Saurabh Gaikwad
Predicting the Type and Target of Offensive Social Media Posts in Marathi
Nov 22, 2022Abstract:The presence of offensive language on social media is very common motivating platforms to invest in strategies to make communities safer. This includes developing robust machine learning systems capable of recognizing offensive content online. Apart from a few notable exceptions, most research on automatic offensive language identification has dealt with English and a few other high resource languages such as French, German, and Spanish. In this paper we address this gap by tackling offensive language identification in Marathi, a low-resource Indo-Aryan language spoken in India. We introduce the Marathi Offensive Language Dataset v.2.0 or MOLD 2.0 and present multiple experiments on this dataset. MOLD 2.0 is a much larger version of MOLD with expanded annotation to the levels B (type) and C (target) of the popular OLID taxonomy. MOLD 2.0 is the first hierarchical offensive language dataset compiled for Marathi, thus opening new avenues for research in low-resource Indo-Aryan languages. Finally, we also introduce SeMOLD, a larger dataset annotated following the semi-supervised methods presented in SOLID.
Cross-lingual Offensive Language Identification for Low Resource Languages: The Case of Marathi
Sep 08, 2021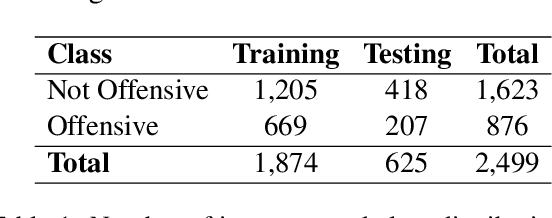
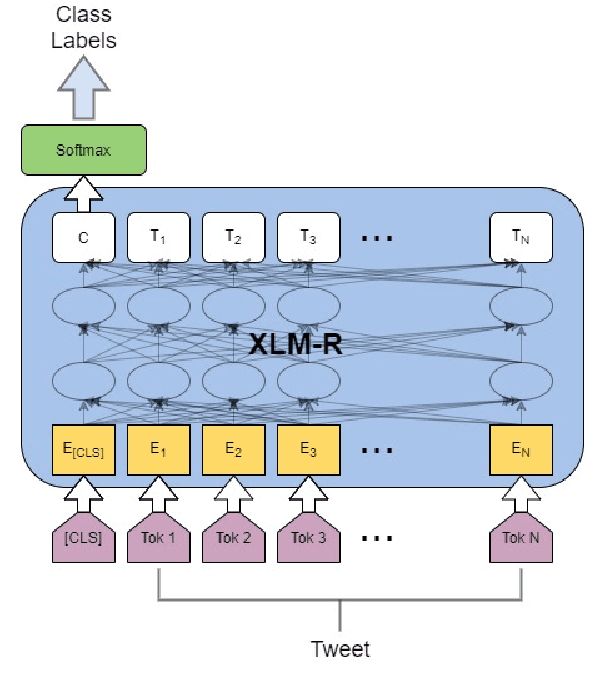

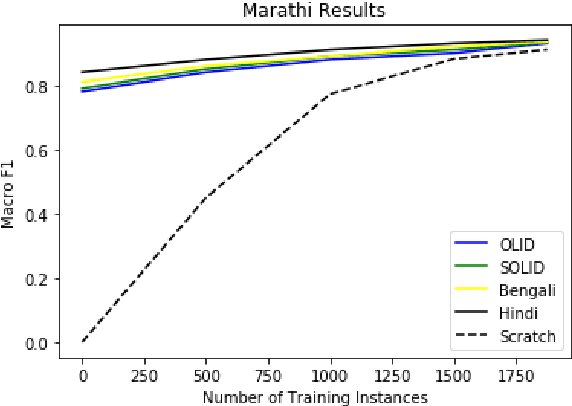
Abstract:The widespread presence of offensive language on social media motivated the development of systems capable of recognizing such content automatically. Apart from a few notable exceptions, most research on automatic offensive language identification has dealt with English. To address this shortcoming, we introduce MOLD, the Marathi Offensive Language Dataset. MOLD is the first dataset of its kind compiled for Marathi, thus opening a new domain for research in low-resource Indo-Aryan languages. We present results from several machine learning experiments on this dataset, including zero-short and other transfer learning experiments on state-of-the-art cross-lingual transformers from existing data in Bengali, English, and Hindi.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge