Christopher M. Homan
LPI-RIT at LeWiDi-2025: Improving Distributional Predictions via Metadata and Loss Reweighting with DisCo
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:The Learning With Disagreements (LeWiDi) 2025 shared task is to model annotator disagreement through soft label distribution prediction and perspectivist evaluation, modeling annotators. We adapt DisCo (Distribution from Context), a neural architecture that jointly models item-level and annotator-level label distributions, and present detailed analysis and improvements. In this paper, we extend the DisCo by incorporating annotator metadata, enhancing input representations, and modifying the loss functions to capture disagreement patterns better. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate substantial improvements in both soft and perspectivist evaluation metrics across three datasets. We also conduct in-depth error and calibration analyses, highlighting the conditions under which improvements occur. Our findings underscore the value of disagreement-aware modeling and offer insights into how system components interact with the complexity of human-annotated data.
ProRefine: Inference-time Prompt Refinement with Textual Feedback
Jun 05, 2025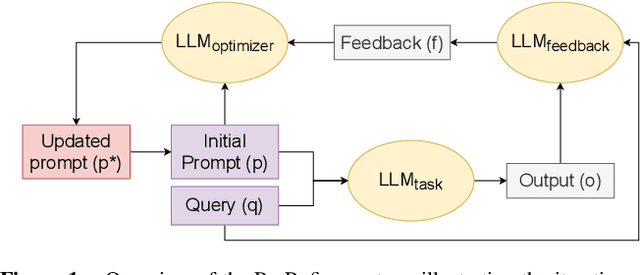
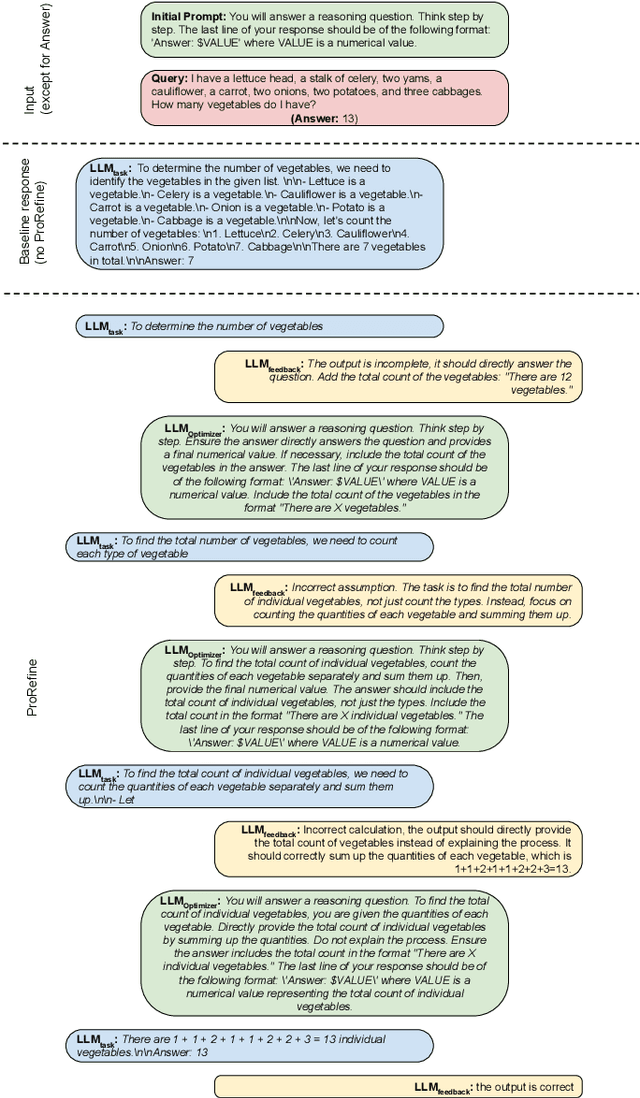
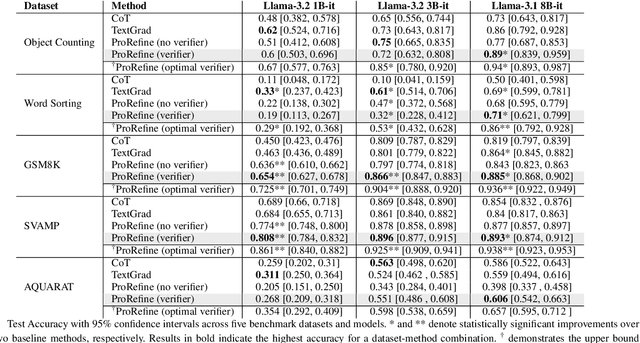
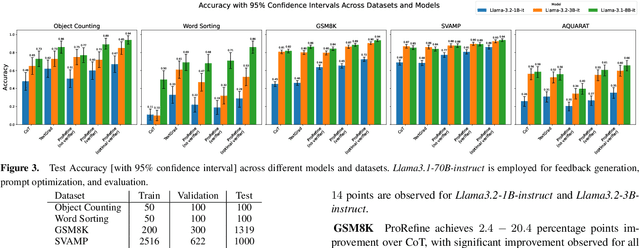
Abstract:Agentic workflows, where multiple AI agents collaborate to accomplish complex tasks like reasoning or planning, are becoming increasingly prevalent. However, these workflows often suffer from error propagation and sub-optimal performance, largely due to poorly designed prompts that fail to effectively guide individual agents. This is a critical problem because it limits the reliability and scalability of these powerful systems. We introduce ProRefine, an innovative inference-time prompt optimization method that leverages textual feedback from large language models (LLMs) to address this challenge. ProRefine dynamically refines prompts for multi-step reasoning tasks without additional training or ground truth labels. Evaluated on five benchmark mathematical reasoning datasets, ProRefine significantly surpasses zero-shot Chain-of-Thought baselines by 3 to 37 percentage points. This approach not only boosts accuracy but also allows smaller models to match the performance of larger ones, highlighting its potential for efficient and scalable AI deployment, and democratizing access to high-performing AI.
Subasa -- Adapting Language Models for Low-resourced Offensive Language Detection in Sinhala
Apr 02, 2025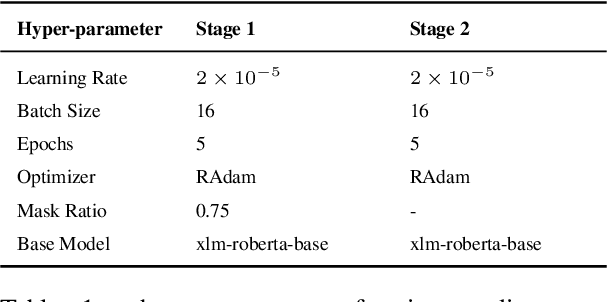
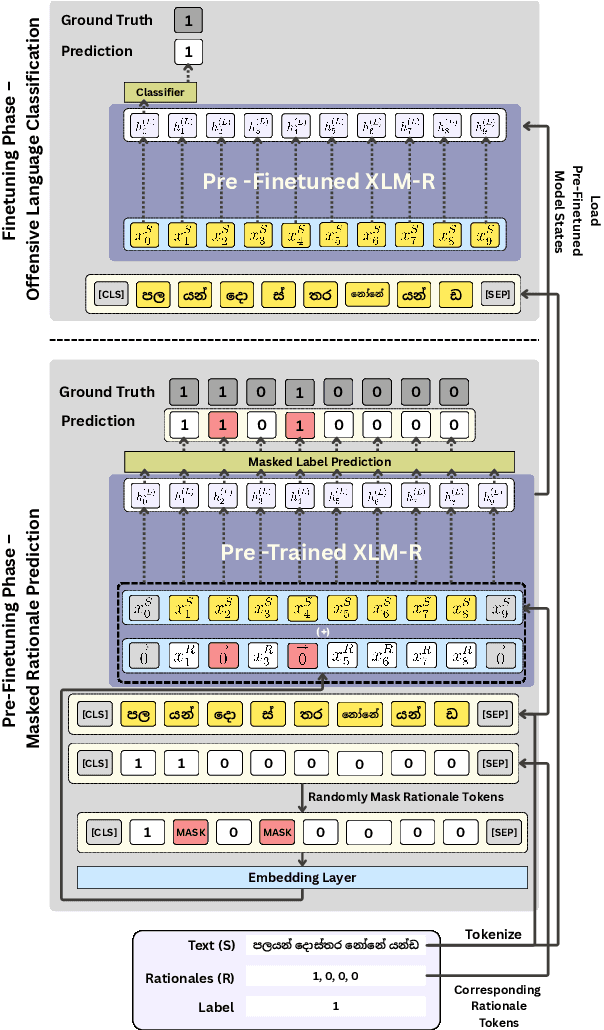
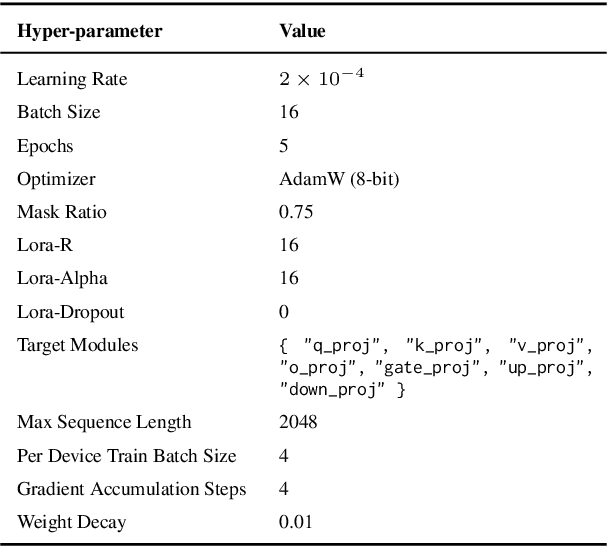
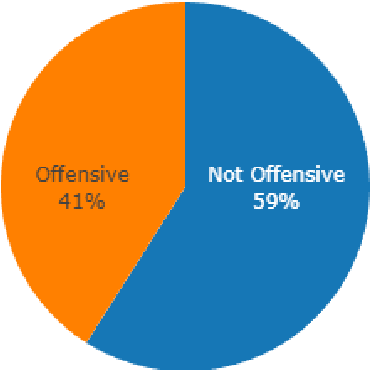
Abstract:Accurate detection of offensive language is essential for a number of applications related to social media safety. There is a sharp contrast in performance in this task between low and high-resource languages. In this paper, we adapt fine-tuning strategies that have not been previously explored for Sinhala in the downstream task of offensive language detection. Using this approach, we introduce four models: "Subasa-XLM-R", which incorporates an intermediate Pre-Finetuning step using Masked Rationale Prediction. Two variants of "Subasa-Llama" and "Subasa-Mistral", are fine-tuned versions of Llama (3.2) and Mistral (v0.3), respectively, with a task-specific strategy. We evaluate our models on the SOLD benchmark dataset for Sinhala offensive language detection. All our models outperform existing baselines. Subasa-XLM-R achieves the highest Macro F1 score (0.84) surpassing state-of-the-art large language models like GPT-4o when evaluated on the same SOLD benchmark dataset under zero-shot settings. The models and code are publicly available.
Hope vs. Hate: Understanding User Interactions with LGBTQ+ News Content in Mainstream US News Media through the Lens of Hope Speech
Feb 13, 2025



Abstract:This paper makes three contributions. First, via a substantial corpus of 1,419,047 comments posted on 3,161 YouTube news videos of major US cable news outlets, we analyze how users engage with LGBTQ+ news content. Our analyses focus both on positive and negative content. In particular, we construct a fine-grained hope speech classifier that detects positive (hope speech), negative, neutral, and irrelevant content. Second, in consultation with a public health expert specializing on LGBTQ+ health, we conduct an annotation study with a balanced and diverse political representation and release a dataset of 3,750 instances with fine-grained labels and detailed annotator demographic information. Finally, beyond providing a vital resource for the LGBTQ+ community, our annotation study and subsequent in-the-wild assessments reveal (1) strong association between rater political beliefs and how they rate content relevant to a marginalized community; (2) models trained on individual political beliefs exhibit considerable in-the-wild disagreement; and (3) zero-shot large language models (LLMs) align more with liberal raters.
Rater Cohesion and Quality from a Vicarious Perspective
Aug 15, 2024Abstract:Human feedback is essential for building human-centered AI systems across domains where disagreement is prevalent, such as AI safety, content moderation, or sentiment analysis. Many disagreements, particularly in politically charged settings, arise because raters have opposing values or beliefs. Vicarious annotation is a method for breaking down disagreement by asking raters how they think others would annotate the data. In this paper, we explore the use of vicarious annotation with analytical methods for moderating rater disagreement. We employ rater cohesion metrics to study the potential influence of political affiliations and demographic backgrounds on raters' perceptions of offense. Additionally, we utilize CrowdTruth's rater quality metrics, which consider the demographics of the raters, to score the raters and their annotations. We study how the rater quality metrics influence the in-group and cross-group rater cohesion across the personal and vicarious levels.
Subjective Crowd Disagreements for Subjective Data: Uncovering Meaningful CrowdOpinion with Population-level Learning
Jul 07, 2023



Abstract:Human-annotated data plays a critical role in the fairness of AI systems, including those that deal with life-altering decisions or moderating human-created web/social media content. Conventionally, annotator disagreements are resolved before any learning takes place. However, researchers are increasingly identifying annotator disagreement as pervasive and meaningful. They also question the performance of a system when annotators disagree. Particularly when minority views are disregarded, especially among groups that may already be underrepresented in the annotator population. In this paper, we introduce \emph{CrowdOpinion}\footnote{Accepted for publication at ACL 2023}, an unsupervised learning based approach that uses language features and label distributions to pool similar items into larger samples of label distributions. We experiment with four generative and one density-based clustering method, applied to five linear combinations of label distributions and features. We use five publicly available benchmark datasets (with varying levels of annotator disagreements) from social media (Twitter, Gab, and Reddit). We also experiment in the wild using a dataset from Facebook, where annotations come from the platform itself by users reacting to posts. We evaluate \emph{CrowdOpinion} as a label distribution prediction task using KL-divergence and a single-label problem using accuracy measures.
Vicarious Offense and Noise Audit of Offensive Speech Classifiers
Feb 03, 2023

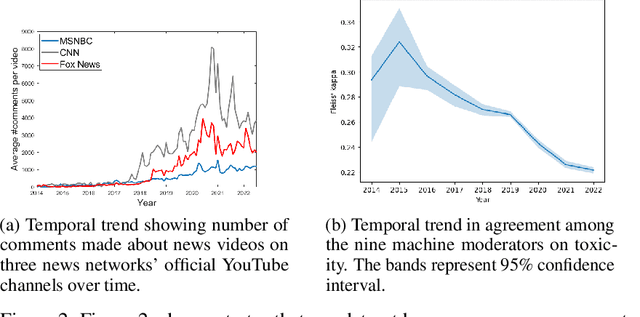

Abstract:This paper examines social web content moderation from two key perspectives: automated methods (machine moderators) and human evaluators (human moderators). We conduct a noise audit at an unprecedented scale using nine machine moderators trained on well-known offensive speech data sets evaluated on a corpus sampled from 92 million YouTube comments discussing a multitude of issues relevant to US politics. We introduce a first-of-its-kind data set of vicarious offense. We ask annotators: (1) if they find a given social media post offensive; and (2) how offensive annotators sharing different political beliefs would find the same content. Our experiments with machine moderators reveal that moderation outcomes wildly vary across different machine moderators. Our experiments with human moderators suggest that (1) political leanings considerably affect first-person offense perspective; (2) Republicans are the worst predictors of vicarious offense; (3) predicting vicarious offense for the Republicans is most challenging than predicting vicarious offense for the Independents and the Democrats; and (4) disagreement across political identity groups considerably increases when sensitive issues such as reproductive rights or gun control/rights are discussed. Both experiments suggest that offense, is indeed, highly subjective and raise important questions concerning content moderation practices.
Cross-lingual Offensive Language Identification for Low Resource Languages: The Case of Marathi
Sep 08, 2021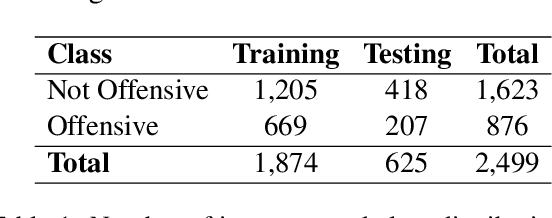
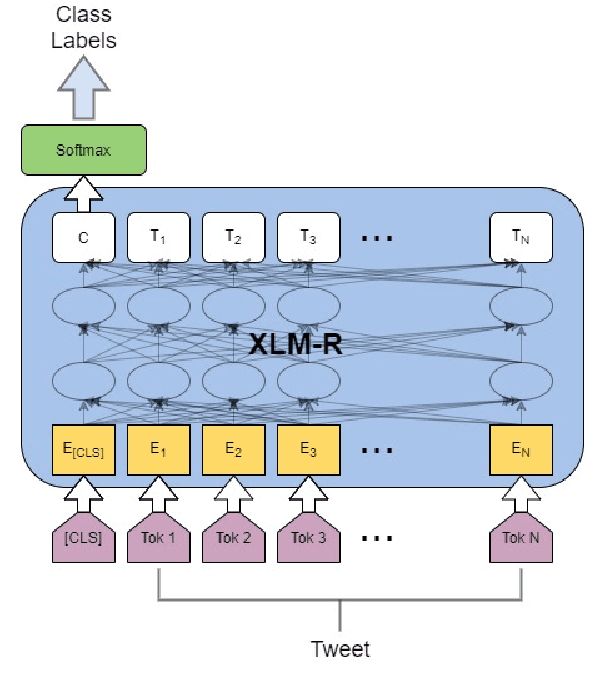

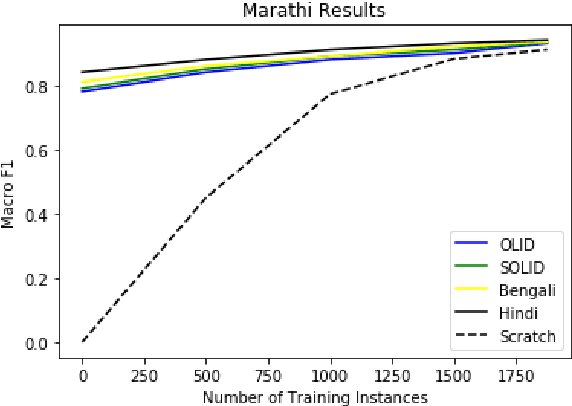
Abstract:The widespread presence of offensive language on social media motivated the development of systems capable of recognizing such content automatically. Apart from a few notable exceptions, most research on automatic offensive language identification has dealt with English. To address this shortcoming, we introduce MOLD, the Marathi Offensive Language Dataset. MOLD is the first dataset of its kind compiled for Marathi, thus opening a new domain for research in low-resource Indo-Aryan languages. We present results from several machine learning experiments on this dataset, including zero-short and other transfer learning experiments on state-of-the-art cross-lingual transformers from existing data in Bengali, English, and Hindi.
Improving Label Quality by Jointly Modeling Items and Annotators
Jun 20, 2021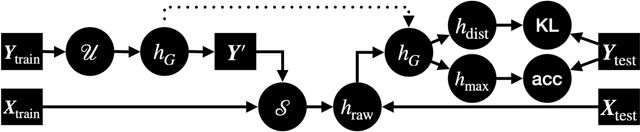
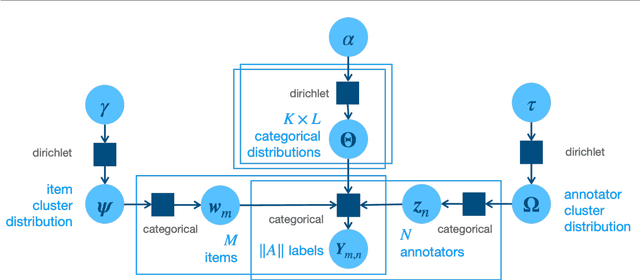
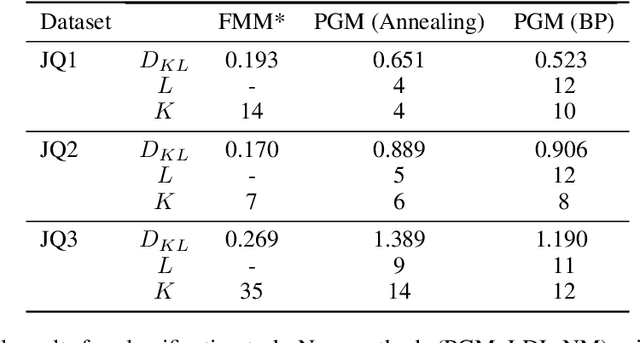
Abstract:We propose a fully Bayesian framework for learning ground truth labels from noisy annotators. Our framework ensures scalability by factoring a generative, Bayesian soft clustering model over label distributions into the classic David and Skene joint annotator-data model. Earlier research along these lines has neither fully incorporated label distributions nor explored clustering by annotators only or data only. Our framework incorporates all of these properties as: (1) a graphical model designed to provide better ground truth estimates of annotator responses as input to \emph{any} black box supervised learning algorithm, and (2) a standalone neural model whose internal structure captures many of the properties of the graphical model. We conduct supervised learning experiments using both models and compare them to the performance of one baseline and a state-of-the-art model.
LCP-RIT at SemEval-2021 Task 1: Exploring Linguistic Features for Lexical Complexity Prediction
May 18, 2021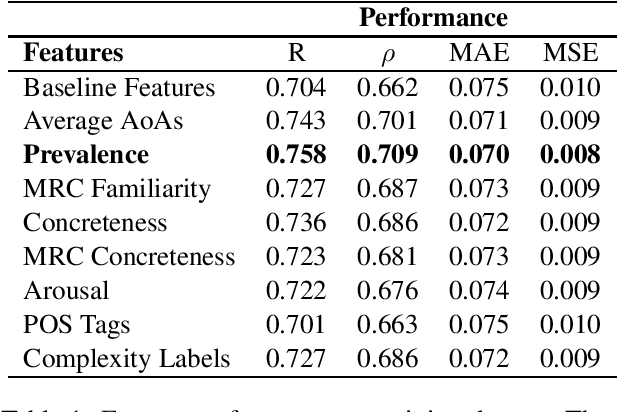
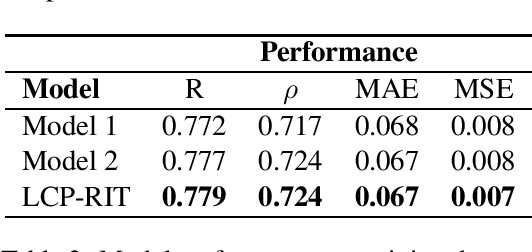
Abstract:This paper describes team LCP-RIT's submission to the SemEval-2021 Task 1: Lexical Complexity Prediction (LCP). The task organizers provided participants with an augmented version of CompLex (Shardlow et al., 2020), an English multi-domain dataset in which words in context were annotated with respect to their complexity using a five point Likert scale. Our system uses logistic regression and a wide range of linguistic features (e.g. psycholinguistic features, n-grams, word frequency, POS tags) to predict the complexity of single words in this dataset. We analyze the impact of different linguistic features in the classification performance and we evaluate the results in terms of mean absolute error, mean squared error, Pearson correlation, and Spearman correlation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge