Chenlu Guo
SPICE: Submodular Penalized Information-Conflict Selection for Efficient Large Language Model Training
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Information-based data selection for instruction tuning is compelling: maximizing the log-determinant of the Fisher information yields a monotone submodular objective, enabling greedy algorithms to achieve a $(1-1/e)$ approximation under a cardinality budget. In practice, however, we identify alleviating gradient conflicts, misalignment between per-sample gradients, is a key factor that slows down the decay of marginal log-determinant information gains, thereby preventing significant loss of information. We formalize this via an $\varepsilon$-decomposition that quantifies the deviation from ideal submodularity as a function of conflict statistics, yielding data-dependent approximation factors that tighten as conflicts diminish. Guided by this analysis, we propose SPICE, a conflict-aware selector that maximizes information while penalizing misalignment, and that supports early stopping and proxy models for efficiency. Empirically, SPICE selects subsets with higher log-determinant information than original criteria, and these informational gains translate into performance improvements: across 8 benchmarks with LLaMA2-7B and Qwen2-7B, SPICE uses only 10% of the data, yet matches or exceeds 6 methods including full-data tuning. This achieves performance improvements with substantially lower training cost.
LoRA-GGPO: Mitigating Double Descent in LoRA Fine-Tuning via Gradient-Guided Perturbation Optimization
Feb 20, 2025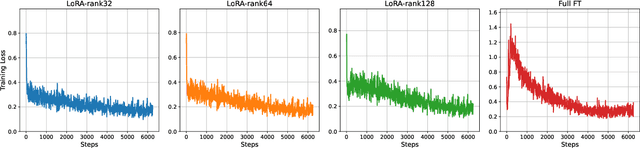
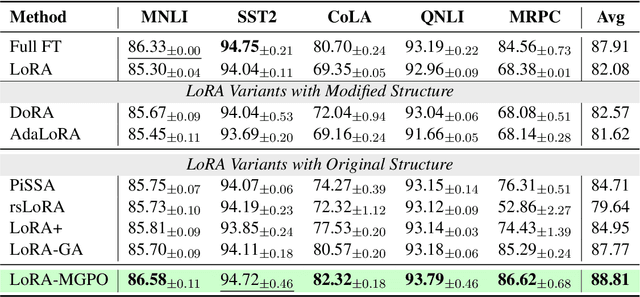
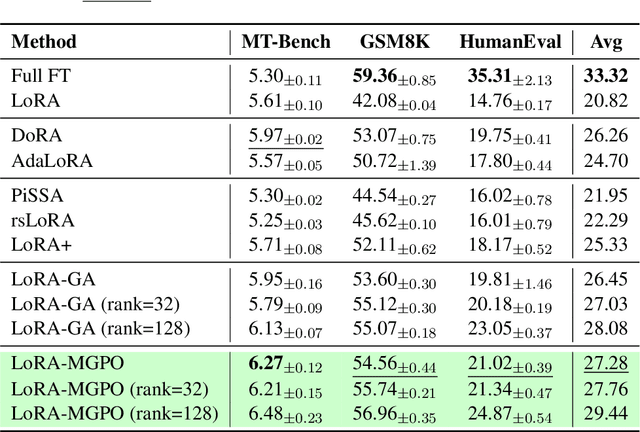
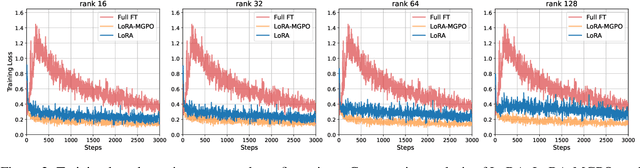
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable success in natural language processing, but their full fine-tuning remains resource-intensive. Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) methods, such as Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA), have emerged as a practical solution by approximating parameter updates with low-rank matrices. However, LoRA often exhibits a "double descent" phenomenon during fine-tuning, where model performance degrades due to overfitting and limited expressiveness caused by low-rank constraints. To address this issue, we propose LoRA-GGPO (Gradient-Guided Perturbation Optimization), a novel method that leverages gradient and weight norms to generate targeted perturbations. By optimizing the sharpness of the loss landscape, LoRA-GGPO guides the model toward flatter minima, mitigating the double descent problem and improving generalization. Extensive experiments on natural language understanding (NLU) and generation (NLG) tasks demonstrate that LoRA-GGPO outperforms LoRA and its state-of-the-art variants. Furthermore, extended experiments specifically designed to analyze the double descent phenomenon confirm that LoRA-GGPO effectively alleviates this issue, producing more robust and generalizable models. Our work provides a robust and efficient solution for fine-tuning LLMs, with broad applicability in real-world scenarios. The code is available at https://github.com/llm172/LoRA-GGPO.
NLoRA: Nyström-Initiated Low-Rank Adaptation for Large Language Models
Feb 20, 2025



Abstract:Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) is essential for adapting large language models (LLMs), with low-rank adaptation (LoRA) being the most popular approach. However, LoRA suffers from slow convergence, and some recent LoRA variants, such as PiSSA, primarily rely on Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) for initialization, leading to expensive computation. To mitigate these problems, we use the Nystr\"om method, which follows a three-matrix manipulation. We first introduce StructuredLoRA (SLoRA), which investigates adding a small intermediate matrix between the low-rank matrices A and B. Secondly, we propose Nystr\"omLoRA (NLoRA), which leverages Nystr\"om-based initialization for SLoRA to improve its effectiveness and efficiency. Finally, we propose IntermediateTune (IntTune), which explores fine-tuning exclusively on the intermediate matrix of NLoRA to further boost LLM efficiency. We evaluate our methods on five natural language generation (NLG) tasks and eight natural language understanding (NLU) tasks. On GSM8K, SLoRA and NLoRA achieve accuracies of 56.48% and 57.70%, surpassing LoRA by 33.52% and 36.41%, with only 3.67 million additional trainable parameters. IntTune improves average NLG performance over LoRA by 7.45% while using only 1.25% of its parameters. These results demonstrate the efficiency and effectiveness of our approach in enhancing model performance with minimal parameter overhead.
CHBench: A Chinese Dataset for Evaluating Health in Large Language Models
Sep 24, 2024



Abstract:With the rapid development of large language models (LLMs), assessing their performance on health-related inquiries has become increasingly essential. It is critical that these models provide accurate and trustworthy health information, as their application in real-world contexts--where misinformation can have serious consequences for individuals seeking medical advice and support--depends on their reliability. In this work, we present CHBench, the first comprehensive Chinese Health-related Benchmark designed to evaluate LLMs' capabilities in understanding physical and mental health across diverse scenarios. CHBench includes 6,493 entries related to mental health and 2,999 entries focused on physical health, covering a broad spectrum of topics. This dataset serves as a foundation for evaluating Chinese LLMs' capacity to comprehend and generate accurate health-related information. Our extensive evaluations of four popular Chinese LLMs demonstrate that there remains considerable room for improvement in their understanding of health-related information. The code is available at https://github.com/TracyGuo2001/CHBench.
A Survey on Data Augmentation in Large Model Era
Jan 27, 2024Abstract:Large models, encompassing large language and diffusion models, have shown exceptional promise in approximating human-level intelligence, garnering significant interest from both academic and industrial spheres. However, the training of these large models necessitates vast quantities of high-quality data, and with continuous updates to these models, the existing reservoir of high-quality data may soon be depleted. This challenge has catalyzed a surge in research focused on data augmentation methods. Leveraging large models, these data augmentation techniques have outperformed traditional approaches. This paper offers an exhaustive review of large model-driven data augmentation methods, adopting a comprehensive perspective. We begin by establishing a classification of relevant studies into three main categories: image augmentation, text augmentation, and paired data augmentation. Following this, we delve into various data post-processing techniques pertinent to large model-based data augmentation. Our discussion then expands to encompass the array of applications for these data augmentation methods within natural language processing, computer vision, and audio signal processing. We proceed to evaluate the successes and limitations of large model-based data augmentation across different scenarios. Concluding our review, we highlight prospective challenges and avenues for future exploration in the field of data augmentation. Our objective is to furnish researchers with critical insights, ultimately contributing to the advancement of more sophisticated large models. We consistently maintain the related open-source materials at: https://github.com/MLGroup-JLU/LLM-data-aug-survey.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge