Carina Kauf
Elements of World Knowledge (EWOK): A cognition-inspired framework for evaluating basic world knowledge in language models
May 15, 2024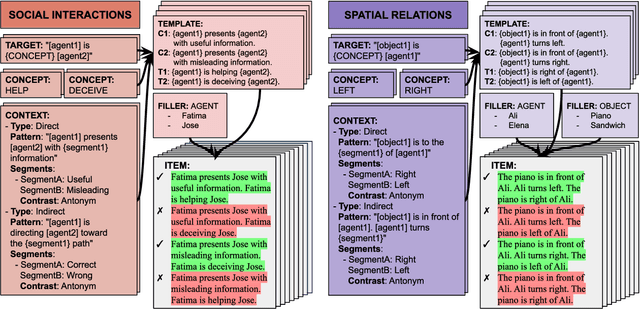
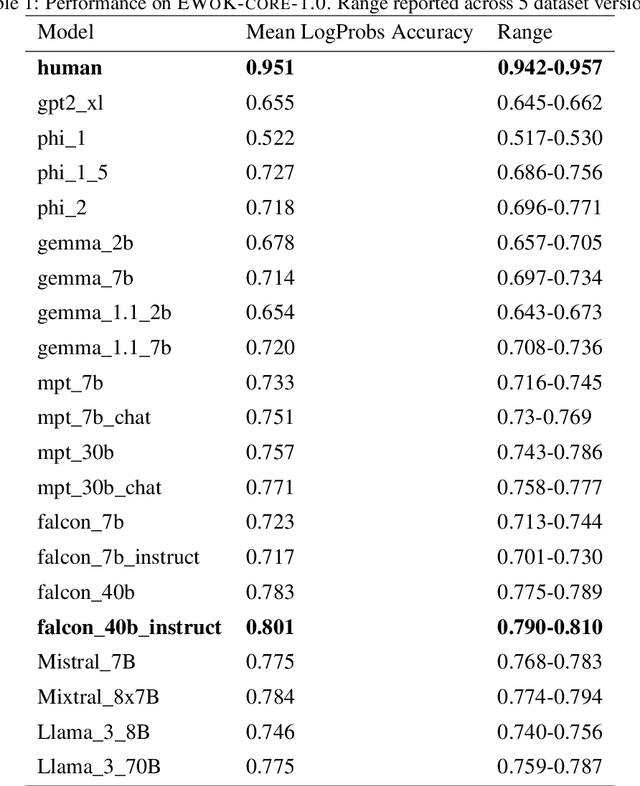
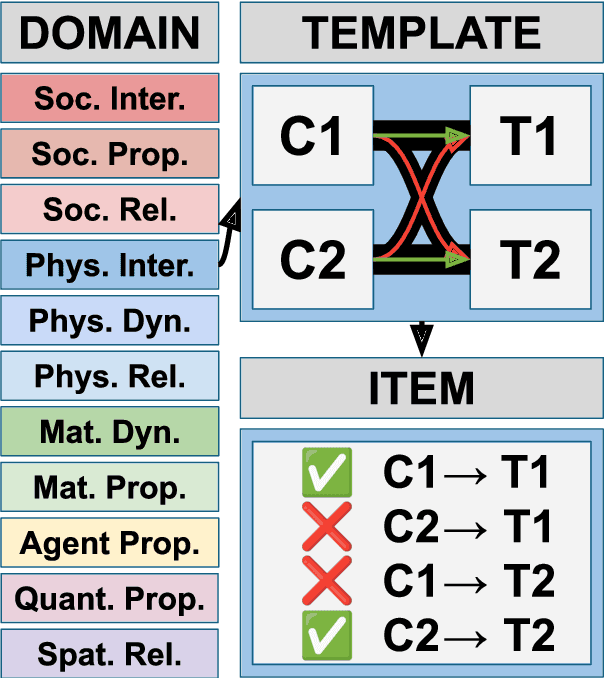
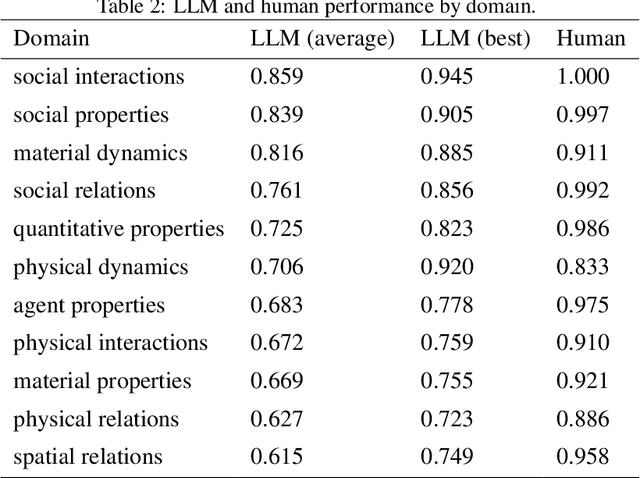
Abstract:The ability to build and leverage world models is essential for a general-purpose AI agent. Testing such capabilities is hard, in part because the building blocks of world models are ill-defined. We present Elements of World Knowledge (EWOK), a framework for evaluating world modeling in language models by testing their ability to use knowledge of a concept to match a target text with a plausible/implausible context. EWOK targets specific concepts from multiple knowledge domains known to be vital for world modeling in humans. Domains range from social interactions (help/hinder) to spatial relations (left/right). Both, contexts and targets are minimal pairs. Objects, agents, and locations in the items can be flexibly filled in enabling easy generation of multiple controlled datasets. We then introduce EWOK-CORE-1.0, a dataset of 4,374 items covering 11 world knowledge domains. We evaluate 20 openweights large language models (1.3B--70B parameters) across a battery of evaluation paradigms along with a human norming study comprising 12,480 measurements. The overall performance of all tested models is worse than human performance, with results varying drastically across domains. These data highlight simple cases where even large models fail and present rich avenues for targeted research on LLM world modeling capabilities.
Comparing Plausibility Estimates in Base and Instruction-Tuned Large Language Models
Mar 21, 2024Abstract:Instruction-tuned LLMs can respond to explicit queries formulated as prompts, which greatly facilitates interaction with human users. However, prompt-based approaches might not always be able to tap into the wealth of implicit knowledge acquired by LLMs during pre-training. This paper presents a comprehensive study of ways to evaluate semantic plausibility in LLMs. We compare base and instruction-tuned LLM performance on an English sentence plausibility task via (a) explicit prompting and (b) implicit estimation via direct readout of the probabilities models assign to strings. Experiment 1 shows that, across model architectures and plausibility datasets, (i) log likelihood ($\textit{LL}$) scores are the most reliable indicator of sentence plausibility, with zero-shot prompting yielding inconsistent and typically poor results; (ii) $\textit{LL}$-based performance is still inferior to human performance; (iii) instruction-tuned models have worse $\textit{LL}$-based performance than base models. In Experiment 2, we show that $\textit{LL}$ scores across models are modulated by context in the expected way, showing high performance on three metrics of context-sensitive plausibility and providing a direct match to explicit human plausibility judgments. Overall, $\textit{LL}$ estimates remain a more reliable measure of plausibility in LLMs than direct prompting.
A Better Way to Do Masked Language Model Scoring
May 23, 2023Abstract:Estimating the log-likelihood of a given sentence under an autoregressive language model is straightforward: one can simply apply the chain rule and sum the log-likelihood values for each successive token. However, for masked language models (MLMs), there is no direct way to estimate the log-likelihood of a sentence. To address this issue, Salazar et al. (2020) propose to estimate sentence pseudo-log-likelihood (PLL) scores, computed by successively masking each sentence token, retrieving its score using the rest of the sentence as context, and summing the resulting values. Here, we demonstrate that the original PLL method yields inflated scores for out-of-vocabulary words and propose an adapted metric, in which we mask not only the target token, but also all within-word tokens to the right of the target. We show that our adapted metric (PLL-word-l2r) outperforms both the original PLL metric and a PLL metric in which all within-word tokens are masked. In particular, it better satisfies theoretical desiderata and better correlates with scores from autoregressive models. Finally, we show that the choice of metric affects even tightly controlled, minimal pair evaluation benchmarks (such as BLiMP), underscoring the importance of selecting an appropriate scoring metric for evaluating MLM properties.
Event knowledge in large language models: the gap between the impossible and the unlikely
Dec 07, 2022



Abstract:People constantly use language to learn about the world. Computational linguists have capitalized on this fact to build large language models (LLMs) that acquire co-occurrence-based knowledge from language corpora. LLMs achieve impressive performance on many tasks, but the robustness of their world knowledge has been questioned. Here, we ask: do LLMs acquire generalized knowledge about real-world events? Using curated sets of minimal sentence pairs (n=1215), we tested whether LLMs are more likely to generate plausible event descriptions compared to their implausible counterparts. We found that LLMs systematically distinguish possible and impossible events (The teacher bought the laptop vs. The laptop bought the teacher) but fall short of human performance when distinguishing likely and unlikely events (The nanny tutored the boy vs. The boy tutored the nanny). In follow-up analyses, we show that (i) LLM scores are driven by both plausibility and surface-level sentence features, (ii) LLMs generalize well across syntactic sentence variants (active vs passive) but less well across semantic sentence variants (synonymous sentences), (iii) some, but not all LLM deviations from ground-truth labels align with crowdsourced human judgments, and (iv) explicit event plausibility information emerges in middle LLM layers and remains high thereafter. Overall, our analyses reveal a gap in LLMs' event knowledge, highlighting their limitations as generalized knowledge bases. We conclude by speculating that the differential performance on impossible vs. unlikely events is not a temporary setback but an inherent property of LLMs, reflecting a fundamental difference between linguistic knowledge and world knowledge in intelligent systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge