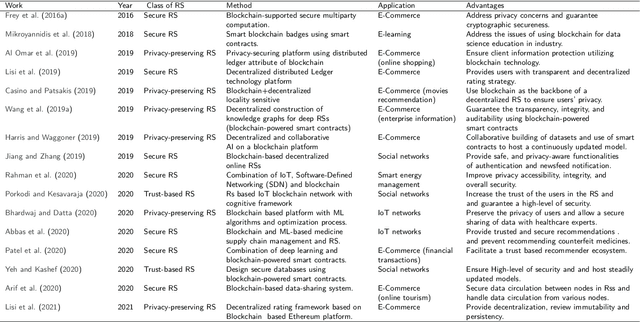
Abstract:Recommender systems have been widely used in different application domains including energy-preservation, e-commerce, healthcare, social media, etc. Such applications require the analysis and mining of massive amounts of various types of user data, including demographics, preferences, social interactions, etc. in order to develop accurate and precise recommender systems. Such datasets often include sensitive information, yet most recommender systems are focusing on the models' accuracy and ignore issues related to security and the users' privacy. Despite the efforts to overcome these problems using different risk reduction techniques, none of them has been completely successful in ensuring cryptographic security and protection of the users' private information. To bridge this gap, the blockchain technology is presented as a promising strategy to promote security and privacy preservation in recommender systems, not only because of its security and privacy salient features, but also due to its resilience, adaptability, fault tolerance and trust characteristics. This paper presents a holistic review of blockchain-based recommender systems covering challenges, open issues and solutions. Accordingly, a well-designed taxonomy is introduced to describe the security and privacy challenges, overview existing frameworks and discuss their applications and benefits when using blockchain before indicating opportunities for future research.
* 25 pages, 6 figures, 3 tables
TEACHING -- Trustworthy autonomous cyber-physical applications through human-centred intelligence
Jul 14, 2021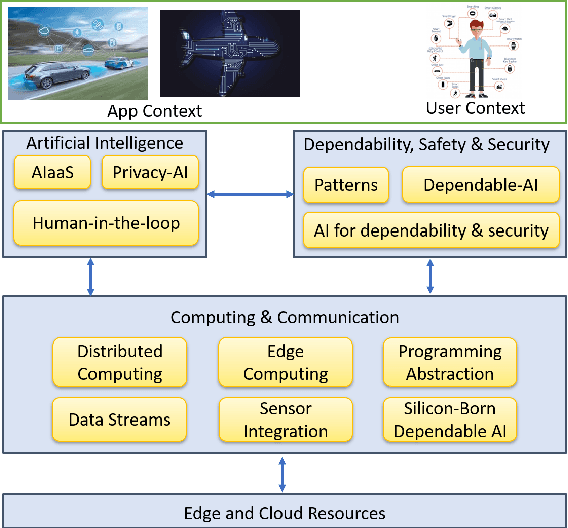
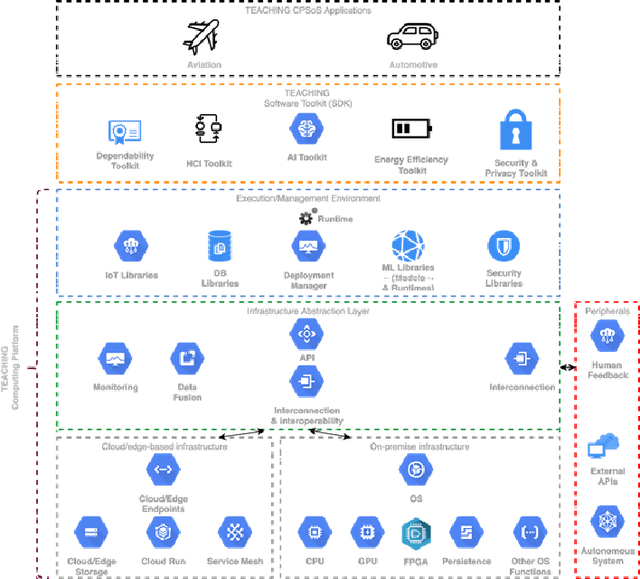
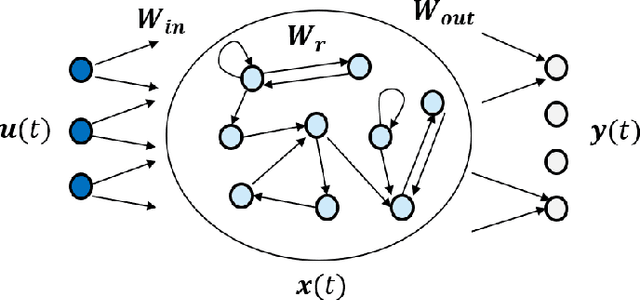
Abstract:This paper discusses the perspective of the H2020 TEACHING project on the next generation of autonomous applications running in a distributed and highly heterogeneous environment comprising both virtual and physical resources spanning the edge-cloud continuum. TEACHING puts forward a human-centred vision leveraging the physiological, emotional, and cognitive state of the users as a driver for the adaptation and optimization of the autonomous applications. It does so by building a distributed, embedded and federated learning system complemented by methods and tools to enforce its dependability, security and privacy preservation. The paper discusses the main concepts of the TEACHING approach and singles out the main AI-related research challenges associated with it. Further, we provide a discussion of the design choices for the TEACHING system to tackle the aforementioned challenges
A survey of recommender systems for energy efficiency in buildings: Principles, challenges and prospects
Feb 09, 2021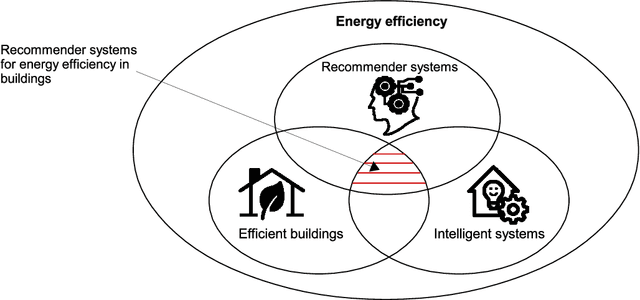
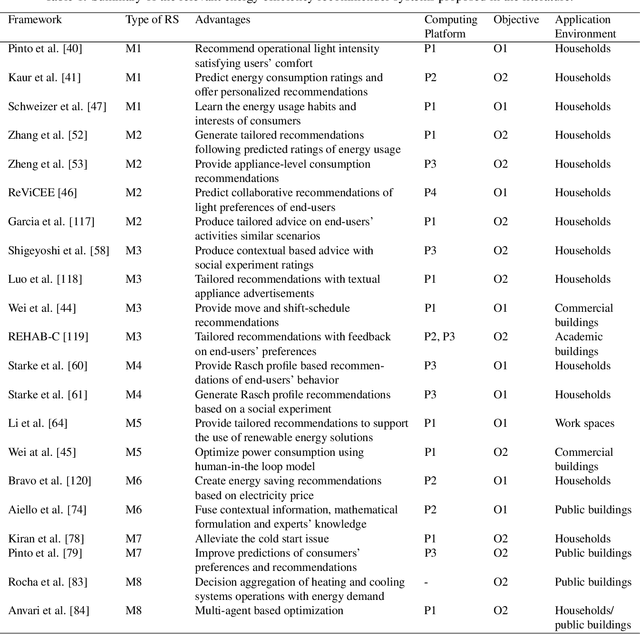

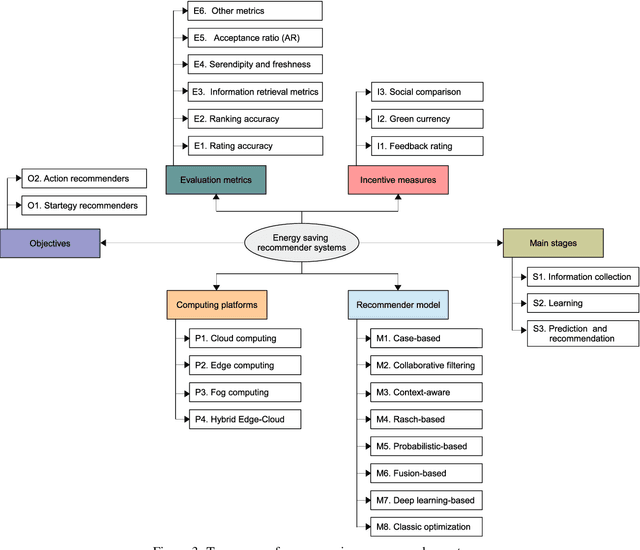
Abstract:Recommender systems have significantly developed in recent years in parallel with the witnessed advancements in both internet of things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. Accordingly, as a consequence of IoT and AI, multiple forms of data are incorporated in these systems, e.g. social, implicit, local and personal information, which can help in improving recommender systems' performance and widen their applicability to traverse different disciplines. On the other side, energy efficiency in the building sector is becoming a hot research topic, in which recommender systems play a major role by promoting energy saving behavior and reducing carbon emissions. However, the deployment of the recommendation frameworks in buildings still needs more investigations to identify the current challenges and issues, where their solutions are the keys to enable the pervasiveness of research findings, and therefore, ensure a large-scale adoption of this technology. Accordingly, this paper presents, to the best of the authors' knowledge, the first timely and comprehensive reference for energy-efficiency recommendation systems through (i) surveying existing recommender systems for energy saving in buildings; (ii) discussing their evolution; (iii) providing an original taxonomy of these systems based on specified criteria, including the nature of the recommender engine, its objective, computing platforms, evaluation metrics and incentive measures; and (iv) conducting an in-depth, critical analysis to identify their limitations and unsolved issues. The derived challenges and areas of future implementation could effectively guide the energy research community to improve the energy-efficiency in buildings and reduce the cost of developed recommender systems-based solutions.
* 35 pages, 11 figures, 1 table
The emergence of Explainability of Intelligent Systems: Delivering Explainable and Personalised Recommendations for Energy Efficiency
Oct 26, 2020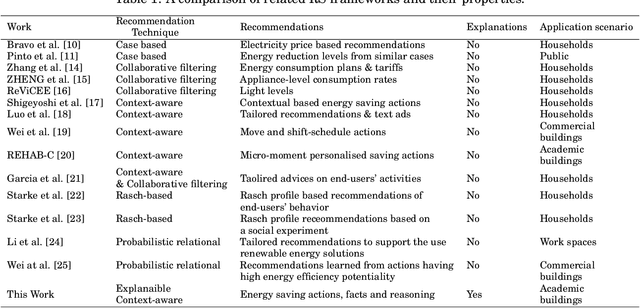
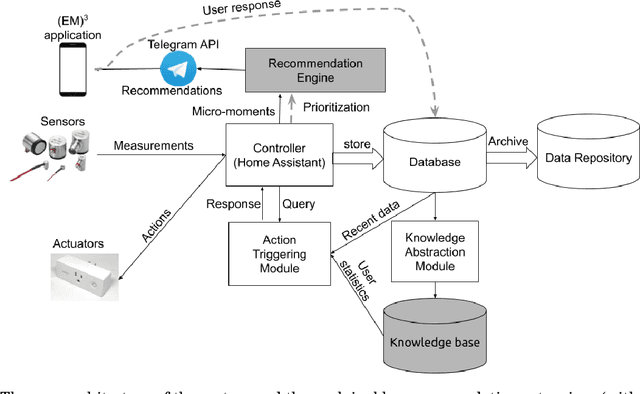
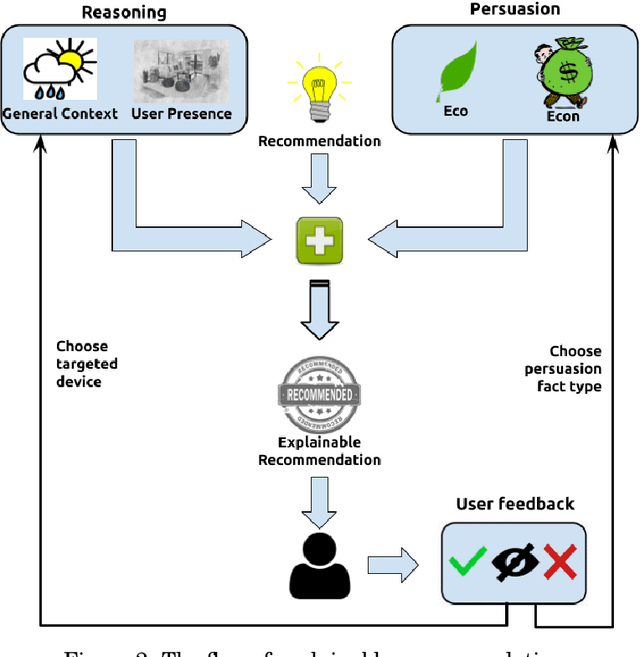
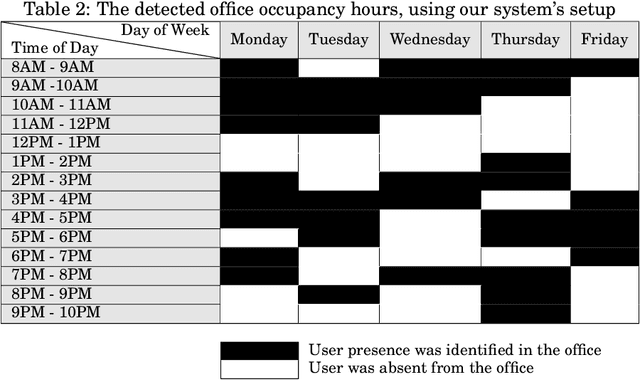
Abstract:The recent advances in artificial intelligence namely in machine learning and deep learning, have boosted the performance of intelligent systems in several ways. This gave rise to human expectations, but also created the need for a deeper understanding of how intelligent systems think and decide. The concept of explainability appeared, in the extent of explaining the internal system mechanics in human terms. Recommendation systems are intelligent systems that support human decision making, and as such, they have to be explainable in order to increase user trust and improve the acceptance of recommendations. In this work, we focus on a context-aware recommendation system for energy efficiency and develop a mechanism for explainable and persuasive recommendations, which are personalized to user preferences and habits. The persuasive facts either emphasize on the economical saving prospects (Econ) or on a positive ecological impact (Eco) and explanations provide the reason for recommending an energy saving action. Based on a study conducted using a Telegram bot, different scenarios have been validated with actual data and human feedback. Current results show a total increase of 19\% on the recommendation acceptance ratio when both economical and ecological persuasive facts are employed. This revolutionary approach on recommendation systems, demonstrates how intelligent recommendations can effectively encourage energy saving behavior.
* 19 pages, 8 figures, 1 table
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge