Chifu Yang
Effects of Muscle Synergy during Overhead Work with a Passive Shoulder Exoskeleton: A Case Study
Nov 23, 2024Abstract:Objective: Shoulder exoskeletons can effectively assist with overhead work. However, their impacts on muscle synergy remain unclear. The objective is to systematically investigate the effects of the shoulder exoskeleton on muscle synergies during overhead work.Methods: Eight male participants were recruited to perform a screwing task both with (Intervention) and without (Normal) the exoskeleton. Eight muscles were monitored and muscle synergies were extracted using non-negative matrix factorization and electromyographic topographic maps. Results: The number of synergies extracted was the same (n = 2) in both conditions. Specifically, the first synergies in both conditions were identical, with the highest weight of AD and MD; while the second synergies were different between conditions, with highest weight of PM and MD, respectively. As for the first synergy in the Intervention condition, the activation profile significantly decreased, and the average recruitment level and activation duration were significantly lower (p<0.05). The regression analysis for the muscle synergies across conditions shows the changes of muscle synergies did not influence the sparseness of muscle synergies (p=0.7341). In the topographic maps, the mean value exhibited a significant decrease (p<0.001) and the entropy significantly increased (p<0.01). Conclusion: The exoskeleton does not alter the number of synergies and existing major synergies but may induce new synergies. It can also significantly decrease neural activation and may influence the heterogeneity of the distribution of monitored muscle activations. Significance: This study provides insights into the potential mechanisms of exoskeleton-assisted overhead work and guidance on improving the performance of exoskeletons.
A Novel Passive Occupational Shoulder Exoskeleton With Adjustable Peak Assistive Torque Angle For Overhead Tasks
Nov 21, 2024Abstract:Objective: Overhead tasks are a primary inducement to work-related musculoskeletal disorders. Aiming to reduce shoulder physical loads, passive shoulder exoskeletons are increasingly prevalent in the industry due to their lightweight, affordability, and effectiveness. However, they can only handle specific tasks and struggle to balance compactness with a sufficient range of motion effectively. Method: We proposed a novel passive occupational shoulder exoskeleton designed to handle various overhead tasks at different arm elevation angles, ensuring sufficient ROM while maintaining compactness. By formulating kinematic models and simulations, an ergonomic shoulder structure was developed. Then, we presented a torque generator equipped with an adjustable peak assistive torque angle to switch between low and high assistance phases through a passive clutch mechanism. Ten healthy participants were recruited to validate its functionality by performing the screwing task. Results: Measured range of motion results demonstrated that the exoskeleton can ensure a sufficient ROM in both sagittal (164$^\circ$) and horizontal (158$^\circ$) flexion/extension movements. The experimental results of the screwing task showed that the exoskeleton could reduce muscle activation (up to 49.6%), perceived effort and frustration, and provide an improved user experience (scored 79.7 out of 100). Conclusion: These results indicate that the proposed exoskeleton can guarantee natural movements and provide efficient assistance during overhead work, and thus have the potential to reduce the risk of musculoskeletal disorders. Significance: The proposed exoskeleton provides insights into multi-task adaptability and efficient assistance, highlighting the potential for expanding the application of exoskeletons.
Detecting and Correcting IMU Movements During Joint Angle Estimation
Jun 09, 2021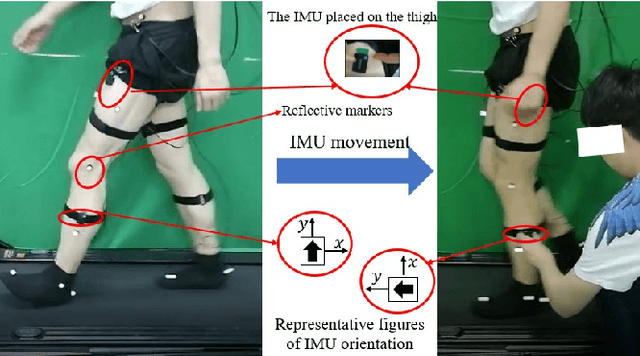
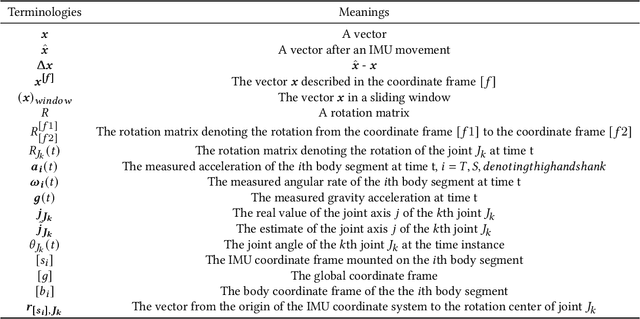
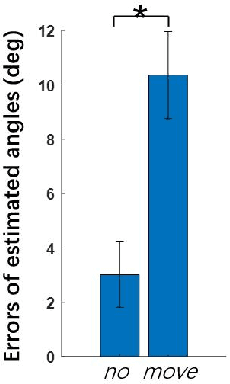
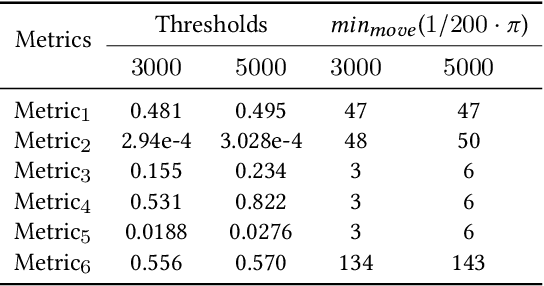
Abstract:Inertial measurement units (IMUs) increasingly function as a basic component of wearable sensor network (WSN)systems. IMU-based joint angle estimation (JAE) is a relatively typical usage of IMUs, with extensive applications. However, the issue that IMUs move with respect to their original placement during JAE is still a research gap, and limits the robustness of deploying the technique in real-world application scenarios. In this study, we propose to detect and correct the IMU movement online in a relatively computationally lightweight manner. Particularly, we first experimentally investigate the influence of IMU movements. Second, we design the metrics for detecting IMU movements by mathematically formulating how the IMU movement affects the IMU measurements. Third, we determine the optimal thresholds of metrics by synthetic IMU data from a significantly amended simulation model. Finally, a correction method is proposed to correct the effects of IMU movements. We demonstrate our method on both synthetic data and real-user data. The results demonstrate our method is a promising solution to detecting and correcting IMU movements during JAE.
Continuous Prediction of Lower-Limb Kinematics From Multi-Modal Biomedical Signals
Mar 22, 2021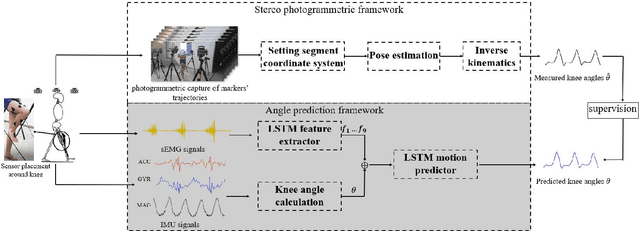
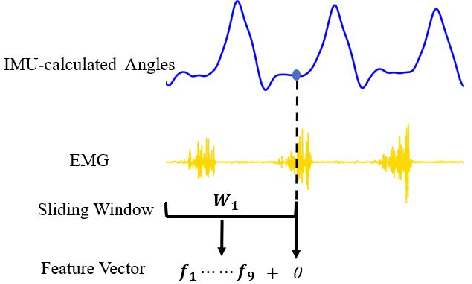
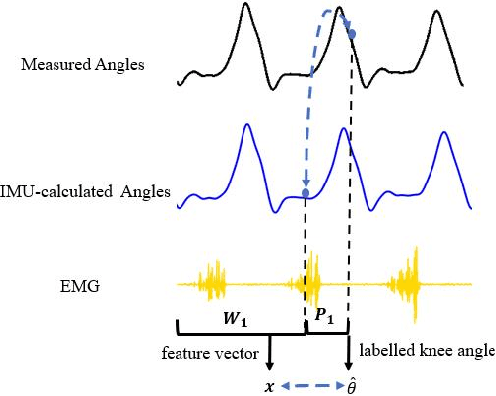
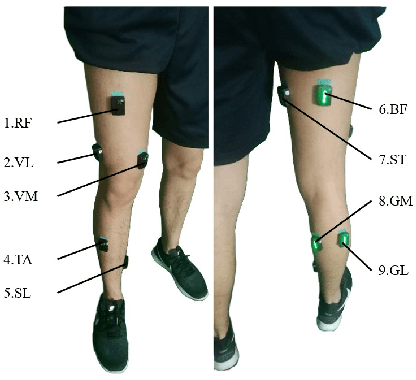
Abstract:The fast-growing techniques of measuring and fusing multi-modal biomedical signals enable advanced motor intent decoding schemes of lowerlimb exoskeletons, meeting the increasing demand for rehabilitative or assistive applications of take-home healthcare. Challenges of exoskeletons motor intent decoding schemes remain in making a continuous prediction to compensate for the hysteretic response caused by mechanical transmission. In this paper, we solve this problem by proposing an ahead of time continuous prediction of lower limb kinematics, with the prediction of knee angles during level walking as a case study. Firstly, an end-to-end kinematics prediction network(KinPreNet), consisting of a feature extractor and an angle predictor, is proposed and experimentally compared with features and methods traditionally used in ahead-of-time prediction of gait phases. Secondly, inspired by the electromechanical delay(EMD), we further explore our algorithm's capability of compensating response delay of mechanical transmission by validating the performance of the different sections of prediction time. And we experimentally reveal the time boundary of compensating the hysteretic response. Thirdly, a comparison of employing EMG signals or not is performed to reveal the EMG and kinematic signals collaborated contributions to the continuous prediction. During the experiments, EMG signals of nine muscles and knee angles calculated from inertial measurement unit (IMU) signals are recorded from ten healthy subjects. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study of continuously predicting lower-limb kinematics in an ahead-of-time manner based on the electromechanical delay (EMD).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge