Bruno Gonçalves
American cultural regions mapped through the lexical analysis of social media
Aug 16, 2022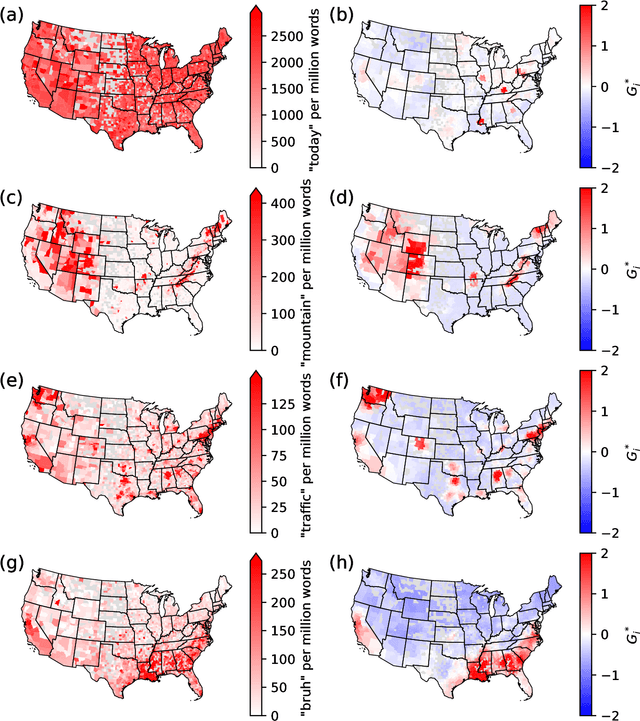
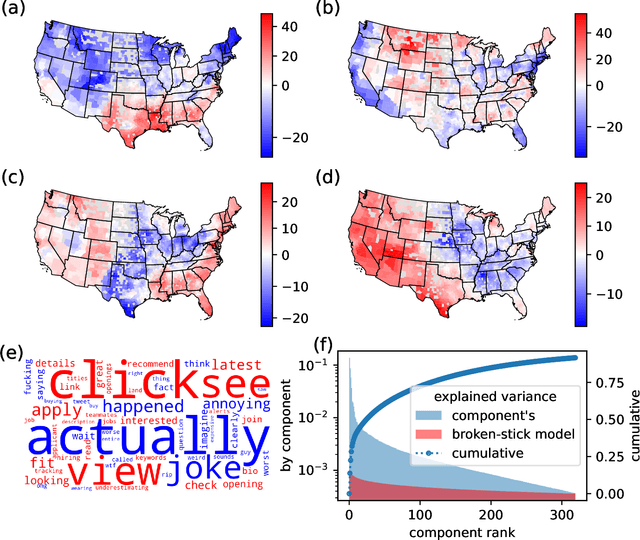
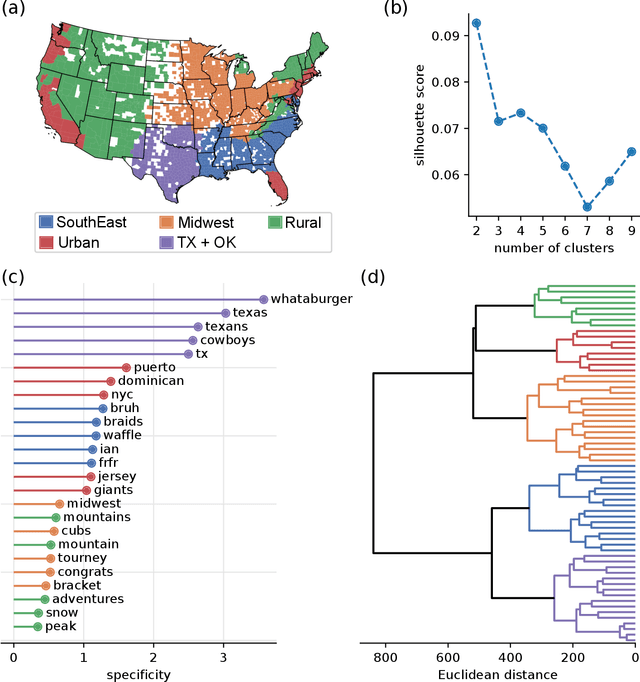
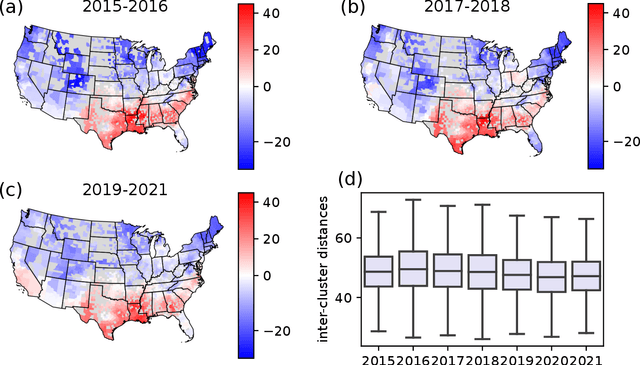
Abstract:Cultural areas represent a useful concept that cross-fertilizes diverse fields in social sciences. Knowledge of how humans organize and relate their ideas and behavior within a society helps to understand their actions and attitudes towards different issues. However, the selection of common traits that shape a cultural area is somewhat arbitrary. What is needed is a method that can leverage the massive amounts of data coming online, especially through social media, to identify cultural regions without ad-hoc assumptions, biases or prejudices. In this work, we take a crucial step towards this direction by introducing a method to infer cultural regions based on the automatic analysis of large datasets from microblogging posts. Our approach is based on the principle that cultural affiliation can be inferred from the topics that people discuss among themselves. Specifically, we measure regional variations in written discourse generated in American social media. From the frequency distributions of content words in geotagged Tweets, we find the words' usage regional hotspots, and from there we derive principal components of regional variation. Through a hierarchical clustering of the data in this lower-dimensional space, our method yields clear cultural areas and the topics of discussion that define them. We obtain a manifest North-South separation, which is primarily influenced by the African American culture, and further contiguous (East-West) and non-contiguous (urban-rural) divisions that provide a comprehensive picture of today's cultural areas in the US.
Mapping the Americanization of English in Space and Time
May 28, 2018



Abstract:As global political preeminence gradually shifted from the United Kingdom to the United States, so did the capacity to culturally influence the rest of the world. In this work, we analyze how the world-wide varieties of written English are evolving. We study both the spatial and temporal variations of vocabulary and spelling of English using a large corpus of geolocated tweets and the Google Books datasets corresponding to books published in the US and the UK. The advantage of our approach is that we can address both standard written language (Google Books) and the more colloquial forms of microblogging messages (Twitter). We find that American English is the dominant form of English outside the UK and that its influence is felt even within the UK borders. Finally, we analyze how this trend has evolved over time and the impact that some cultural events have had in shaping it.
* 16 pages, 6 figures, 2 tables. Published version
Semantic homophily in online communication: evidence from Twitter
Mar 20, 2017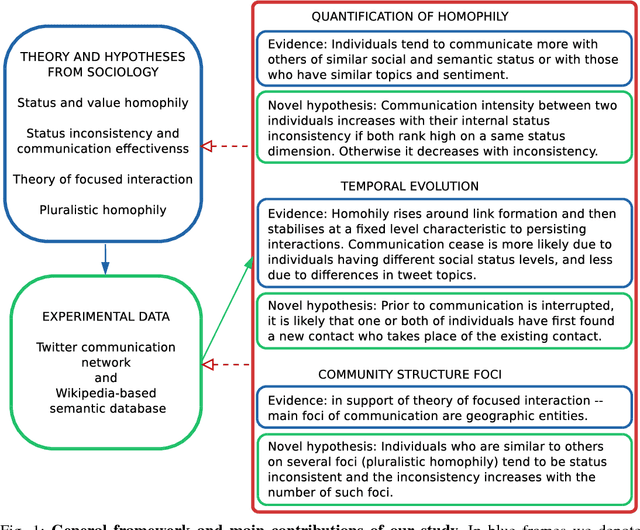
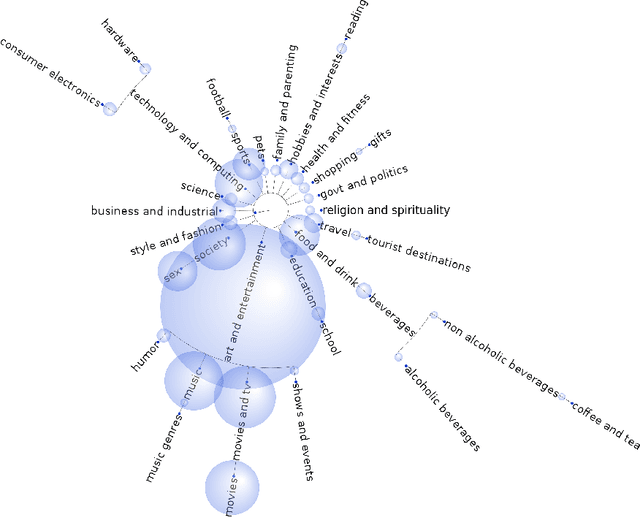
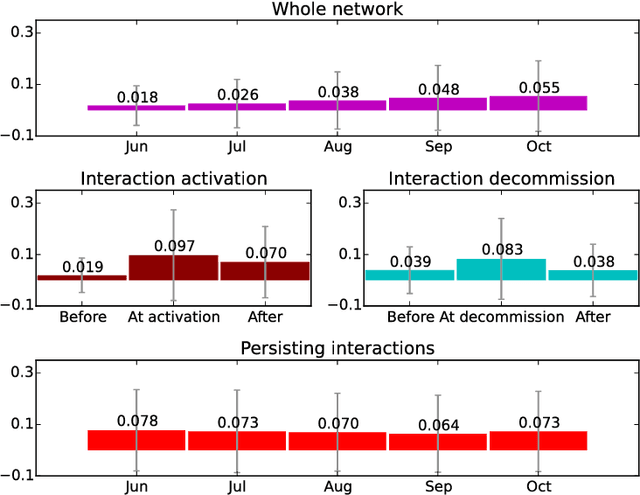
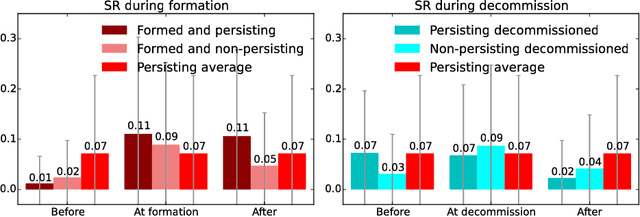
Abstract:People are observed to assortatively connect on a set of traits. This phenomenon, termed assortative mixing or sometimes homophily, can be quantified through assortativity coefficient in social networks. Uncovering the exact causes of strong assortative mixing found in social networks has been a research challenge. Among the main suggested causes from sociology are the tendency of similar individuals to connect (often itself referred as homophily) and the social influence among already connected individuals. An important question to researchers and in practice can be tackled, as we present here: understanding the exact mechanisms of interplay between these tendencies and the underlying social network structure. Namely, in addition to the mentioned assortativity coefficient, there are several other static and temporal network properties and substructures that can be linked to the tendencies of homophily and social influence in the social network and we herein investigate those. Concretely, we tackle a computer-mediated \textit{communication network} (based on Twitter mentions) and a particular type of assortative mixing that can be inferred from the semantic features of communication content that we term \textit{semantic homophily}. Our work, to the best of our knowledge, is the first to offer an in-depth analysis on semantic homophily in a communication network and the interplay between them. We quantify diverse levels of semantic homophily, identify the semantic aspects that are the drivers of observed homophily, show insights in its temporal evolution and finally, we present its intricate interplay with the communication network on Twitter. By analyzing these mechanisms we increase understanding on what are the semantic aspects that shape and how they shape the human computer-mediated communication.
Learning about Spanish dialects through Twitter
Feb 06, 2017



Abstract:This paper maps the large-scale variation of the Spanish language by employing a corpus based on geographically tagged Twitter messages. Lexical dialects are extracted from an analysis of variants of tens of concepts. The resulting maps show linguistic variation on an unprecedented scale across the globe. We discuss the properties of the main dialects within a machine learning approach and find that varieties spoken in urban areas have an international character in contrast to country areas where dialects show a more regional uniformity.
* 16 pages, 5 figures, 1 table
The happiness paradox: your friends are happier than you
Feb 08, 2016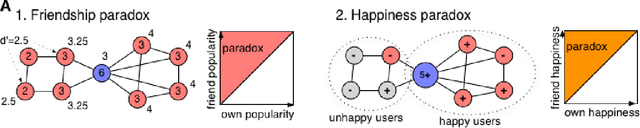

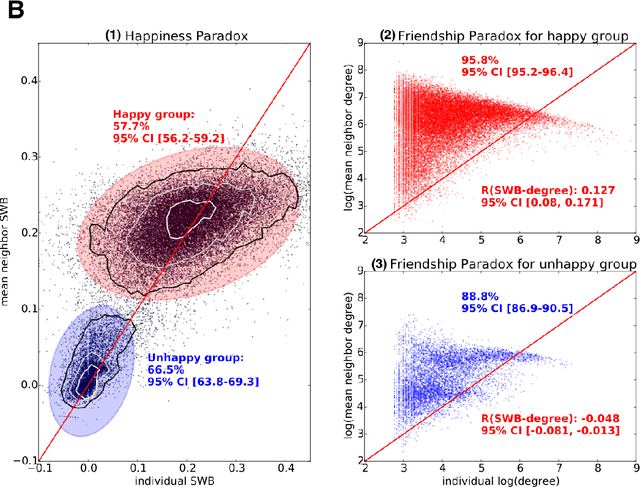
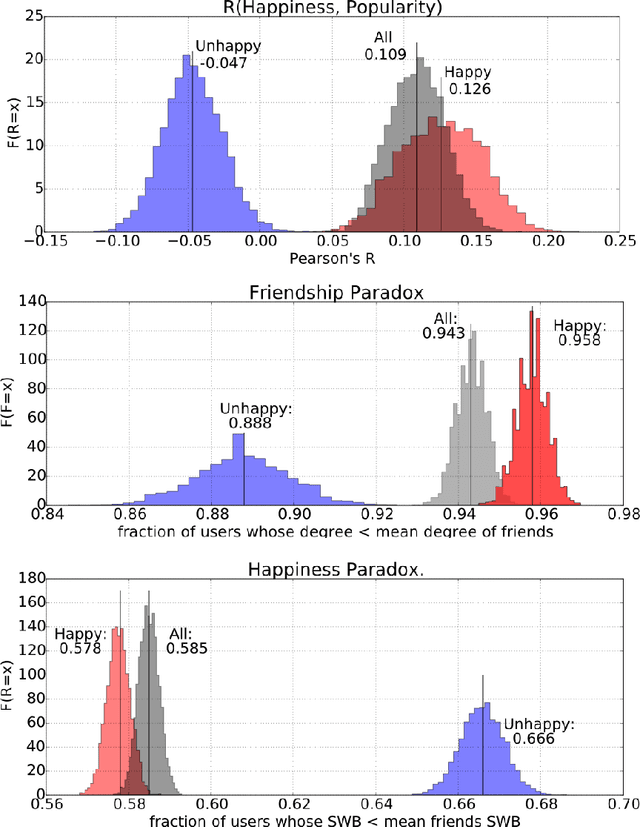
Abstract:Most individuals in social networks experience a so-called Friendship Paradox: they are less popular than their friends on average. This effect may explain recent findings that widespread social network media use leads to reduced happiness. However the relation between popularity and happiness is poorly understood. A Friendship paradox does not necessarily imply a Happiness paradox where most individuals are less happy than their friends. Here we report the first direct observation of a significant Happiness Paradox in a large-scale online social network of $39,110$ Twitter users. Our results reveal that popular individuals are indeed happier and that a majority of individuals experience a significant Happiness paradox. The magnitude of the latter effect is shaped by complex interactions between individual popularity, happiness, and the fact that users cluster assortatively by level of happiness. Our results indicate that the topology of online social networks and the distribution of happiness in some populations can cause widespread psycho-social effects that affect the well-being of billions of individuals.
Topical differences between Chinese language Twitter and Sina Weibo
Dec 22, 2015
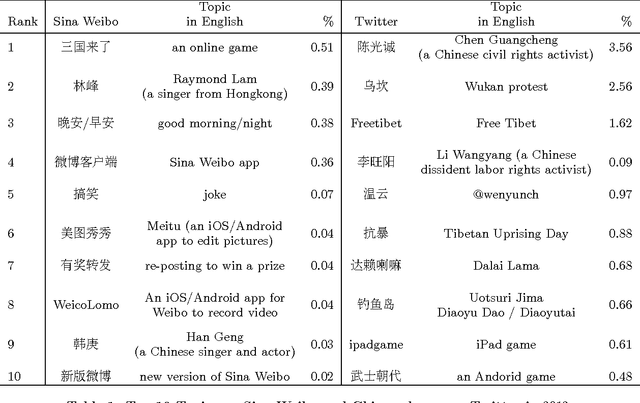
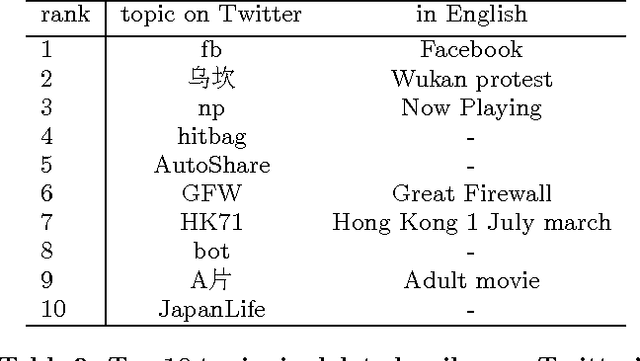
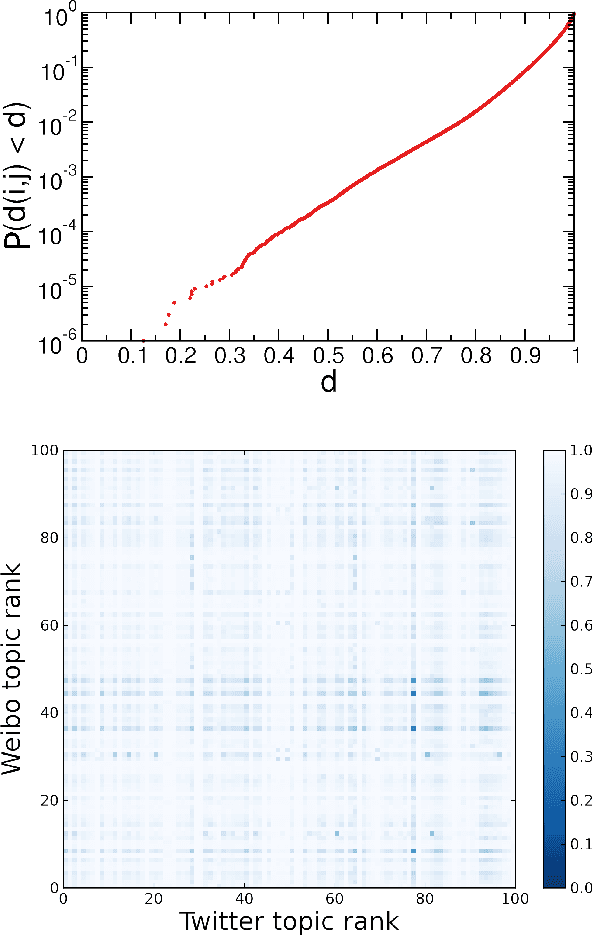
Abstract:Sina Weibo, China's most popular microblogging platform, is currently used by over $500M$ users and is considered to be a proxy of Chinese social life. In this study, we contrast the discussions occurring on Sina Weibo and on Chinese language Twitter in order to observe two different strands of Chinese culture: people within China who use Sina Weibo with its government imposed restrictions and those outside that are free to speak completely anonymously. We first propose a simple ad-hoc algorithm to identify topics of Tweets and Weibo. Different from previous works on micro-message topic detection, our algorithm considers topics of the same contents but with different \#tags. Our algorithm can also detect topics for Tweets and Weibos without any \#tags. Using a large corpus of Weibo and Chinese language tweets, covering the period from January $1$ to December $31$, $2012$, we obtain a list of topics using clustered \#tags that we can then use to compare the two platforms. Surprisingly, we find that there are no common entries among the Top $100$ most popular topics. Furthermore, only $9.2\%$ of tweets correspond to the Top $1000$ topics on Sina Weibo platform, and conversely only $4.4\%$ of weibos were found to discuss the most popular Twitter topics. Our results reveal significant differences in social attention on the two platforms, with most popular topics on Sina Weibo relating to entertainment while most tweets corresponded to cultural or political contents that is practically non existent in Sina Weibo.
* 5 pages, 2 figures, 2 tables, 2 algorithms
Crowdsourcing Dialect Characterization through Twitter
Jul 26, 2014



Abstract:We perform a large-scale analysis of language diatopic variation using geotagged microblogging datasets. By collecting all Twitter messages written in Spanish over more than two years, we build a corpus from which a carefully selected list of concepts allows us to characterize Spanish varieties on a global scale. A cluster analysis proves the existence of well defined macroregions sharing common lexical properties. Remarkably enough, we find that Spanish language is split into two superdialects, namely, an urban speech used across major American and Spanish citites and a diverse form that encompasses rural areas and small towns. The latter can be further clustered into smaller varieties with a stronger regional character.
* 10 pages, 5 figures
The Twitter of Babel: Mapping World Languages through Microblogging Platforms
Dec 20, 2012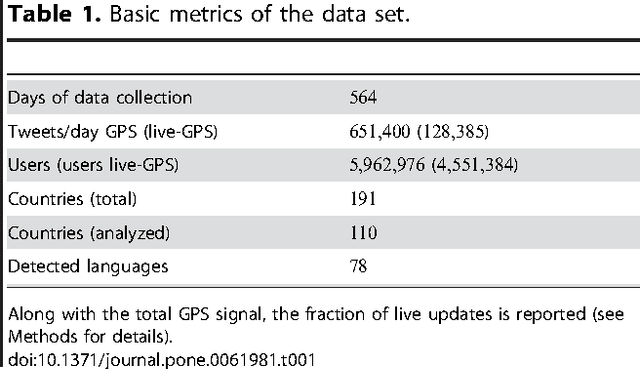
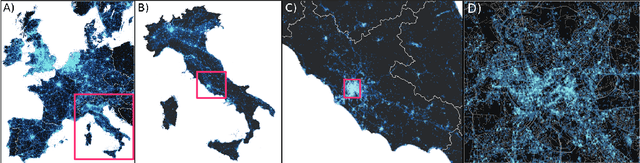
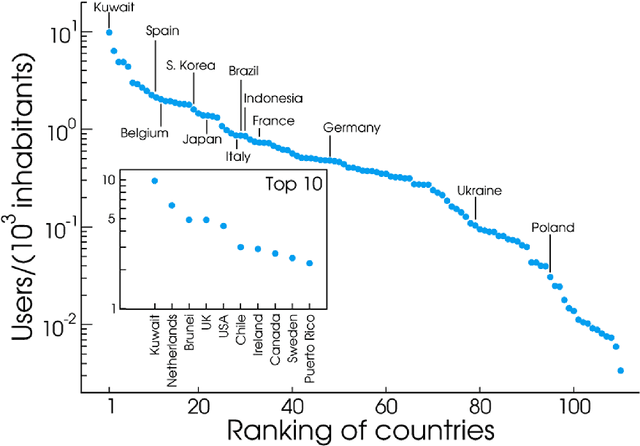
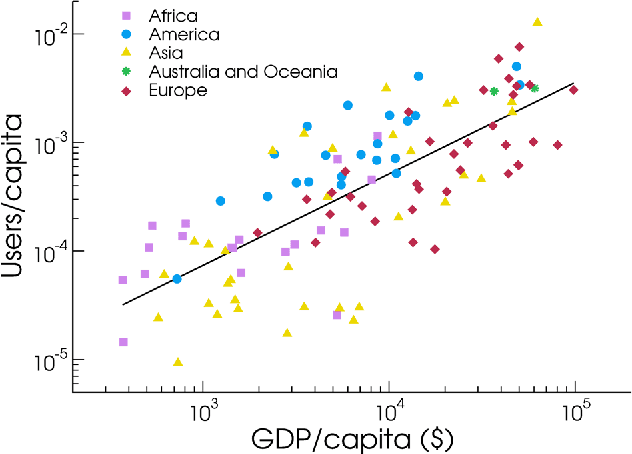
Abstract:Large scale analysis and statistics of socio-technical systems that just a few short years ago would have required the use of consistent economic and human resources can nowadays be conveniently performed by mining the enormous amount of digital data produced by human activities. Although a characterization of several aspects of our societies is emerging from the data revolution, a number of questions concerning the reliability and the biases inherent to the big data "proxies" of social life are still open. Here, we survey worldwide linguistic indicators and trends through the analysis of a large-scale dataset of microblogging posts. We show that available data allow for the study of language geography at scales ranging from country-level aggregation to specific city neighborhoods. The high resolution and coverage of the data allows us to investigate different indicators such as the linguistic homogeneity of different countries, the touristic seasonal patterns within countries and the geographical distribution of different languages in multilingual regions. This work highlights the potential of geolocalized studies of open data sources to improve current analysis and develop indicators for major social phenomena in specific communities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge