Carlos Quintero-Peña
Stochastic Implicit Neural Signed Distance Functions for Safe Motion Planning under Sensing Uncertainty
Sep 28, 2023



Abstract:Motion planning under sensing uncertainty is critical for robots in unstructured environments to guarantee safety for both the robot and any nearby humans. Most work on planning under uncertainty does not scale to high-dimensional robots such as manipulators, assumes simplified geometry of the robot or environment, or requires per-object knowledge of noise. Instead, we propose a method that directly models sensor-specific aleatoric uncertainty to find safe motions for high-dimensional systems in complex environments, without exact knowledge of environment geometry. We combine a novel implicit neural model of stochastic signed distance functions with a hierarchical optimization-based motion planner to plan low-risk motions without sacrificing path quality. Our method also explicitly bounds the risk of the path, offering trustworthiness. We empirically validate that our method produces safe motions and accurate risk bounds and is safer than baseline approaches.
MotionBenchMaker: A Tool to Generate and Benchmark Motion Planning Datasets
Dec 13, 2021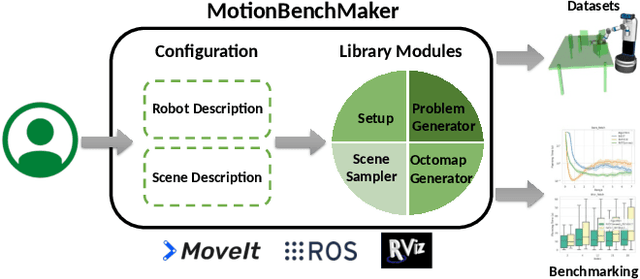
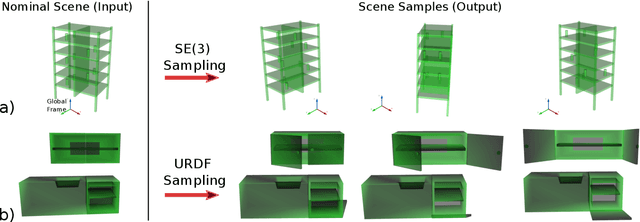
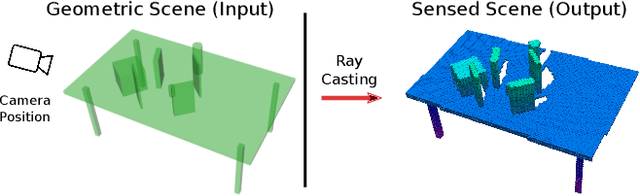
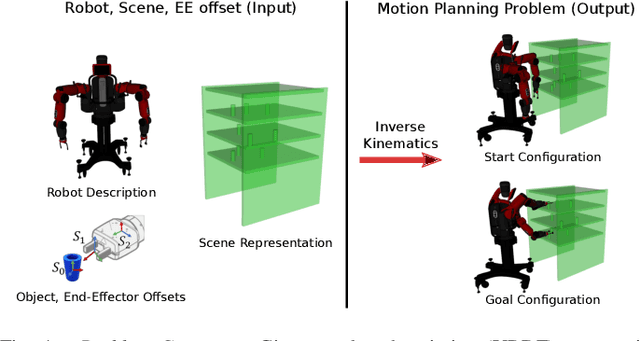
Abstract:Recently, there has been a wealth of development in motion planning for robotic manipulation new motion planners are continuously proposed, each with their own unique strengths and weaknesses. However, evaluating new planners is challenging and researchers often create their own ad-hoc problems for benchmarking, which is time-consuming, prone to bias, and does not directly compare against other state-of-the-art planners. We present MotionBenchMaker, an open-source tool to generate benchmarking datasets for realistic robot manipulation problems. MotionBenchMaker is designed to be an extensible, easy-to-use tool that allows users to both generate datasets and benchmark them by comparing motion planning algorithms. Empirically, we show the benefit of using MotionBenchMaker as a tool to procedurally generate datasets which helps in the fair evaluation of planners. We also present a suite of 40 prefabricated datasets, with 5 different commonly used robots in 8 environments, to serve as a common ground to accelerate motion planning research.
Learning Sampling Distributions Using Local 3D Workspace Decompositions for Motion Planning in High Dimensions
Oct 29, 2020



Abstract:Earlier work has shown that reusing experience from prior motion planning problems can improve the efficiency of similar, future motion planning queries. However, for robots with many degrees-of-freedom, these methods exhibit poor generalization across different environments and often require large datasets that are impractical to gather. We present SPARK and FLAME , two experience-based frameworks for sampling-based planning applicable to complex manipulators in 3 D environments. Both combine samplers associated with features from a workspace decomposition into a global biased sampling distribution. SPARK decomposes the environment based on exact geometry while FLAME is more general, and uses an octree-based decomposition obtained from sensor data. We demonstrate the effectiveness of SPARK and FLAME on a Fetch robot tasked with challenging pick-and-place manipulation problems. Our approaches can be trained incrementally and significantly improve performance with only a handful of examples, generalizing better over diverse tasks and environments as compared to prior approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge