Thomas Louf
American cultural regions mapped through the lexical analysis of social media
Aug 16, 2022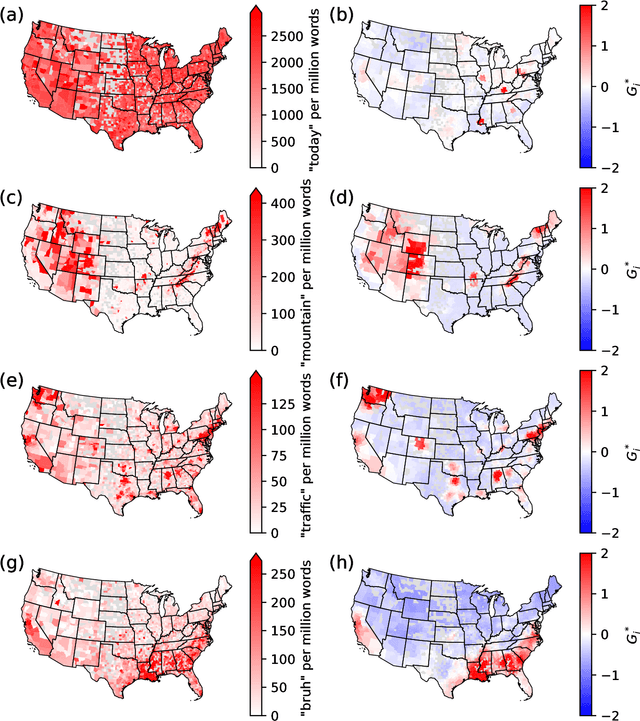
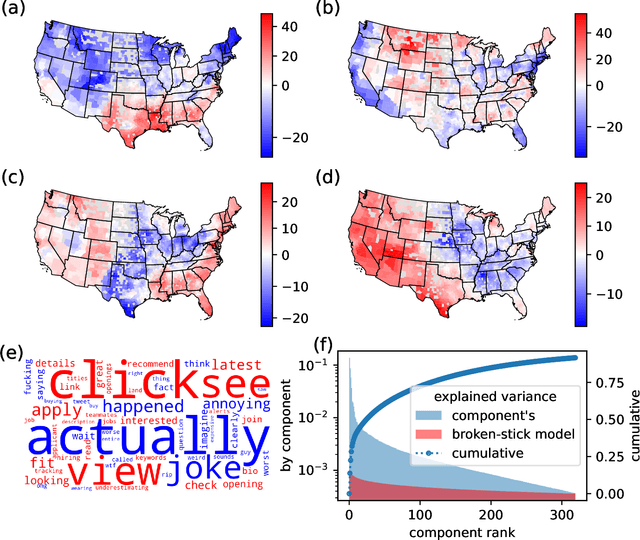
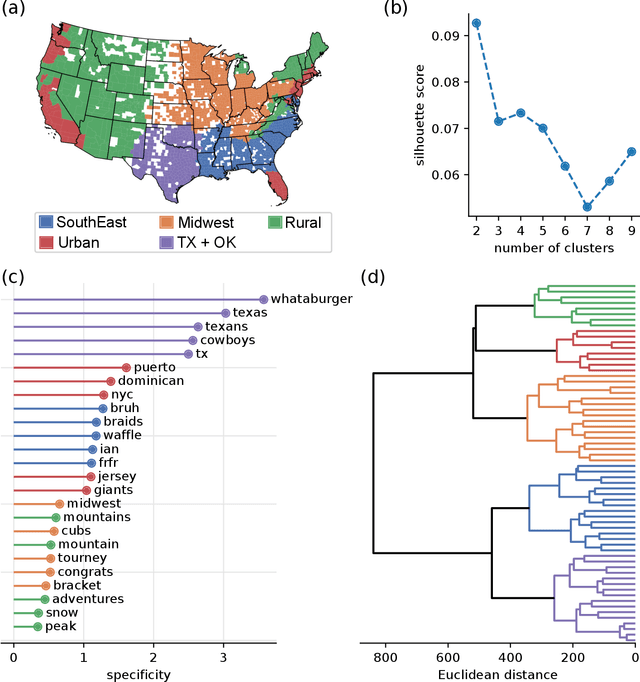
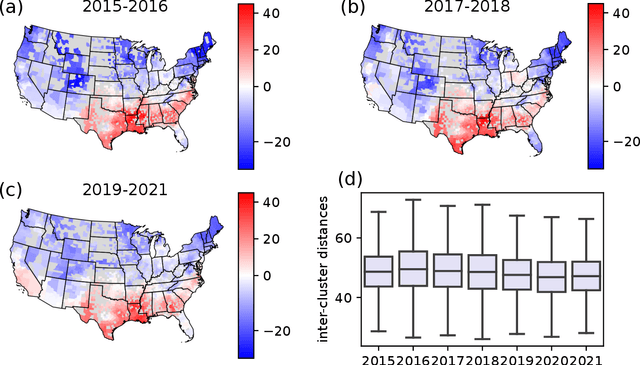
Abstract:Cultural areas represent a useful concept that cross-fertilizes diverse fields in social sciences. Knowledge of how humans organize and relate their ideas and behavior within a society helps to understand their actions and attitudes towards different issues. However, the selection of common traits that shape a cultural area is somewhat arbitrary. What is needed is a method that can leverage the massive amounts of data coming online, especially through social media, to identify cultural regions without ad-hoc assumptions, biases or prejudices. In this work, we take a crucial step towards this direction by introducing a method to infer cultural regions based on the automatic analysis of large datasets from microblogging posts. Our approach is based on the principle that cultural affiliation can be inferred from the topics that people discuss among themselves. Specifically, we measure regional variations in written discourse generated in American social media. From the frequency distributions of content words in geotagged Tweets, we find the words' usage regional hotspots, and from there we derive principal components of regional variation. Through a hierarchical clustering of the data in this lower-dimensional space, our method yields clear cultural areas and the topics of discussion that define them. We obtain a manifest North-South separation, which is primarily influenced by the African American culture, and further contiguous (East-West) and non-contiguous (urban-rural) divisions that provide a comprehensive picture of today's cultural areas in the US.
Capturing the diversity of multilingual societies
May 12, 2021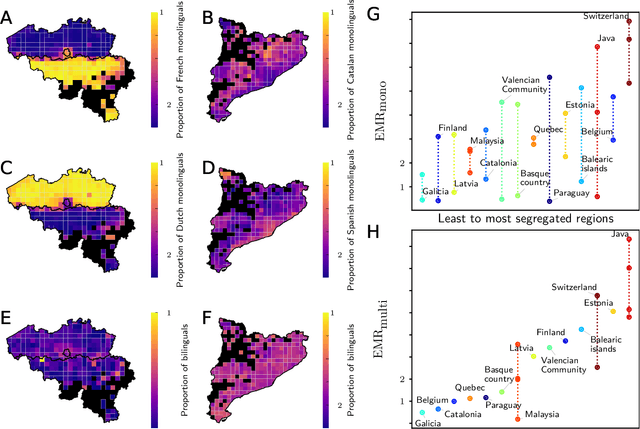
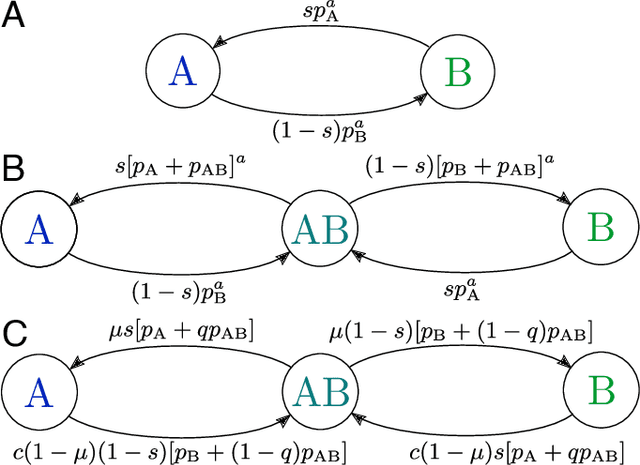
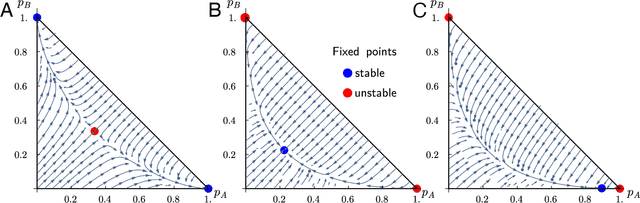
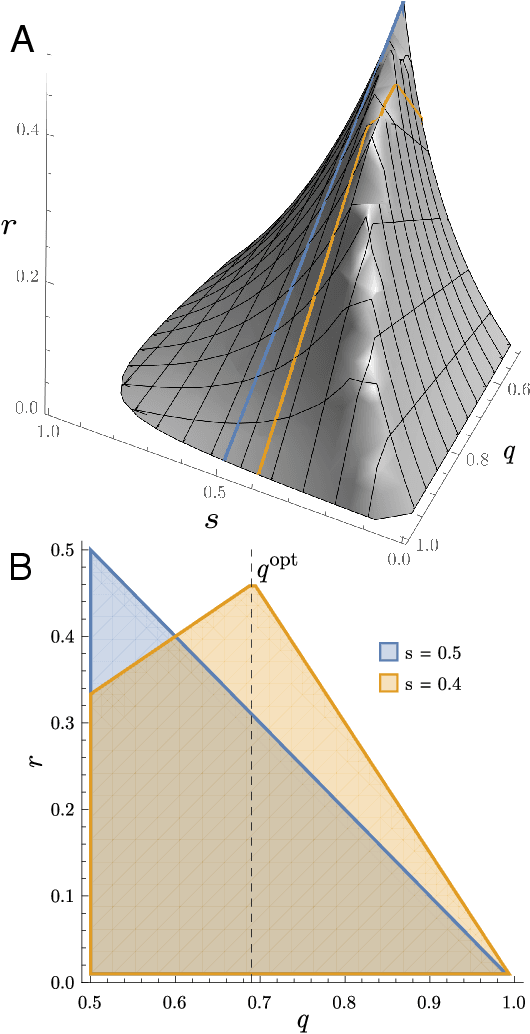
Abstract:Cultural diversity encoded within languages of the world is at risk, as many languages have become endangered in the last decades in a context of growing globalization. To preserve this diversity, it is first necessary to understand what drives language extinction, and which mechanisms might enable coexistence. Here, we consider the processes at work in language shift through a conjunction of theoretical and data-driven perspectives. A large-scale empirical study of spatial patterns of languages in multilingual societies using Twitter and census data yields a wide diversity. It ranges from an almost complete mixing of language speakers, including multilinguals, to segregation with a neat separation of the linguistic domains and with multilinguals mainly at their boundaries. To understand how these different states can emerge and, especially, become stable, we propose a model in which coexistence of languages may be reached when learning the other language is facilitated and when bilinguals favor the use of the endangered language. Simulations carried out in a metapopulation framework highlight the importance of spatial interactions arising from people mobility to explain the stability of a mixed state or the presence of a boundary between two linguistic regions. Changes in the parameters regulating the relation between the languages can destabilize a system, which undergoes global transitions. According to our model, the evolution of the system once it undergoes a transition is highly history-dependent. It is easy to change the status quo but going back to a previous state may not be simple or even possible.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge