Christopher C. Lamb
Mind the Gap: On Bridging the Semantic Gap between Machine Learning and Information Security
May 04, 2020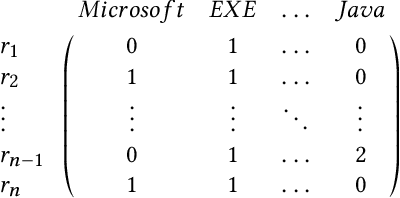
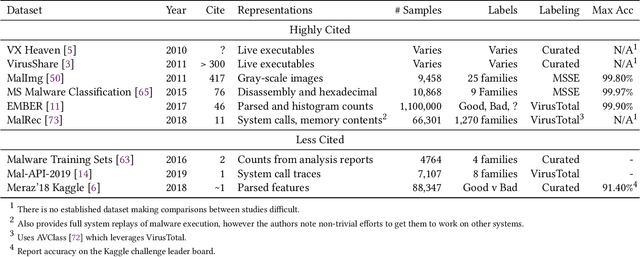

Abstract:Despite the potential of Machine learning (ML) to learn the behavior of malware, detect novel malware samples, and significantly improve information security (InfoSec) we see few, if any, high-impact ML techniques in deployed systems, notwithstanding multiple reported successes in open literature. We hypothesize that the failure of ML in making high-impacts in InfoSec are rooted in a disconnect between the two communities as evidenced by a semantic gap---a difference in how executables are described (e.g. the data and features extracted from the data). Specifically, current datasets and representations used by ML are not suitable for learning the behaviors of an executable and differ significantly from those used by the InfoSec community. In this paper, we survey existing datasets used for classifying malware by ML algorithms and the features that are extracted from the data. We observe that: 1) the current set of extracted features are primarily syntactic, not behavioral, 2) datasets generally contain extreme exemplars producing a dataset in which it is easy to discriminate classes, and 3) the datasets provide significantly different representations of the data encountered in real-world systems. For ML to make more of an impact in the InfoSec community requires a change in the data (including the features and labels) that is used to bridge the current semantic gap. As a first step in enabling more behavioral analyses, we label existing malware datasets with behavioral features using open-source threat reports associated with malware families. This behavioral labeling alters the analysis from identifying intent (e.g. good vs bad) or malware family membership to an analysis of which behaviors are exhibited by an executable. We offer the annotations with the hope of inspiring future improvements in the data that will further bridge the semantic gap between the ML and InfoSec communities.
Dynamic Analysis of Executables to Detect and Characterize Malware
Sep 28, 2018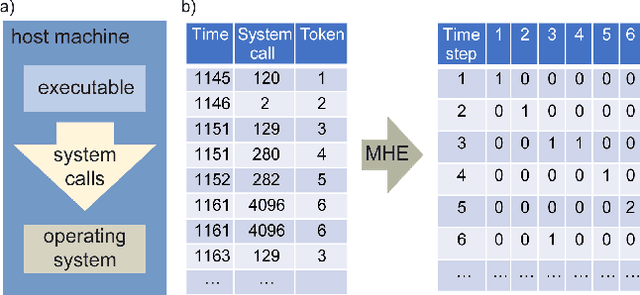
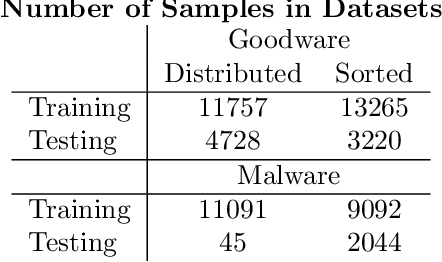
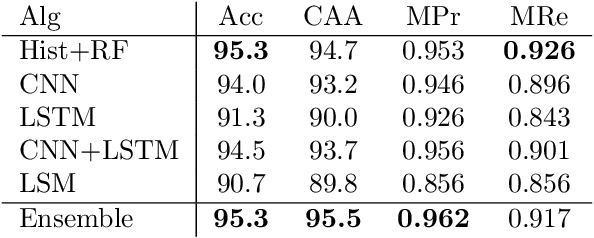
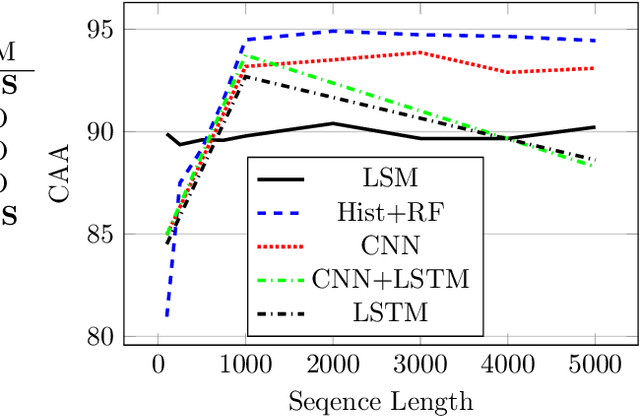
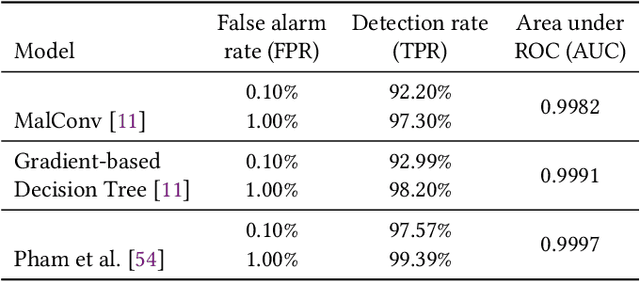
Abstract:It is needed to ensure the integrity of systems that process sensitive information and control many aspects of everyday life. We examine the use of machine learning algorithms to detect malware using the system calls generated by executables-alleviating attempts at obfuscation as the behavior is monitored rather than the bytes of an executable. We examine several machine learning techniques for detecting malware including random forests, deep learning techniques, and liquid state machines. The experiments examine the effects of concept drift on each algorithm to understand how well the algorithms generalize to novel malware samples by testing them on data that was collected after the training data. The results suggest that each of the examined machine learning algorithms is a viable solution to detect malware-achieving between 90% and 95% class-averaged accuracy (CAA). In real-world scenarios, the performance evaluation on an operational network may not match the performance achieved in training. Namely, the CAA may be about the same, but the values for precision and recall over the malware can change significantly. We structure experiments to highlight these caveats and offer insights into expected performance in operational environments. In addition, we use the induced models to gain a better understanding about what differentiates the malware samples from the goodware, which can further be used as a forensics tool to understand what the malware (or goodware) was doing to provide directions for investigation and remediation.
Neurogenesis Deep Learning
Mar 28, 2017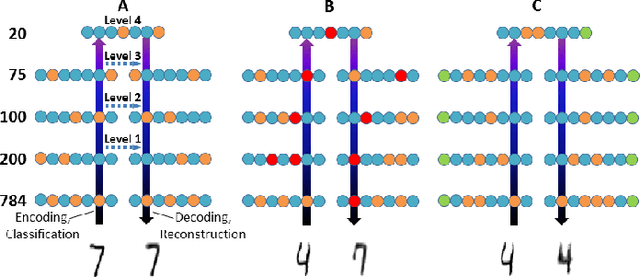
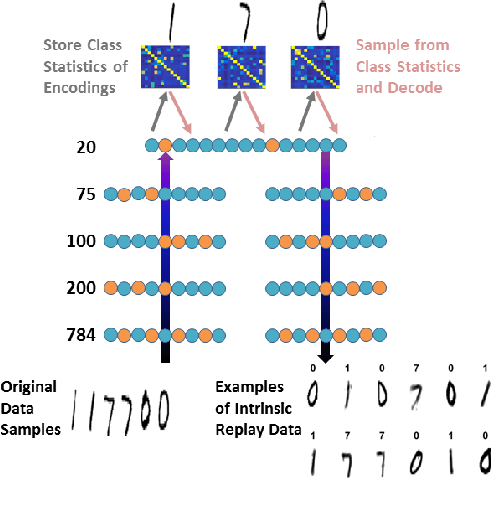

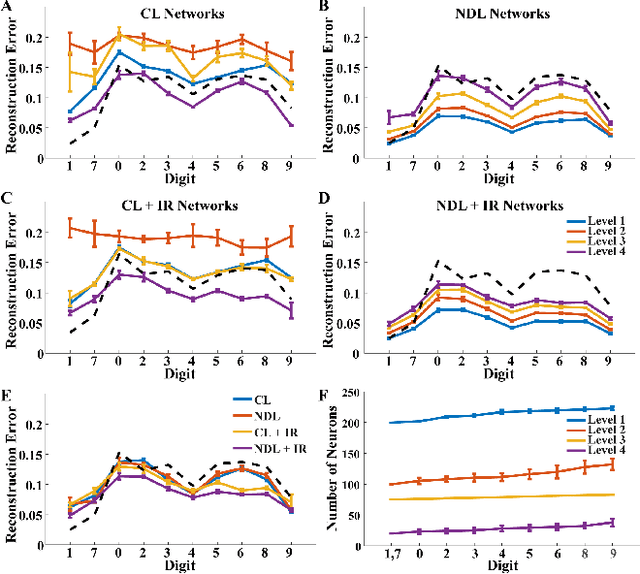
Abstract:Neural machine learning methods, such as deep neural networks (DNN), have achieved remarkable success in a number of complex data processing tasks. These methods have arguably had their strongest impact on tasks such as image and audio processing - data processing domains in which humans have long held clear advantages over conventional algorithms. In contrast to biological neural systems, which are capable of learning continuously, deep artificial networks have a limited ability for incorporating new information in an already trained network. As a result, methods for continuous learning are potentially highly impactful in enabling the application of deep networks to dynamic data sets. Here, inspired by the process of adult neurogenesis in the hippocampus, we explore the potential for adding new neurons to deep layers of artificial neural networks in order to facilitate their acquisition of novel information while preserving previously trained data representations. Our results on the MNIST handwritten digit dataset and the NIST SD 19 dataset, which includes lower and upper case letters and digits, demonstrate that neurogenesis is well suited for addressing the stability-plasticity dilemma that has long challenged adaptive machine learning algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge