Christos Chronis
Public space security management using digital twin technologies
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:As the security of public spaces remains a critical issue in today's world, Digital Twin technologies have emerged in recent years as a promising solution for detecting and predicting potential future threats. The applied methodology leverages a Digital Twin of a metro station in Athens, Greece, using the FlexSim simulation software. The model encompasses points of interest and passenger flows, and sets their corresponding parameters. These elements influence and allow the model to provide reasonable predictions on the security management of the station under various scenarios. Experimental tests are conducted with different configurations of surveillance cameras and optimizations of camera angles to evaluate the effectiveness of the space surveillance setup. The results show that the strategic positioning of surveillance cameras and the adjustment of their angles significantly improves the detection of suspicious behaviors and with the use of the DT it is possible to evaluate different scenarios and find the optimal camera setup for each case. In summary, this study highlights the value of Digital Twins in real-time simulation and data-driven security management. The proposed approach contributes to the ongoing development of smart security solutions for public spaces and provides an innovative framework for threat detection and prevention.
AI-as-a-Service Toolkit for Human-Centered Intelligence in Autonomous Driving
Feb 09, 2022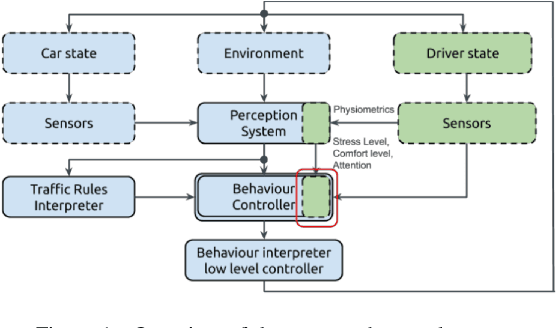
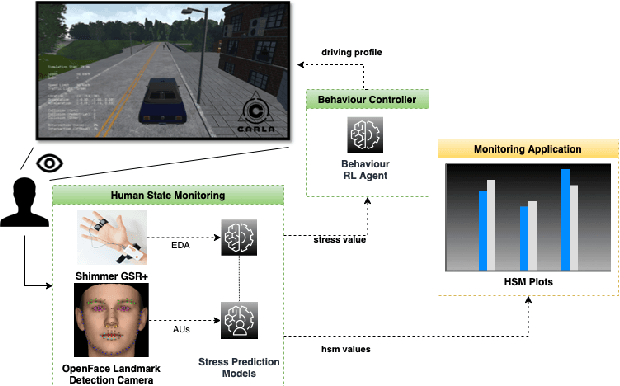
Abstract:This paper presents a proof-of-concept implementation of the AI-as-a-Service toolkit developed within the H2020 TEACHING project and designed to implement an autonomous driving personalization system according to the output of an automatic driver's stress recognition algorithm, both of them realizing a Cyber-Physical System of Systems. In addition, we implemented a data-gathering subsystem to collect data from different sensors, i.e., wearables and cameras, to automatize stress recognition. The system was attached for testing to a driving simulation software, CARLA, which allows testing the approach's feasibility with minimum cost and without putting at risk drivers and passengers. At the core of the relative subsystems, different learning algorithms were implemented using Deep Neural Networks, Recurrent Neural Networks, and Reinforcement Learning.
The emergence of Explainability of Intelligent Systems: Delivering Explainable and Personalised Recommendations for Energy Efficiency
Oct 26, 2020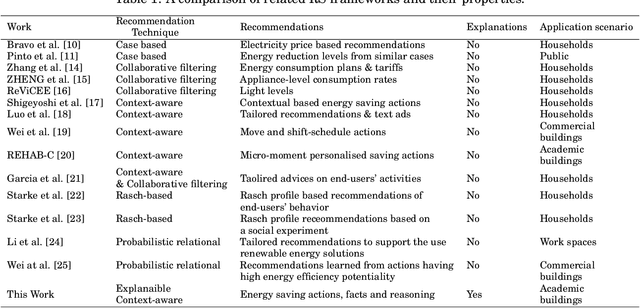
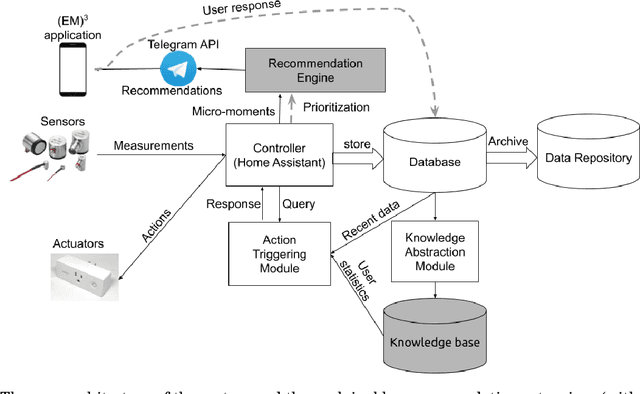
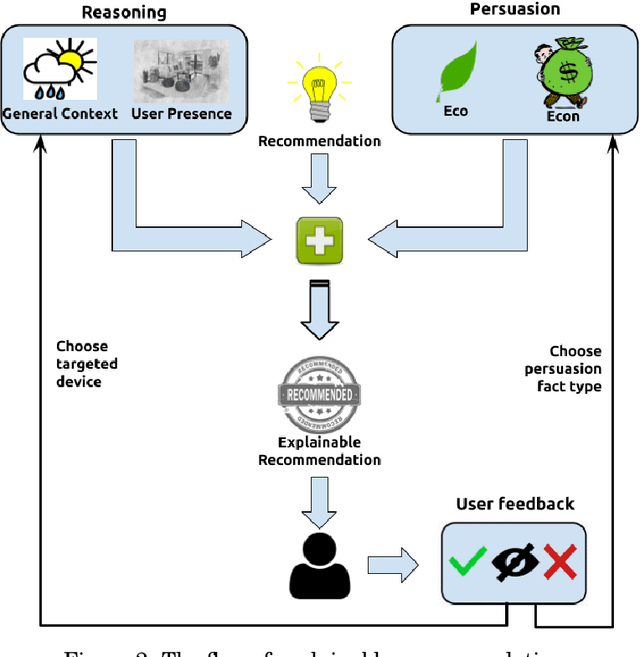
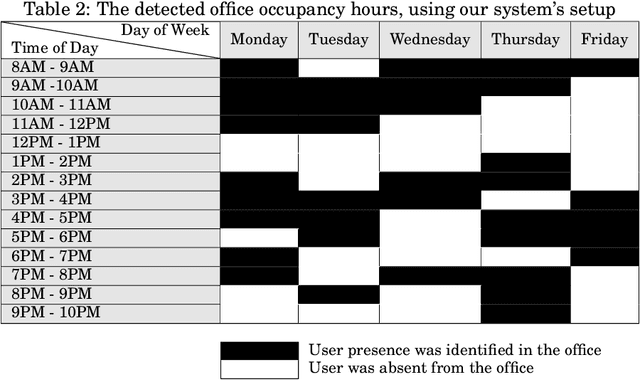
Abstract:The recent advances in artificial intelligence namely in machine learning and deep learning, have boosted the performance of intelligent systems in several ways. This gave rise to human expectations, but also created the need for a deeper understanding of how intelligent systems think and decide. The concept of explainability appeared, in the extent of explaining the internal system mechanics in human terms. Recommendation systems are intelligent systems that support human decision making, and as such, they have to be explainable in order to increase user trust and improve the acceptance of recommendations. In this work, we focus on a context-aware recommendation system for energy efficiency and develop a mechanism for explainable and persuasive recommendations, which are personalized to user preferences and habits. The persuasive facts either emphasize on the economical saving prospects (Econ) or on a positive ecological impact (Eco) and explanations provide the reason for recommending an energy saving action. Based on a study conducted using a Telegram bot, different scenarios have been validated with actual data and human feedback. Current results show a total increase of 19\% on the recommendation acceptance ratio when both economical and ecological persuasive facts are employed. This revolutionary approach on recommendation systems, demonstrates how intelligent recommendations can effectively encourage energy saving behavior.
* 19 pages, 8 figures, 1 table
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge