Chenfeng Guo
RINGO: Real-time Navigation with a Guiding Trajectory for Aerial Manipulators in Unknown Environments
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:Motion planning for aerial manipulators in constrained environments has typically been limited to known environments or simplified to that of multi-rotors, which leads to poor adaptability and overly conservative trajectories. This paper presents RINGO: Real-time Navigation with a Guiding Trajectory, a novel planning framework that enables aerial manipulators to navigate unknown environments in real time. The proposed method simultaneously considers the positions of both the multi-rotor and the end-effector. A pre-obtained multi-rotor trajectory serves as a guiding reference, allowing the end-effector to generate a smooth, collision-free, and workspace-compatible trajectory. Leveraging the convex hull property of B-spline curves, we theoretically guarantee that the trajectory remains within the reachable workspace. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work that enables real-time navigation of aerial manipulators in unknown environments. The simulation and experimental results show the effectiveness of the proposed method. The proposed method generates less conservative trajectories than approaches that consider only the multi-rotor.
FCM-RDpA: TSK Fuzzy Regression Model Construction Using Fuzzy C-Means Clustering, Regularization, DropRule, and Powerball AdaBelief
Nov 30, 2020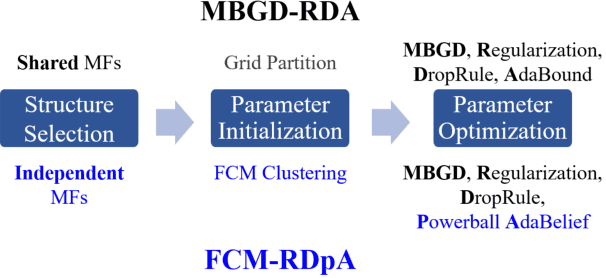
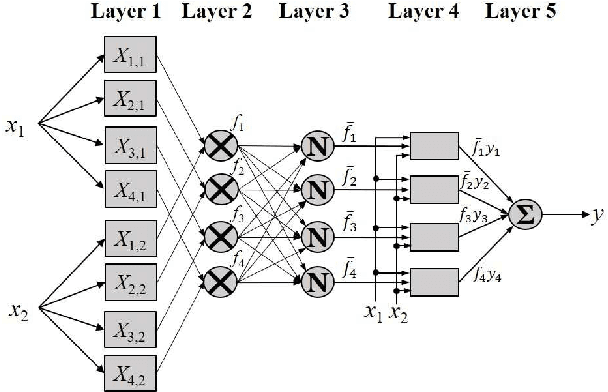
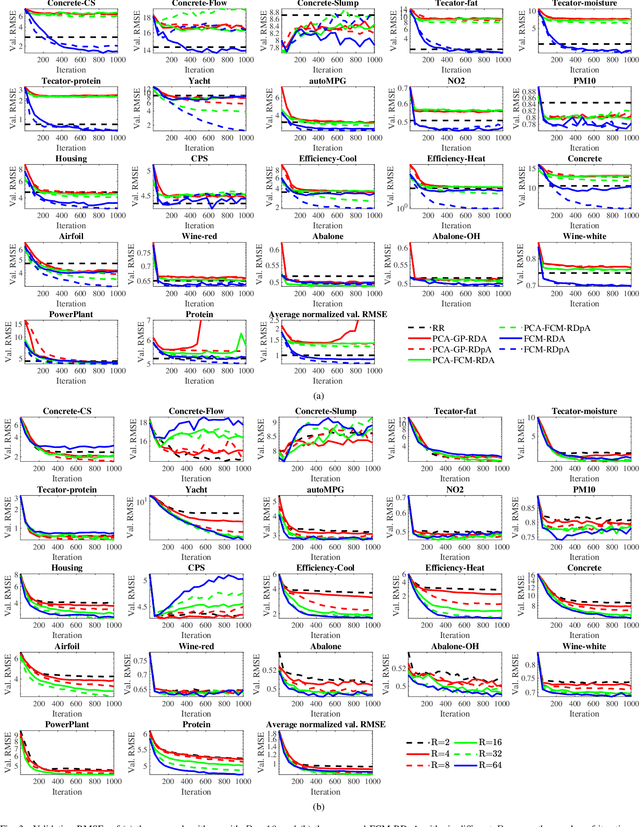
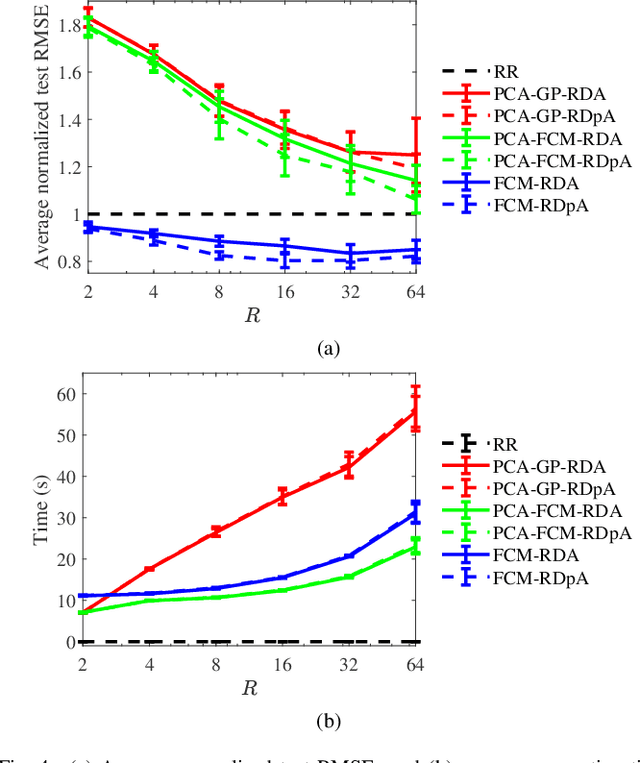
Abstract:To effectively optimize Takagi-Sugeno-Kang (TSK) fuzzy systems for regression problems, a mini-batch gradient descent with regularization, DropRule, and AdaBound (MBGD-RDA) algorithm was recently proposed. This paper further proposes FCM-RDpA, which improves MBGD-RDA by replacing the grid partition approach in rule initialization by fuzzy c-means clustering, and AdaBound by Powerball AdaBelief, which integrates recently proposed Powerball gradient and AdaBelief to further expedite and stabilize parameter optimization. Extensive experiments on 22 regression datasets with various sizes and dimensionalities validated the superiority of FCM-RDpA over MBGD-RDA, especially when the feature dimensionality is higher. We also propose an additional approach, FCM-RDpAx, that further improves FCM-RDpA by using augmented features in both the antecedents and consequents of the rules.
Canonical Correlation Analysis (CCA) Based Multi-View Learning: An Overview
Jul 03, 2019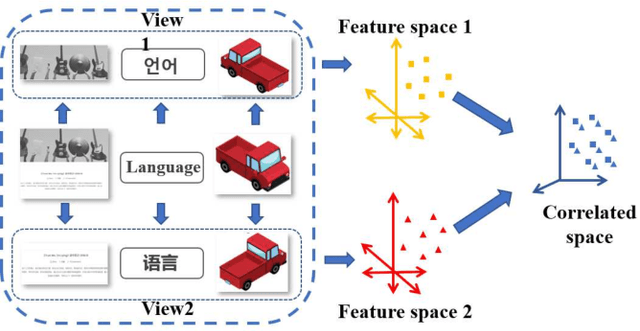
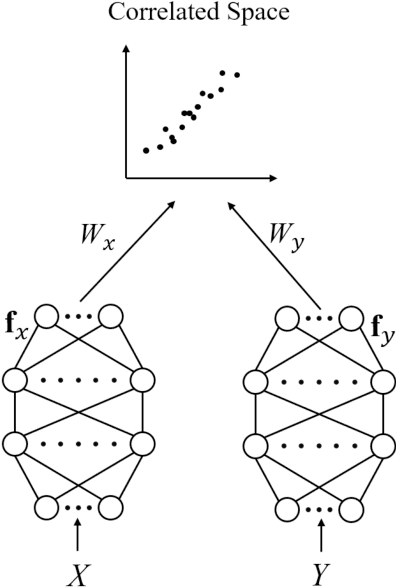
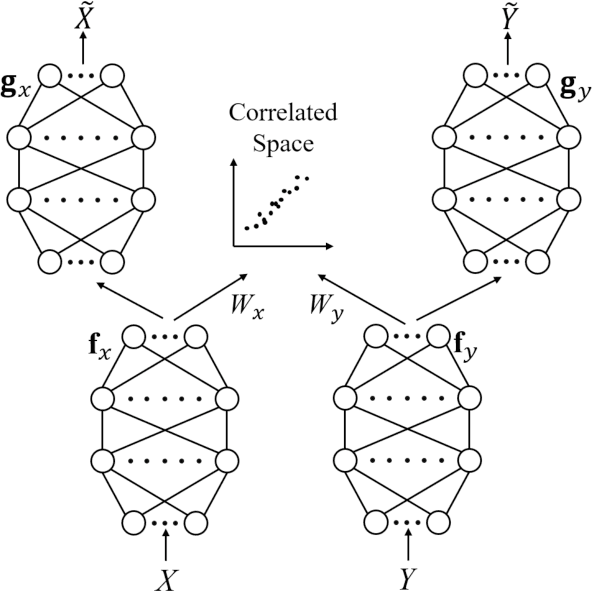
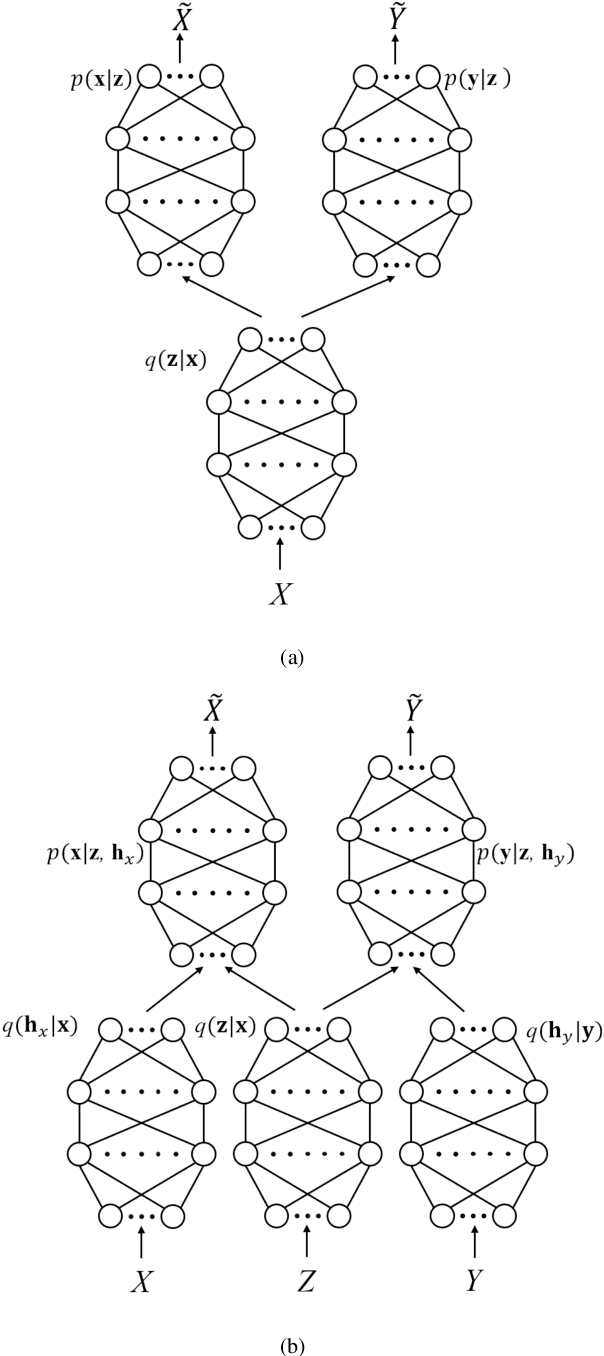
Abstract:Multi-view learning (MVL) is a strategy for fusing data from different sources or subsets. Canonical correlation analysis (CCA) is very important in MVL, whose main idea is to map data from different views onto a common space with the maximum correlation. The traditional CCA can only be used to calculate the linear correlation between two views. Moreover, it is unsupervised, and the label information is wasted in supervised learning tasks. Many nonlinear, supervised, or generalized extensions have been proposed to overcome these limitations. However, to our knowledge, there is no up-to-date overview of these approaches. This paper fills this gap, by providing a comprehensive overview of many classical and latest CCA approaches, and describing their typical applications in pattern recognition, multi-modal retrieval and classification, and multi-view embedding.
Feature Dimensionality Reduction for Video Affect Classification: A Comparative Study
Aug 08, 2018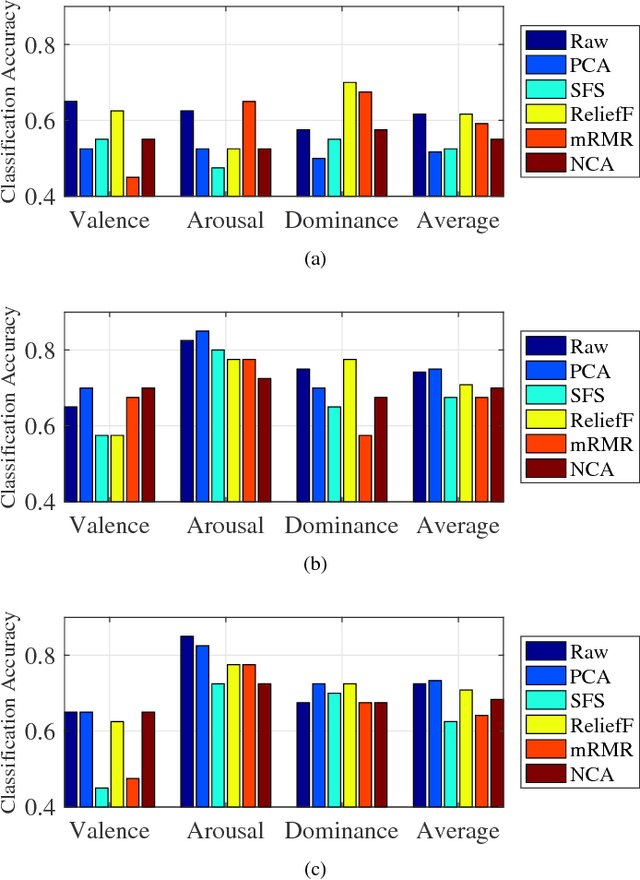
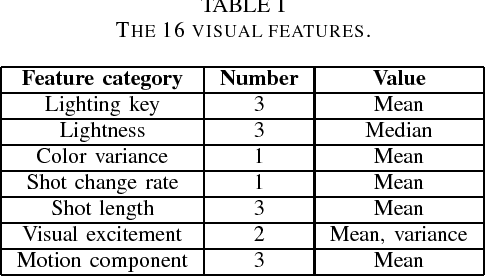
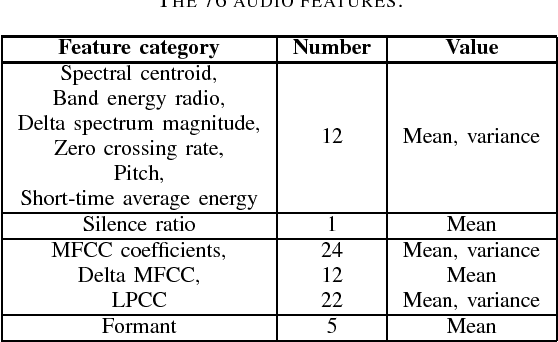
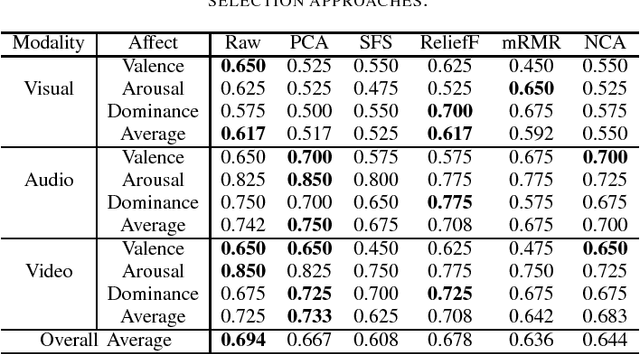
Abstract:Affective computing has become a very important research area in human-machine interaction. However, affects are subjective, subtle, and uncertain. So, it is very difficult to obtain a large number of labeled training samples, compared with the number of possible features we could extract. Thus, dimensionality reduction is critical in affective computing. This paper presents our preliminary study on dimensionality reduction for affect classification. Five popular dimensionality reduction approaches are introduced and compared. Experiments on the DEAP dataset showed that no approach can universally outperform others, and performing classification using the raw features directly may not always be a bad choice.
OMG - Emotion Challenge Solution
Apr 30, 2018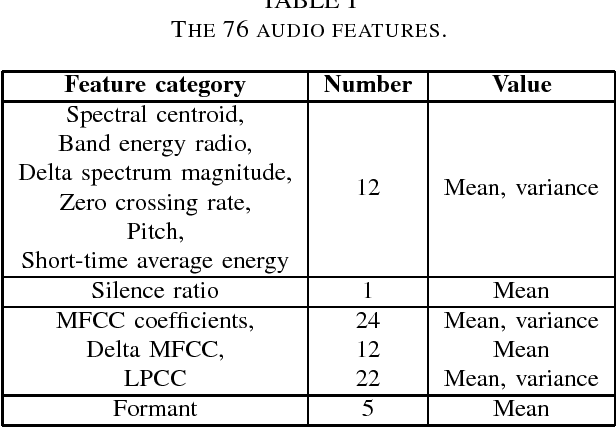
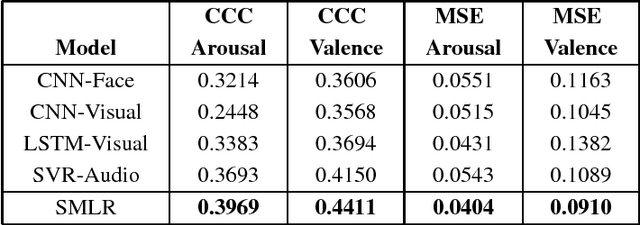
Abstract:This short paper describes our solution to the 2018 IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence One-Minute Gradual-Emotional Behavior Challenge, whose goal was to estimate continuous arousal and valence values from short videos. We designed four base regression models using visual and audio features, and then used a spectral approach to fuse them to obtain improved performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge