Chaoyi Zhu
TimeWak: Temporal Chained-Hashing Watermark for Time Series Data
Jun 06, 2025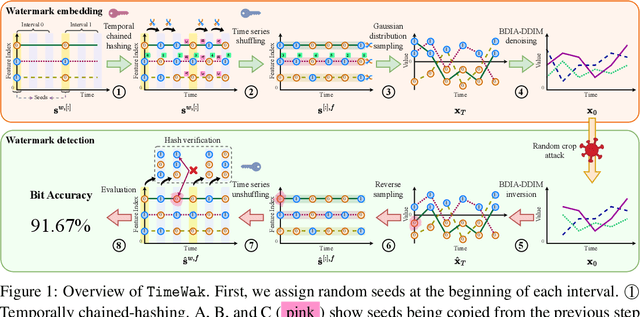
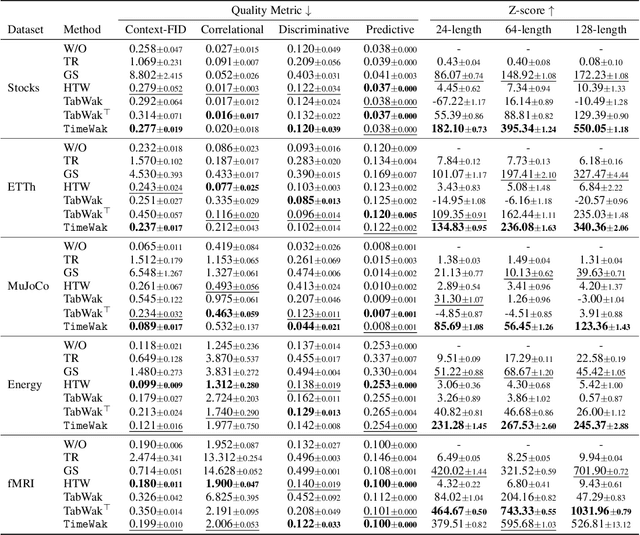
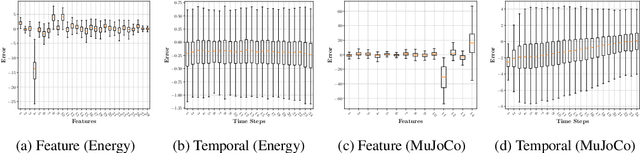
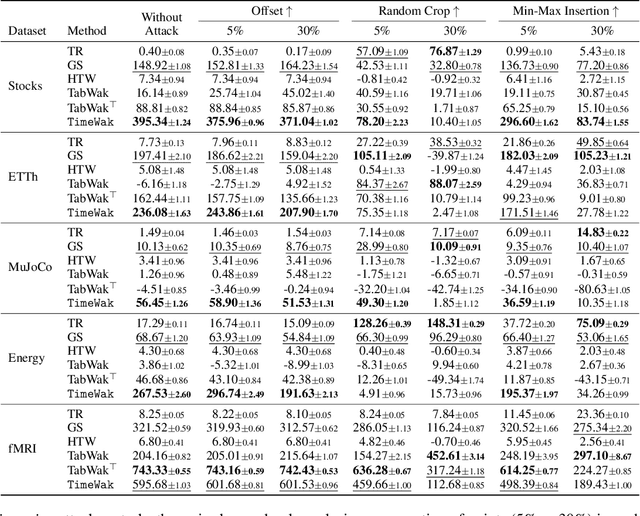
Abstract:Synthetic time series generated by diffusion models enable sharing privacy-sensitive datasets, such as patients' functional MRI records. Key criteria for synthetic data include high data utility and traceability to verify the data source. Recent watermarking methods embed in homogeneous latent spaces, but state-of-the-art time series generators operate in real space, making latent-based watermarking incompatible. This creates the challenge of watermarking directly in real space while handling feature heterogeneity and temporal dependencies. We propose TimeWak, the first watermarking algorithm for multivariate time series diffusion models. To handle temporal dependence and spatial heterogeneity, TimeWak embeds a temporal chained-hashing watermark directly within the real temporal-feature space. The other unique feature is the $\epsilon$-exact inversion, which addresses the non-uniform reconstruction error distribution across features from inverting the diffusion process to detect watermarks. We derive the error bound of inverting multivariate time series and further maintain high watermark detectability. We extensively evaluate TimeWak on its impact on synthetic data quality, watermark detectability, and robustness under various post-editing attacks, against 5 datasets and baselines of different temporal lengths. Our results show that TimeWak achieves improvements of 61.96% in context-FID score, and 8.44% in correlational scores against the state-of-the-art baseline, while remaining consistently detectable.
Optimization-Free Universal Watermark Forgery with Regenerative Diffusion Models
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Watermarking becomes one of the pivotal solutions to trace and verify the origin of synthetic images generated by artificial intelligence models, but it is not free of risks. Recent studies demonstrate the capability to forge watermarks from a target image onto cover images via adversarial optimization without knowledge of the target generative model and watermark schemes. In this paper, we uncover a greater risk of an optimization-free and universal watermark forgery that harnesses existing regenerative diffusion models. Our proposed forgery attack, PnP (Plug-and-Plant), seamlessly extracts and integrates the target watermark via regenerating the image, without needing any additional optimization routine. It allows for universal watermark forgery that works independently of the target image's origin or the watermarking model used. We explore the watermarked latent extracted from the target image and visual-textual context of cover images as priors to guide sampling of the regenerative process. Extensive evaluation on 24 scenarios of model-data-watermark combinations demonstrates that PnP can successfully forge the watermark (up to 100% detectability and user attribution), and maintain the best visual perception. By bypassing model retraining and enabling adaptability to any image, our approach significantly broadens the scope of forgery attacks, presenting a greater challenge to the security of current watermarking techniques for diffusion models and the authority of watermarking schemes in synthetic data generation and governance.
Duwak: Dual Watermarks in Large Language Models
Mar 12, 2024Abstract:As large language models (LLM) are increasingly used for text generation tasks, it is critical to audit their usages, govern their applications, and mitigate their potential harms. Existing watermark techniques are shown effective in embedding single human-imperceptible and machine-detectable patterns without significantly affecting generated text quality and semantics. However, the efficiency in detecting watermarks, i.e., the minimum number of tokens required to assert detection with significance and robustness against post-editing, is still debatable. In this paper, we propose, Duwak, to fundamentally enhance the efficiency and quality of watermarking by embedding dual secret patterns in both token probability distribution and sampling schemes. To mitigate expression degradation caused by biasing toward certain tokens, we design a contrastive search to watermark the sampling scheme, which minimizes the token repetition and enhances the diversity. We theoretically explain the interdependency of the two watermarks within Duwak. We evaluate Duwak extensively on Llama2 under various post-editing attacks, against four state-of-the-art watermarking techniques and combinations of them. Our results show that Duwak marked text achieves the highest watermarked text quality at the lowest required token count for detection, up to 70% tokens less than existing approaches, especially under post paraphrasing.
Quantifying and Mitigating Privacy Risks for Tabular Generative Models
Mar 12, 2024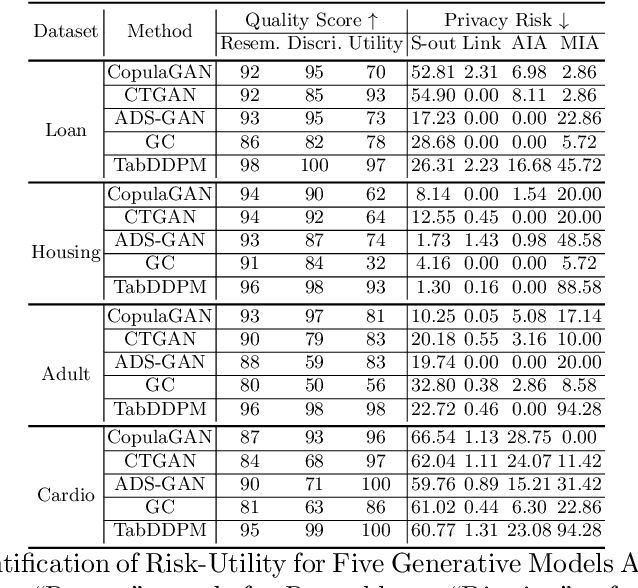
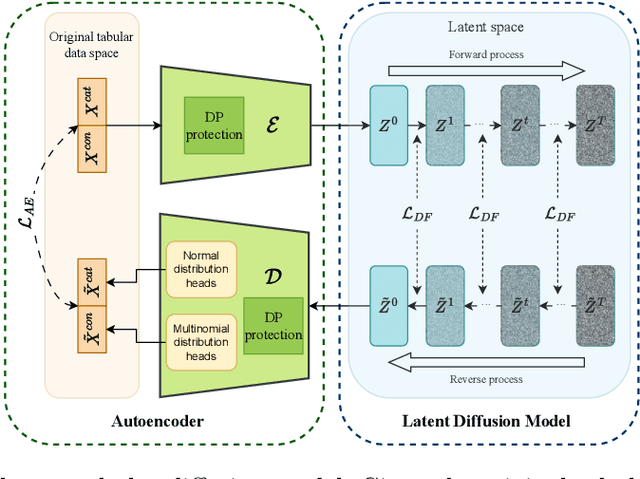
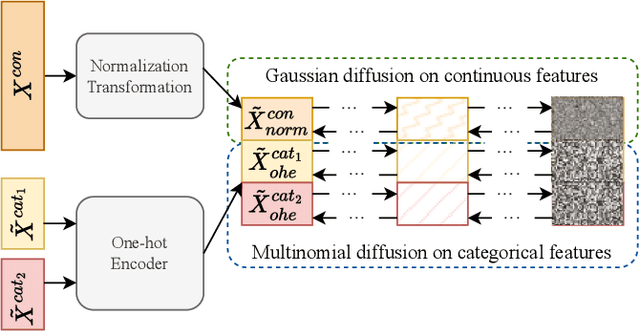
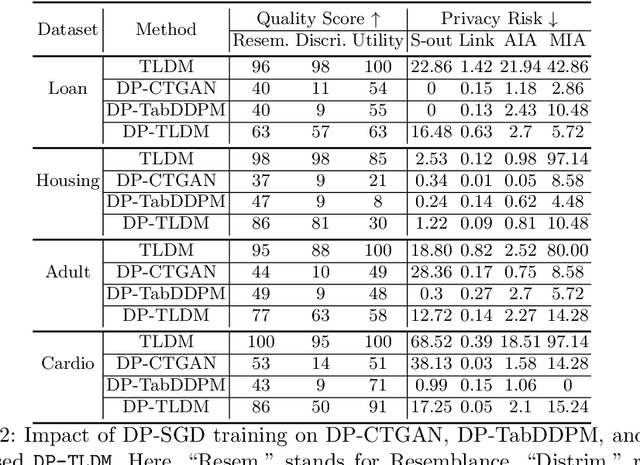
Abstract:Synthetic data from generative models emerges as the privacy-preserving data-sharing solution. Such a synthetic data set shall resemble the original data without revealing identifiable private information. The backbone technology of tabular synthesizers is rooted in image generative models, ranging from Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to recent diffusion models. Recent prior work sheds light on the utility-privacy tradeoff on tabular data, revealing and quantifying privacy risks on synthetic data. We first conduct an exhaustive empirical analysis, highlighting the utility-privacy tradeoff of five state-of-the-art tabular synthesizers, against eight privacy attacks, with a special focus on membership inference attacks. Motivated by the observation of high data quality but also high privacy risk in tabular diffusion, we propose DP-TLDM, Differentially Private Tabular Latent Diffusion Model, which is composed of an autoencoder network to encode the tabular data and a latent diffusion model to synthesize the latent tables. Following the emerging f-DP framework, we apply DP-SGD to train the auto-encoder in combination with batch clipping and use the separation value as the privacy metric to better capture the privacy gain from DP algorithms. Our empirical evaluation demonstrates that DP-TLDM is capable of achieving a meaningful theoretical privacy guarantee while also significantly enhancing the utility of synthetic data. Specifically, compared to other DP-protected tabular generative models, DP-TLDM improves the synthetic quality by an average of 35% in data resemblance, 15% in the utility for downstream tasks, and 50% in data discriminability, all while preserving a comparable level of privacy risk.
Paradigm shift in electron-based crystallography via machine learning
Feb 10, 2019



Abstract:Accurately determining the crystallographic structure of a material, organic or inorganic, is a critical primary step in material development and analysis. The most common practices involve analysis of diffraction patterns produced in laboratory XRD, TEM, and synchrotron X-ray sources. However, these techniques are slow, require careful sample preparation, can be difficult to access, and are prone to human error during analysis. This paper presents a newly developed methodology that represents a paradigm change in electron diffraction-based structure analysis techniques, with the potential to revolutionize multiple crystallography-related fields. A machine learning-based approach for rapid and autonomous identification of the crystal structure of metals and alloys, ceramics, and geological specimens, without any prior knowledge of the sample, is presented and demonstrated utilizing the electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) technique. Electron backscatter diffraction patterns are collected from materials with well-known crystal structures, then a deep neural network model is constructed for classification to a specific Bravais lattice or point group. The applicability of this approach is evaluated on diffraction patterns from samples unknown to the computer without any human input or data filtering. This is in comparison to traditional Hough transform EBSD, which requires that you have already determined the phases present in your sample. The internal operations of the neural network are elucidated through visualizing the symmetry features learned by the convolutional neural network. It is determined that the model looks for the same features a crystallographer would use, even though it is not explicitly programmed to do so. This study opens the door to fully automated, high-throughput determination of crystal structures via several electron-based diffraction techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge